The Effects of a Food Literacy Program on Eating Behaviors among Adults with Uncontrolled Hypertension in a Local Community
Keywords:
Literacy Program, Food Literacy, Eating Behaviors, Uncontrolled HypertensionAbstract
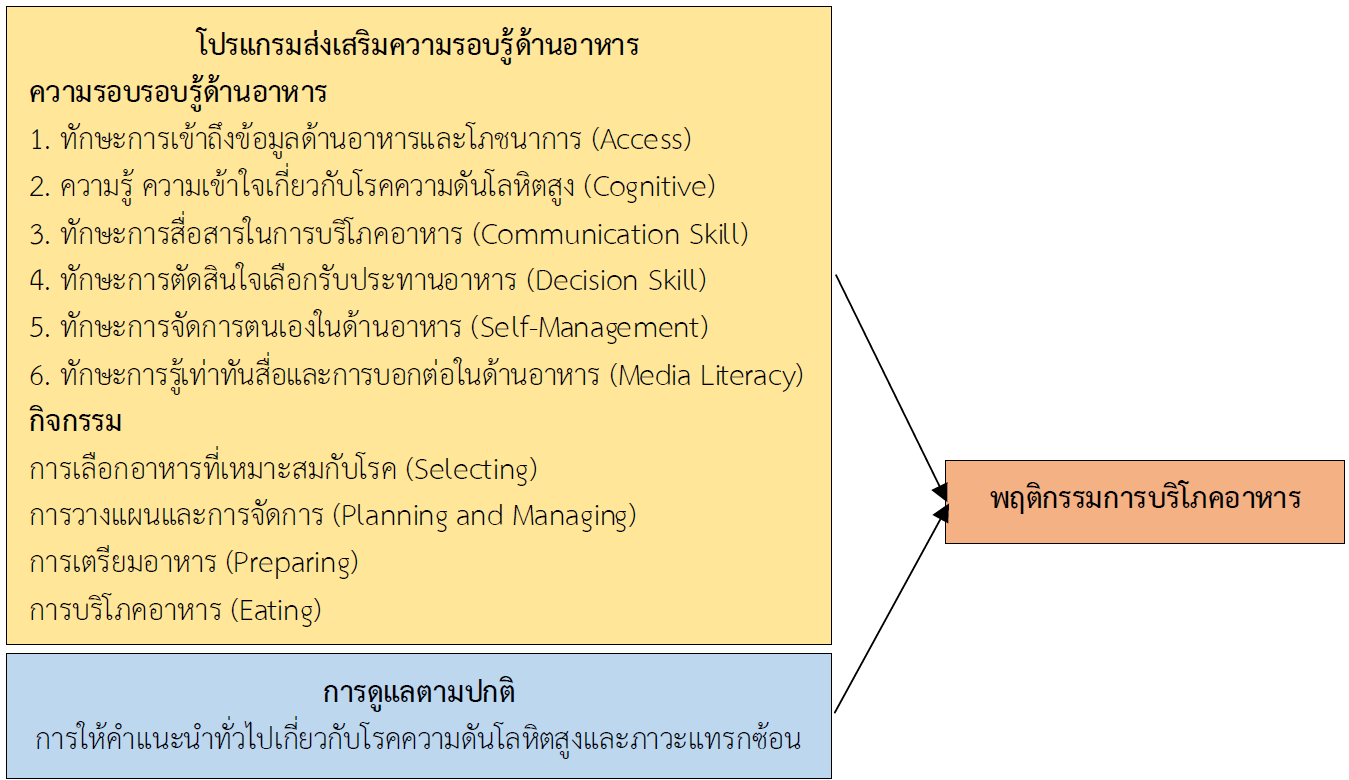
This two-group pretest-posttest quasi-experimental design aimed to investigate and compare dietary behavior scores of adults with uncontrolled hypertension. The participants were 40 adults with uncontrolled hypertension in a Chiang Mai Province local community. Participants were assigned to a study group (n = 20) or a comparison group (n = 20). The research instruments consisted of a new program to promote food literacy among adults with high blood pressure, as well as data collection tools, namely a demographic questionnaire, a food literacy questionnaire, and a food consumption behavior questionnaire. All were verified for content accuracy by six experts with a content validity of 1.0 and reliability levels at .80 and .87, respectively. The data were analyzed with descriptive statistics, paired t–test, and independent t–test statistics.
The results showed that, after receiving the program, the study group had higher food literacy scores than before with statistical significance (p-value <.001). After conducting the program, the comparison group had significantly higher food consumption behavior scores than the comparison group (p-value = .029).
The results of this research can be used as a guideline for community practice for nurses and health teams to implement food literacy programs, and to promote dietary behavior among adults with uncontrolled hypertension in local communities.
References
Arnthong, M., & Hunnirun, P. (2022). Development of health literacy model on laboratory results and self-care behaviors among elderly with chronic diseases in the 9th regional health. Journal of Buddhist Anthropology. 7(4), 474-492.
Burns, N., & Groove, S. K. (2009). The Practice of Nursing Research: Appraisal, Synthesis, and Generation of Evidence. St. Louis: Saunders Elsevier.
Doungpibol, P. (2016). The development of self-management skills on eating behaviors for delayed chronic kidney disease in CKD clinic Watphleng hospital. Journal of Research for Health Improvement and Quality of Life, 2(3), 13-24. (in Thai)
Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health. (2017). 20-year National Strategic Plan for Prevention and Control of Disease and Health Hazards (2017-2036). Bangkok: Graphic and Design Publishing House.
Department of Disease Control. (2021). Manual for the Process of Creating Health Knowledge in Preventing and Controlling Disease and Health Hazards. Retrieved January 31, 2023 from https://ddc.moph.go.th. (in Thai)
Division of Noncommunicable Diseases, Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health. (2022). Details of Indicators for Monitoring and Monitoring the Quality of Non-Communicable Disease Operations Services. (Diabetes and High Blood Pressure) for Fiscal Year 2022. Retrieved January 31, 2023 from https://ddc.moph.go.th. (in Thai)
Jard-ngoen, G., & Poonnotok, W. (2023). Effective of health behavior modification program in virtual clinic. Journal of Health and Environmental Education, 8(1), 73-86. (in Thai)
Jobsri, C. (2022). Oral Health Literacy Influencing Oral Health Behavior Among Parents of Pre-School Children in Muang District, Nakhon Sawan province. Doctoral Dissertation, Naresuan University.
Inthakamhaeng, A. (2017). Health Literacy: Measurement and Development. Bangkok: Sukhumvit Publishing.
Makpha, S., & Ouphakhom, W. (2023). The development of rational drug use literacy promoting of chronic patients in Phichit province. Regional Health Promotion Center 9 Journal, 17(1), 339-353. (in Thai)
Muangpae, P. (2022). Predictive Factors of Salt and Sodium Consumption Behavior Among People with Risk of Hypertension in Nong Phai District, Phetchabun. [Master's Thesis], Naresuan University. (in Thai)
Nangyaem, A., Deenan, A., & Chunlestskul, K. (2007). Factors predicting disease-specific eating behavior of patients with high blood pressure. Journal of Nursing Science Chulalongkorn University, 19(3), 84-96. (in Thai)
Nunyapruk, C., Therawiwat, M., Kaeodumkoeng, K., & Imamee, N. (2019). Factors related to blood pressure control behaviors among hypertensive patients in Ranod hospital, Songkhla province. Journal of Health Education, 42(1), 190-203. (in Thai)
Nutbeam, D. (2008). Health literacy as a public health goal: A challenge for contemporary health education and communication strategies into the 21st century. Health Promotion International, 15(3), 259-267.
Panchathongkarm, S. (2023). Health literacy prevents diabetes and hypertension. working age in health promotion establishments, health region 4. Journal of Health and Environmental Education, 8(2), 1-8. (in Thai)
Sumrouyg, S. (2023). Nursing care of diabetic patients who cannot control their blood sugar in the chronic disease at clinical Phrayuen hospital: Comparative with two case studies. Journal of Health and Environmental Education, 8(1), 61-72. (in Thai)
Sujamnong, S., Therawiwat, M. & Imamee, N. (2013). Factors related to self-management of hypertensive patients, Taladkwan district health promoting hospital, Nonthaburi province. Journal of Boromarajonani College of Nursing, 29(2), 20-30. (in Thai)
Sirithai, N, & Piripun, C. (2022). Self-care of diabetic patients and health literacy: case study of diabetic patients of Ban Nong Kang khen sub-district health promoting hospital, Nonthaburi province, Thailand. Journal of Health Science, 31(2), 289-298. (in Thai)
Strategy and Planning Division, Ministry of Public Health. (2012). Study Report Thailand Death Data Quality. Retrieved January 31, 2023 from https://spd.moph.go.th. (in Thai)
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารเครือข่าย วิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการหรือเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและวิทยาลัยการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้







