The Effects of a Simulation-Based Learning on Knowledge and Practicing Skills of Nursing Students in Nursing Care of Patients with Ventilators
Keywords:
Simulation-Based Learning, Nursing Care of Patients Using a Ventilator, Nursing StudentsAbstract
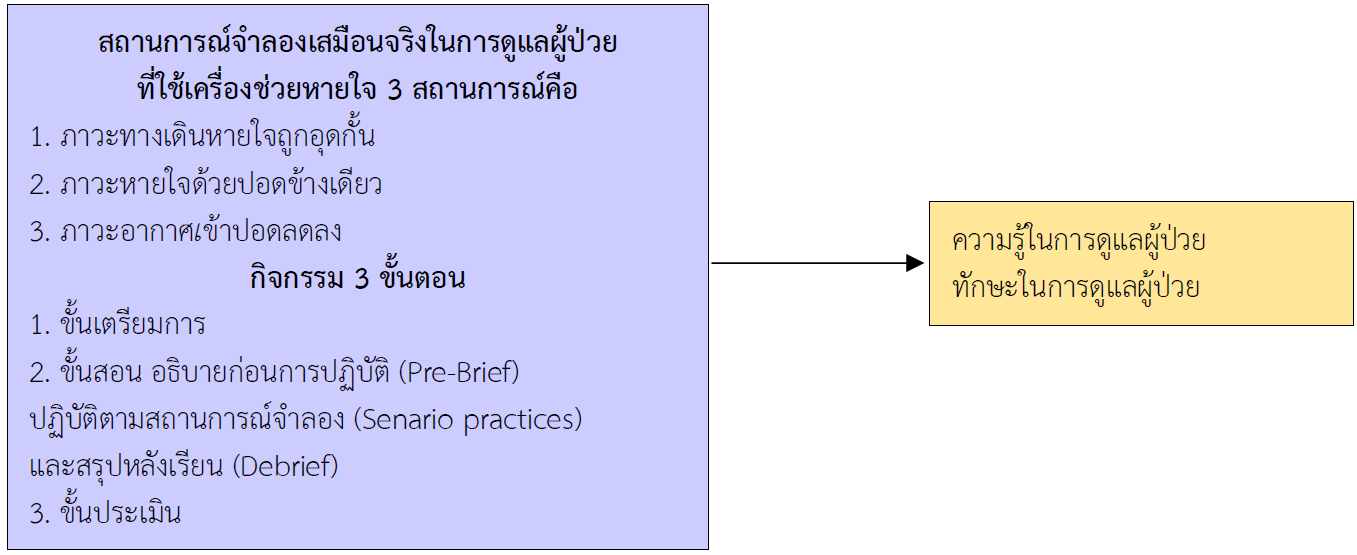
The aim of this quasi-experimental research was to examine the effects of a simulation-based learning program on knowledge and practical skills of nursing students in the care of patients with ventilators, accordingly with the comprehensive nursing care practicum II subject in our curriculum. Participants were junior undergraduate nursing students from Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Nakhon Si Thammarat. The number of participants was 62 nursing students, recruited and assigned to either or control group (31 in each group). The experimental instrument was a simulation-based learning (SBL) program for nursing care of patients with ventilators. Data collection instrument was a knowledge and practical skills questionnaire on nursing care on patients with ventilators. The Kuder-Richardson-20 was used, reaching .66., as well as the CVI, yielding .84. Cronbach’s alpha was applied to practical skills, with a coefficient of .87. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, chi–square test, independent t-test, and paired t-test. The research results were as follows.
1. After receiving the simulation-based learning (SBL) program, nursing students in the experimental group had a higher mean score of knowledge than in the control group at p<0.01 (t=3.51) level.
2. After receiving the simulation-based learning (SBL) program, nursing students in the experimental group had a higher mean score of practicing skills than in the control group at p<0.01 (t=13.06) level.
This research suggests using simulation-based learning with regular learning leads to better knowledge and nursing practice skills.
References
Boonmee, P., Mahamit, S.W, & Kawila, T. (2018). Knowledge, perception, and awareness of risk management and patient safety towards nursing students at Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Phayao. Journal of Nursing and Education, 11(3), 112-124. (in Thai)
Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Nakhon Si Thammarat. (2022). Meeting Report Curriculum Management Committee. Nakhon Si Thammarat: Boromarajonani College of Nursing. (in Thai)
Boromarajonani College of Nursing Nakhon Si Thammarat. (2023). Course Syllabus: Adult 2. Nakhon Si Thammarat: Boromarajonani College of Nursing. (in Thai)
Bunma, W. (2018). Effect of program for promoting emergency patient care skill toward perceived self- efficacy in emergency care among nursing students at Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Chiang Mai. Journal of Nursing and Education, 11(2), 74-86. (in Thai)
Chubkhuntod, P., Thasanoh Elter, P., Gaewgoontol, N., Rutchanee Potchana, R. (2020). Effects of simulation based learning model on knowledge, self-efficacy and abilities of applying nursing process skills during intrapartum care of nursing students. Journal of Health Science. 29(6), 1062-1072. (in Thai)
Cowperthwait, A. (2020). NLN Jeffries simulation framework for simulated participant methodology. Clinical Simulation in Nursing, 42, 12-21. doi.org/10.1016/j.ecns.2019.12.009
Ebrahimi, H. K., Sohrabi, S., Ashtiyani, F. Z., Hafize, F., Esmaeilian, S., & Jafarnejad, S. (2020). Effect of simalation-based CPR education on knowledge and performance of neonatal intensive care unit nurses. Journal of Critical Reviews, 7(7), 1135-1140.
Jamjang. S., Atthamatakul, W., Nilliaum. R., & Wongyara. N. (2021). The effects of simulation-based learning on problem solving ability, and self-confidence in nursing care on the patient with health problem of nursing students. Journal of Prachomklao College of Nursing, Phetchaburi Province, 4(3), 178-192. (in Thai)
Jamjang, S., Yomdit, V., Pongphetdit, B., Pitaksin, D., Changsieng, P., & Montong, A. (2018). Effects of using simulation-based learning for preparation of nursing practicum on perceptions of self efficacy in performing nursing care in a hospital. Nursing Journal of the Ministry of Public Health, 27(Special Issure), 46-58. (in Thai)
Jeffries, P. R. (2005). A framework for designingimplementing and evaluating simulations used as teaching strategies in nursing. Nursing Education Perspectives, 26(2), 96-103.
Kaenbubpha, N., Chomngam, P., Nuangchalerm, N. (2018). The effects of simulation-based teaching on perceived self-efficacy in cardio pulmonary resuscitation of students in Sirindhorn College of Public Health, Ubon Ratchathani Province. Journal of Health Science Boromarajonani College of Nursing Sunpasithiprasong, 2(3), 63-78. (in Thai)
Khemmani, T. (2014). Teaching knowledge to the Learning Process Effective 10th ed. Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Press. (in Thai).
Kim, J. Y., & Kim, E. J. (2015). Effects of simulation on nursing students’ knowledge, clinical reasoning, and self-confidence: A quasi-experimental study. Korean Journal of Adult Nursing, 27(5), 604-611. doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2015.27.5.604
Kolb, D. A. (1984). Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development (Vol. 1). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall. Retrieved January 21, 2024 from https://www.learningfromexperience.com/images/uploads/process-of-experiential-learning.pdf.
Krongthaeo, S., Partiprajak, S., & Udomkasemsab, A. (2022). Effectiveness of the airway management and ventilation training program in undergraduate nursing students. Rama Nurse Journal, 22(1), 93-110. (in Thai)
Kuder, G. F., & Richardson, M. W. (1937). The theory of estimation of test reliability. Psychometrika. 2, 151-160.
Lertlum, L., Tanasansutee, C., Panawatthanapisuit, S., & Bumrungsri, C. (2019). Development of a simulation-based learning model. The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health, 6(Special Issue), 43-58. (in Thai)
Meeboon, S., Tummee, S., & Charoenpon, S. (2022). Development of nursing students preparation model for principles and techniques in nursing practicum through simulation-based learning ward, Phetchaburi Province. Journal of Prachomklao College of Nursing, 5(1), 147-161. (in Thai)
Norkaeo, D., Treenon, P., Chabuakam, N., Kanbupar, N, Teanthong, S., & Kaewmanee, C. (2018). Nursing students knowledge and skills about basic life support (bls): The effects of simulation-based learning. The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health, 5(3), 84-95. (in Thai)
Pangsuk, P., Kingmala, C. (2021). The effect of simulation-based learning on knowledge and self-efficacy of the third year nursing students in caring for emergency patients. Songklanagarind Journal of Nursing, 41(2), 89-100. (in Thai)
Seesanea, P., Kunoy, C., Karunchareonphanit, S., Rupngam, S. (2022). Effects of simulation-based learning on knowledge, clinical judgment, and nursing skills in caring for critical patients with acute myocardial infarction: a case study. Journal of Nursing and Health Research (JNHR), 23(1), 123-133. (in Thai)
Sinthuchai, S., Ubolwan, K., & Boonsin, S. (2017). Effects of high-fidelity simulation based learning on knowledge, satisfaction, and self-confidence among the fourth year nursing students in comprehensive nursing care practicum. Rama Nurse Journal, 41(2), 113-127. (in Thai)
Srijanpal, W., Thatan, S., & Fukfon, K. (2021). Effects of simulation-based learning on perceived self-efficacy of nursing students in caring for patients with septic shock. Journal of The Royal Thai Army Nurses, 22(1), 283-293. (in Thai)
Somsiri, V., Thasaneesuwan, S., & Damkliang, J., (2023). Effects of a simulation-based learning on knowledge and self-confidence in nursing practice for patients with acute coronary syndrome at emergency department among nursing students. Journal of Research in Nursing-Midwifery and Health Sciences, 43(3), 24-38. (in Thai)
Tantalanukul, S., Khiaolueang, D., Srijaiwong, S., Fongkerd, S., & Nawsuwan, K., (2020). Effect of simulation-based learning toward drug used in primary medical care of nursing students Boromarajonani College of Nursing Uttaradit. Udon Thani Rajabhat University Journal of Humanities and Social Sciene, 9(1), 57-72. (in Thai)
Tantalanukul, S. (2021). Development of instructional model with simulated situations to enhance performance in primary medical care of nursing students. Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Uttaradit Journal, 22(1), 124-136. (in Thai)
Tawalbeh, L. I. (2020). Effect of simulation modules on jordanian nursing student knowledge and confidence in performing critical care skills: A randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Africa Nursing Sciences, 13(10024), 1-6. doi.org/10.1016/j.ijans.2020.100242
World Health Organization. (2011). WHO Patient Safety Curriculum Guide: Multi-professional Edition. Geneva: World Health Organization. Retrieved September 13, 2021, from http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44641/9789241501958_eng.pdf.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารเครือข่าย วิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการหรือเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและวิทยาลัยการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้







