Factors Predicting Quality of Life among Older Adults in Narathiwat Province during COVID-19 Pandemic
Keywords:
Predictive factors, Quality of life for the elderly, Coronavirus 2019Abstract
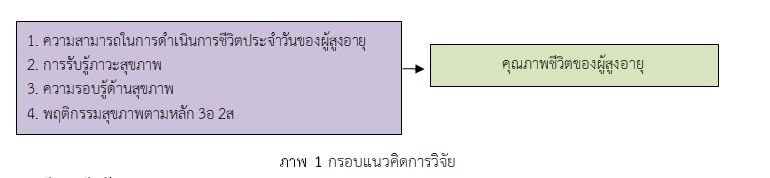
This research aimed to study factors predicting quality of life among older adults in Narathiwat province during the Covid-2019 pandemic. The sample was 142 older adults. Multi-stage sampling was applied. The research tool was a self-reported questionnaire which was validated by three experts, yielding index scores of objective-item congruence (IOC) ranged from .67–1.00, respectively. The questionnaire included five parts, namely 1) activities of daily living, 2) perception of health status, 3) health literacy (except health knowledge and understanding dimension), 4) 3E2S questionnaire on health behaviors, and 5) quality of life. The Cronbach’s alpha coefficients for the questionnaire was .94, .95, .81, .81 and .89, respectively. The health literacy questionnaire on health knowledge and understanding was tested using the Kuder-Richardson 20 method, obtaining a value of .81. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and multiple regression analysis.
1. The results showed that the older adults had activities of daily living and 3E2S health behaviors at a good level (M = 19.53, SD = 1.70 and M = 22.23, SD = 3.53 respectively). The quality of life was at a moderate level (M = 93.61, SD = 21.11). However, the perception of health status and health literacy was at a poor level (M = 108.37, SD = 30.31 and M = 36.23, SD = 7.52 respectively)
2. The perception of health status, activities of daily living and health literacy significantly predicted the quality of life among the older adults in Narathiwat province during the Covid-2019 pandemic accounted for 24.10% (adjR2 = .241; β= .450, .137, and .060, respectively).
Therefore, health personnel should organize project and activities to develop perception of health status, health literacy and activity of daily living to the older adults to increase their quality of life during any pandemic.
References
Boonsatean, W. & Reantippayasakul, O. (2020). Health Literacy: Situation and Impacts on Health Status of the Older Adults. APHEIT Journal of Nursing and Health, 2(1), 1-19. (in Thai)
Boonnarakorn, S., Chansangrat, N., Buamanee, N., Dangsri, P., Phenthai, S., & Atchariyawittaya, N. (2014). Health Leadership of the Elderly Muslims in the 3 Southern Border Provinces. National academic conference on Multidisciplinary on Cultural Diversit Towards the ASEAN Community. (17 July 2014 - 18 July 2014). (in Thai)
Chaimay, B. (2013). Sample Size Determination in Descriptive Study in Public Health. Thaksin Journal, 16(2). 9-18. (in Thai)
Cohen, J. (1977). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. New York: Academic Press.
Department of Disease Control. (2021). The report of COVID-19 situation in Narathiwat province Retrieved February 1, 2021 from: http://ntwo.moph.go.th/covid19/. (in Thai)
Department of Health Service Support. (2018). COVID-19 situation. Retrieved August 20, 2020 from https://hss.moph.go.th/show_topic.php?id=3601. (in Thai)
Department of Medical Services. (2015). Geriatric syndromes. Nonthaburi: Is August Company Limited. (in Thai)
Department of Medical Services, Ministry of Public Health. (2020). Guidelines for caring for the elderly during the COVID-19 outbreak. Retrieved August 20, 2020 from http://covid19.dms.go.th/. (in Thai)
Department of Mental Health. (2002). WHO Quality of Life Indicators, abbreviated set, Thai version. Retrieved August 2, 2022 from http://www.dmh.go.th/test/dowmload/files/whoqol.pdf. (in Thai)
Department of Older Persons. (2023). Elderly Statistic Data June 2023. Retrieved October 25, 2023 from https://www.dop.go.th/th/know/side/1/1/2387. (in Thai)
Ginggeaw, S. & Prasertsri, N. (2016). The Relationship between Health Literacy and Health Behaviors among Older Adults who have Multi-morbidity. Nursing Journal of the Ministry of Public Health, 25(3). 43-54. (in Thai)
Health Systems Research Institute. (1998). Definition of health promotion terminology. (Revised Edition). Nonthaburi: Health Systems Research Institute. (in Thai)
Judpoon, S. (2013). Social welfare management for developing quality of life of the elderly in ubdistrict Administrative Organization, Banlat district, Veridian E-Journal Silpakorn University Phetchaburi. 6(3), 510-519. (in Thai)
Kaewsuksai, R., Kongkun, P., Tongkoop, B., Samaair L., & Boonnarakorn, S. (2021). Relationships Between Knowledge, Perception, and the "New Normal Behaviors" for Preventing Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Infection among People in Narathiwat Province. The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health, 8(2), 67-79. (in Thai)
Kulsoontorn, K., Wingpat, K. & Bodeerat, C. (2021). Guidelines for Caring the Elderly During a COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Roi Kaensarn AcademiVol, 6(11). 288-302. (in Thai)
Narathiwat Public Health Office. (2020). The report of COVID-19 situations in Narathiwat province. Retrieved February 6, 2021 from http://ntwo.moph.go.th/covid19/. (in Thai)
Narathiwat Provincial Statistical Office. (2020). Narathiwat Provincial Statistical Report. Retrieved August 20, 2020 from http://narathiwat.nso.go.th/images/Statisticalinformationservice/ provincialstatisticalreport/2019 provincialstreport/2019 narathiwatstreportcompress.pdf. (in Thai)
Nilnate, W., Hengpraprom, S. & Hanvoravongchai, P. (2016). Level of Health Literacy in Thai Elders, Bangkok, Thailand. Journal of Health Research, 30(5). 315-321.
Noknoi, C. & Boripunt, W. (2017). The quality of life of elders in Songkhla province. Princess of Naradhiwas University Journal, 9(3), 94-110. (in Thai)
Prasartkul, P. (2018). (editor). Situation of the Thai elderly. Bangkok: Amarin Printing & Publishing. (in Thai)
Pradubmook, S, P., Theerasilp, U. & Phetchai, P. (2023). The Elderly’s Life Situations and Determinants of Elderly Violence: The Quantitative Survey in 5 Provinces. Journal of Roi Kaensarn Academi, 8(5), 472-490. (in Thai)
Prateepmanowong, J. (2019). The relationships between activities of daily living, exercise behaviour and quality of life in older persons with coronary artery disease. The Journal of Faculty of Nursing Burapha University, 27 (4). 66-76. (in Thai)
Punthasee, P. & Srisawad, K. (2020). Correlations between Health Belief and 3E 2S Health Behaviors of Elderly in Taejew Community Tungwatdorn Satorn Bangkok Thailand. Journal of Health and Health Management, 6(1), 45-57. (in Thai)
Srithanee, K. (2017). Relationship between Health Literacy and Quality of the Elderly’s Life at the Central Part of the North-East Thailand. Journal of Health Systems Research, 11(1). 26-36. (in Thai)
Suriart, C., Rutchanagul, P. & Thongbai, W. (2014). Health Perceptions, Health Behaviors and Health Service Needs among Inmates with Metabolic Disorders. Ramathibodi Nursing Journal, 20(3), 372-387. (in Thai)
Wongsawat, S. (2020). Knowledge of mind and spiritual care in COVID-19 pandemic. Department of Mental Health, Nonthaburi. Department of Mental Health. (in Thai)
Vanichbuncha, K. (2002). Principles of statistics. (7thed). Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Printing. (in Thai)
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารเครือข่าย วิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการหรือเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและวิทยาลัยการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้







