Social Media Addiction among Adolescents: The Influence of Self-Esteem, Life-Satisfaction, and Depression
Keywords:
Teenagers, Adolescents, Social Media Addiction, Depression, Self-Esteem, Life-SatisfactionAbstract
This descriptive research aimed to study the influence of self-esteem, life-satisfaction, and depression on social media addiction among adolescents in Ubon Ratchathani province of Thailand. The samples were 574 students attending four high schools and three vocational colleges in the 1st semester of 2021 academic year. Multi-stage sampling technique was applied. The instruments were five questionnaires: 1) demographics, 2) social media addiction inventory, 3) the Rosenberg's self-esteem questionnaire, 4) a life-satisfaction questionnaire, and 5) the Center for Epidemiology Study Depression Scale (CES-D) questionnaire. The cronbach’s alpha coefficient reliability for questionnaires 2, 3, 4, and 5 were .78, .83, .80, and .76, respectively. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and multiple linear regression.
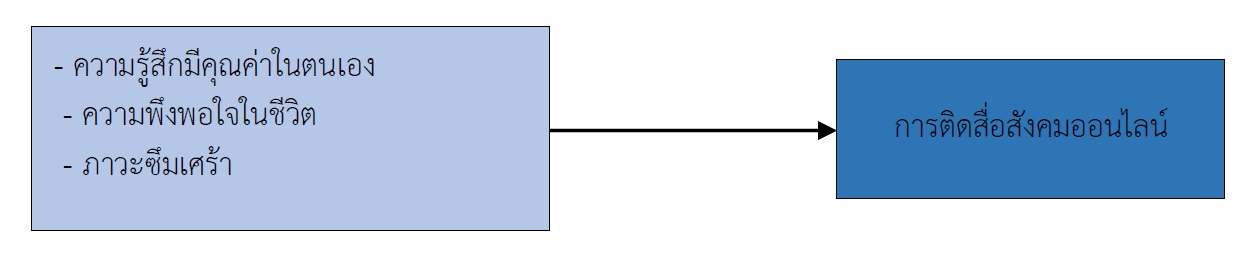
The results showed that the average level for social media addiction amongst students was 22.41 (SD=8.67). Most students were using social media as infatuated users (42.16%), followed by the normal user group (34.15%), and 23.69% of them who were clinically addicted to social media. The self-esteem score was at a medium level (M=27.86, SD=3.83), as well as life satisfaction (25.45, SD=4.68), while the depression score was lower than cut point at 19.48 (SD=10.52). Moreover, the results showed that the influence of self-esteem, life-satisfaction, and depression on social media addiction among adolescents was at statistical significance. In addition, depression (Beta=.229), self-esteem (Beta=-.184), and life satisfaction (Beta = -.087) could significantly explain 10.50% of variance (adj.R2=.105, p<.001). The results illustrated that higher depression, lower self-esteem, and lower life satisfaction can predict social media addiction.
Therefore, stakeholders should provide a protective program to enhance self-esteem and life satisfaction as well as improve knowledge and media literacy in adolescents in order to decrease the risk of social media addiction and other related mental health problems.
References
Andreassen, C. S., Pallesen, S. & Griffiths, M. D. (2017). The Relationship Between Addictive of Social Media, Narcissism, and Self-Esteem: Findings from a Large National Survey. Addictive Behavior, 64(14), 287-293.
Blachnio, A., Przepiorka, A. & Pantic, I. (2016). Association Between Facebook Addiction, Self-Esteem and Life Satisfaction: A Cross-Sectional Study. Computer Human Behavior, 55(1), 701-705.
Boonyarit, I. (2012). Forgiveness in Peer Relationship: Scale Development and Examination of Nomological Network with Mental Health and Well-Being in Thai University Students. Chiang Mai: Chiang Mai University, Thailand.
Caner, N., Efe, Y. S. & Başdaş, Ö. (2021). The Contribution of Social Media addiction to Adolescent LIFE: Social Appearance Anxiety. Current Psychology (New Brunswick, N.j.), 41(12), 8424-8433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03280-y
Chupradit, P., W. & Chupradit, S. (2022). The Influences of Social Media Addiction on Mental Health Status Among University Students in Thailand. Suthiparithat Journal, 36(3), 188-207.
Diener, E. & Diener, M. (2009). Cross-Cultural Correlates of Life Satisfaction and Self-Esteem Culture and Wellbeing. (pp. 71–91). The Netherlands: Springer.
Haan, R. & Zhuwhang, Z. (2020). The Relationship Between Social Media Addiction and Depression: a Quantitative Study Among University Students in Khost, Afghanistan. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth, 25(1), 780–786
Hair, J. F., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R. E. & Black, W. C. (2019). Multivariate Data Analysis (8th ed.). England: Pearson Prentice.
Hawi, N. & Rupert, M. S. (2016). The Relations among Social Media Addiction, Self-esteem, and Life Satisfaction in University Students. Social Science Computer Review, 35(5), 555-575.
Hou, Y., Xiong, D., Jiang, T., Song, L. & Wang, Q. (2019). Social Media Addiction: Its Impact, Mediation, and Intervention. Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace, 13(1), Article 4. doi: 10.5817/CP2019-1-4.
Jan, M., Soomro, S. A. & Armed, N. (2017). Impact of Social Media on Self-Esteem. European Scientific Journal, 13(23), 1857-1881.
Kajai, C. & Namwong, A. (2019). Facebook Addiction, Depression, and Suicidal Risk Among Z Generation Nursing Students. Journal of Public Health Nursing, 33(2), 33-47.
Kajai, C., Thapinta, D. & Skulphan, S. (2018). The Relationship Between Facebook Addiction and Depression among Adolescents Attending State University in Chiang Mai Province. The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health, 5(2), 57-69.
Keles, B., McCrae, N. & Grealish, A. (2019). A Systematic Review: The Influence of Social Media on Depression, Anxiety and Psychological Distress in Adolescents. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth, 25(1), 79-93. doi:10.1080/02673843.2019.1590851
Khumsri, J., Hanprathet, N., Manwong, M., Yingyeun, R. & Phanasathit, M. (2015). Facebook Addiction and Its Relationship with Mental Health among Thai High School Students. Journal of Medical Associated Thai, 98(3), S81-90.
Kirkabulan, K. (2016). Self-Esteem, Daily Internet Use and Social Media Addiction as Predictors of Depression among Turkish Adolescents. Journal of Education and Practice, 7(24), 64-72.
Longstreet, P. & Brook, S. (2017). Life Satisfaction: A Key to Managing Internet & Social Media Addiction. Technology in Society, 50(2), 73-77 doi. 10.1016/j.techsoc.2017.05.003.
Luo, T., Chen, W. & Liao, Y. (2021). Social Media Use in China Before and During COVID-19: Preliminary Results from an Online Retrospective Survey. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 140, 35-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.05.057
Phanichsiri, K. & Tuntasood, B. (2016). Social Media Addiction and Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Symptoms in High School Students in Bangkok. Journal of Psychiatric Association Thailand, 61(3), 191-204.
Pholphet, K. & Tuntasood, B. (2016). Self-Esteem and Facebook Addiction of High School Students in Bangkok Metropolitan Area. Journal of Psychiatric Association Thailand, 61(3), 217-230.
Pornnoppadol, C., Ladawan na Ayudhaya, S., Phoasavasdi, C. & Surapongphiwattana, T. (2017). Development of game addiction protection scale (GAME-P). Journal of Psychiatric Association Thailand, 62(1), 3-16.
Radloff, L. S. (1977). The CES-D scale: A Self-Report Depression Scale for Research in the General Population. Apply Psychology Measurement, 1(1), 385-401.
Rogowska, A. M. & Libera, P. (2022). Life Satisfaction and Instagram Addiction among University Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Bidirectional Mediating Role of Loneliness. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(14). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148414
Rosenberg, M. (1965). Society and the Adolescent Self-Image. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Sedgwick, R., Epstein, S., Dutta, R. & Ougrin, D. (2019). Social Media, Internet Use and Suicide Attempts in Adolescents. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 32(6), 534-541, doi: 10.1097/YCO.0000000000000547
Srisoem, C., Thaweekoon, T. & Nintachan, P. (2021). Self-Esteem, Attitude towards Cyberbullying, and Cyberbullying among High School Students. The Journal of Psychiatric Nursing and Mental Health, 35(1), 112-127.
Tanta, I., Mihovilovic, M. & Sablic, Z. (2014). Uses and Gratification Theory-Why Adolescents Use Facebook?. Medijska Istraživanja/Media Research, 20(2), 85-110.
Thongpradab, J., Thaweekoon, T. & Nintachan, P. (2019). The Relationships Among Facebook Addiction, Self-Esteem and Depression in High School Students. Thai Red Cross Nursing Journal, 12(2), 116-133.
Trangkasombat, U., Larpboomsup, V. & Hawanont, P. (1997). CES-D in Adolescents. Journal of Psychiatrist Association Thailand, 42(1), 2-13. (in Thai).
Wang, C., Lee, M. & Hua, Z. (2015). A Theory of Social Media Dependence: Evidence from Microblog Users. Decision Support Systems, 69(1), 40-49. 10.1016/j.dss.2014.11.002.
Wang, J., Gaskin, J., Wang, H. & Liu, D. (2016). Life Satisfaction Moderates the Associations Between Motives and Excessive Social Networking Site Usage. Addiction Research & Theory, 24(6), 450-457. doi: 10.3109/16066359.2016.1160283
Wilcox, K. & Stephen, A. T. (2013). Are Close Friends the Enemy? Online Social Networks, Self-Esteem, and Self-Control. Journal of Consumption Response, 40(1), 12-57.
Wongpakaran, T. & Wongpakaran. N., (2011). Confirmatory Factor Analysis of Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale: A Study of Thai Student Sample. Journal of Psychiatric Association Thailand, 56(1), 59-70. (In Thai).
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารเครือข่าย วิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการหรือเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและวิทยาลัยการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้







