Clinical Outcomes of a Home Care Case Management for Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 3
Keywords:
Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 3, Home Case Management, Clinical Outcomes, Comparative ResearchAbstract
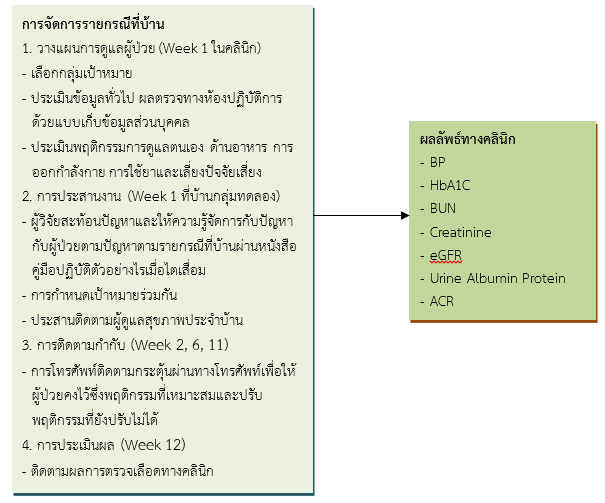
The purposes of this quasi-experimental research were to compare clinical outcomes of a home care case management nursing approach in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 3. Blood pressure, creatinine, urine protein albumin (UPA), albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR), estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1C) were the compared clinical outcomes in-home case management. Comparisons were between control and experimental groups, and between pre- and post clinical home care case management in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 3. Sample size was 20 patients with chronic kidney disease stage 3, calculated by two independent means, using the N4studies program. Data were collected using personal questionnaires and clinical outcomes. The home care case management process consisted of patients care planning, coordinating, monitoring and evaluation. The home care case management instruments were educational media on kidney disease, a practical guide books for patients with chronic kidney disease, and follow-up phone calls. Frequency, percentage, independent t-test, paired t-test, the mann-whitney u test, and the Wilcoxon signed-rank test were used for data analysis.
Results showed that the mean measures for blood pressure, creatinine, UPA, and ACR were not significantly different between control and experimental groups in post home care case management. There were no significant difference either between pre-and post home case management mean diastolic blood pressure (DBP), BUN, UPA, ACR, and HbA1C.
In contrast, mean eGFR significantly increased, and mean BUN significantly decreased (at P<.05). Mean systolic blood pressure (SBP) and creatinine showed a significant decrease as well, while the mean eGFR was significantly higher at P<.05.
The control of blood pressure and the control of urinary protein leakage in patients with chronic kidney disease should be studied in further research. For more effective outcomes, nurses should coordinate with multidisciplinary home care case management. It would be helpful to use the home care case management as a part of the process of self-care behavior development in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 3.
References
Allen, D. (2020). Global Facts: About Kidney Disease. National Kidney Foundation Inc. Retrieved january 9, 2020, from https://www.kidney.org/kidneydisease/global-facts-about-kidney disease.
Anaman, P., & Promdee, A. (2019). Effectiveness of Case Management in Diabetes Patients, Family Doctor Clinic. Mukdahan Hospital. Journal of Health Sciences Boromarajonani Nurse Sanphasitthiprasong, 3(2), 37-55. (in Thai).
Bill, G., & Melinda, G., (2020). Global, Regional, and National Burden of Chronic Kidneydisease, 1990–2017: a Systematic Analysis for the GlobalBurden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet, 395, 709-733.
Bloom, Benjamins. (1976). Human Characteristics and School Learning. New York: McGraw Hill Book Company.
Couser, W. G., Remuzzi, G., Mendis, S., & Tonelli, M. (2011). The Contribution of Chronic Kidney Disease to the Global Burden of Major Noncommunicable Diseases. Kidney International, 80(12), 1258–1270. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2011.368.
Haileamlak, A. (2018). Chronic Kidney Disease is on the Rise. Ethiopian Journal of Health Sciences, 28(6), 681–682. https://doi.org/10.4314/ejhs.v28i6.1
Ing Satit, A., Chayakun, C., Chaiprasert, A.,Tirakupt, P., Siriwong, T., SaengThawan, P., et al. (2017). Disease Progression and Clinical Outcome of Nephrotic Syndrome. Chronic in the Thai SEEK Progression and Outcomes of CKD in Thai SEEK Population. Institute of Public Health System Research (HSRI), 1-41. (in Thai).
Jaimai, A., & Phegphon, K. (2018). Nursing in a Case Management Model for Type 2 Diabetes in the Community. Journal of Nursing Public Health and Education, 2(13), 17-28. (in Thai).
Jha, V., Garcia-Garcia, G., Iseki, K., Li, Z., Naicker, S., Plattner, B., et al. (2013). Chronic Kidney Disease: Global Dimension and Perspectives. Lancet (London, England), 382(9888), 260–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60687-X.
Kaenkarn, W., Dumnok, K., & Anutrakulchai, S. (2019). Effectiveness of a Model of Care for Chronic Kidney Disease Using Integrated Disease Management and Case Management in Primary Care Units. Northeast Journal of Nursing and Health Care, 37(3), 173-182. (in Thai).
Kantchuetsiri, S., ChanCharoenThan, W., ChaiLimpamontree, W., Trakanwanich, T., Kochaseni, P., Yusby, A., et al. (2016). Chronic Kidney Disease Textbook (1st ed.). Bangkok: Text and Journal CompanyPublication Co., Ltd.
Kosonchit, R., & Noimuen Wai, P. (2017). Effectiveness of Case Management in Patients with Diabetes, Pak Phli Hospital. Nakhon Nayok Province. Nursing material, 44(2), 26-38. (in Thai).
Laatiman, S., Sompet, T., Muthumol, P., & Thumdee, D. (2019). Development of Diabetes Care System with a Case Management Model Saraphi Hospital, Saraphi District, Chiang Mai Province. Medical Journal of Udon Thani Hospital, 25(3), 283-293. (in Thai).
Paengkha, W. (2017). Effectiveness of Diabetes Care with Diabetic Nephrotic Stage 2-4 with Case Management, Nam Nao Hospital Network, Nam Nao District, Phetchabun Province. Journal of Medical Studies Region 11, 31(3), 405-414. (in Thai).
Pender, N. J., Murdaugh, C. L., & Parsons, M. A. (2002). Health Promotion in Nursing Practice. 4th (ed). New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc.
Singsangwean, P., Tipwareerom, W., & Juntarawijit, Y. (2019). The Effectof Self-Management Program on Food Consumption Behavior and Exercise and Glomerular Filtration Rate among Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 3 Patients with Hypertension. Journal of Nursing and Health Sciences, 13(3), 50-64. (in Thai).
Supaphan, S. (2019). Development of a Slowing-Down Model in Diabetic and Hypertensive Patients with Case Management at Phu Sing Hospital, Sisaket Province. Journal of Public Health, 28(5), 857. (in Thai).
Rattanaurai., U, & Songbutr., P. (2019). Effects of a Case Management Program in Diabetes Patients with Uncontrolled Sugar Levels. Journal of Public Health, 28(Special), 146-151. (in Thai).
Thangkratok, P. (2017). Role of Professional Nurse in Chronic Disease Management. Journal of Songkhla Nakarin Nursing, 37(2), 154-159. (in Thai).
Surat Thani Provincial Public Health Office. (2019). Health Data Center. Retrieved January 12, 2019 from https://sni.hdc.moph.go.th/hdc/reports/report.php?source.
Sirirawong, S. (2019). World Kidney Day 2019 "Everyone in Thailand Has a Healthy Kidney" Kidney Health for Everyone Everywhere. reporter@hooninside.com. March 6, 2019 from https://www.hooninside.com/news-feed/94048/view/.
World Kidney Day. (2015). Chronic Kidney Disease. (2015). Retrieved January 18, 2019 from http://www.worldkidneyday.org/faqs/chronic-kidney-disease/.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารเครือข่าย วิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการหรือเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและวิทยาลัยการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้







