ผลของโปรแกรมพัฒนาพฤติกรรมการป้องกันโรคความดันโลหิตสูงร่วมกับระบบสุขภาพทางไกล ในกลุ่มเสี่ยงโรคความดันโลหิตสูง อำเภอบ้านดุง จังหวัดอุดรธานี
คำสำคัญ:
ความดันโลหิตสูง, สุขภาพทางไกล, กลุ่มเสี่ยง , พฤติกรรมการป้องกันโรคบทคัดย่อ
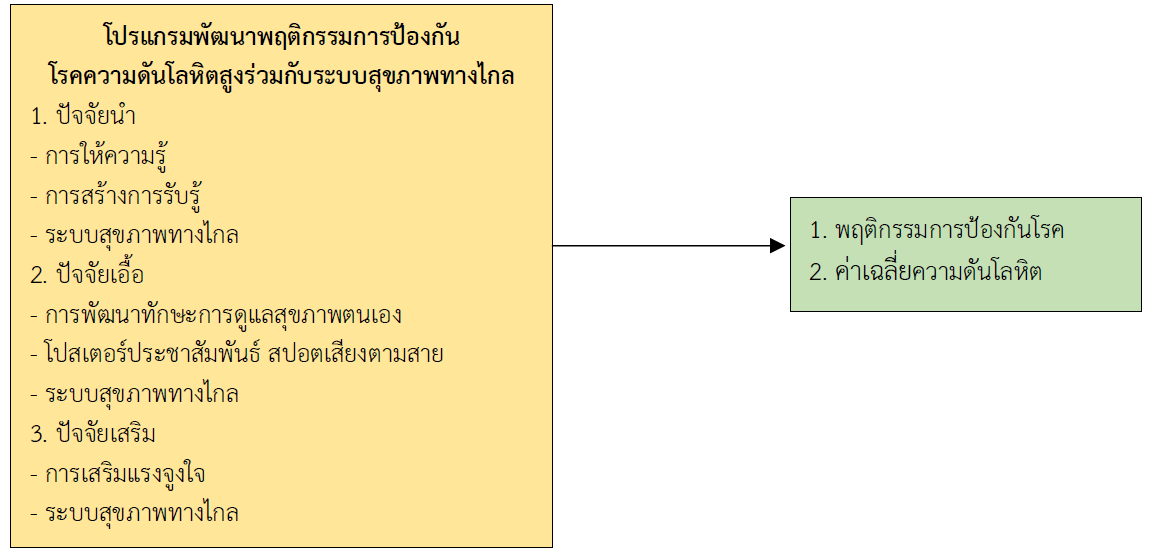
การวิจัยเชิงกึ่งทดลองนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาผลของโปรแกรมพัฒนาพฤติกรรมการป้องกันโรคความดันโลหิตสูงร่วมกับระบบสุขภาพทางไกลในกลุ่มเสี่ยงโรคความดันโลหิตสูง เปรียบเทียบพฤติกรรมการป้องกันโรคความดันโลหิตสูง ค่าเฉลี่ยความดันโลหิตของกลุ่มเสี่ยงโรคความดันโลหิตสูง ของกลุ่มทดลองก่อนและหลังใช้โปรแกรมฯ และระหว่างกลุ่มทดลองและกลุ่มเปรียบเทียบหลังใช้โปรแกรมฯ โดยกลุ่มตัวอย่างคือกลุ่มเสี่ยงโรคความดันโลหิตสูง อายุ 35 - 59 ปี จำนวน 60 คน แบ่งเป็นกลุ่มทดลองและกลุ่มเปรียบเทียบ กลุ่มละ 30 คน คัดเลือกกลุ่มตัวอย่างโดยใช้การสุ่มตัวอย่างแบบง่าย เครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการวิจัย ได้แก่ โปรแกรมพัฒนาพฤติกรรมการป้องกันโรคความดันโลหิตสูงร่วมกับระบบสุขภาพทางไกล ที่ผู้วิจัยสร้างขึ้นโดยประยุกต์ใช้แนวคิดพรีสีด และเครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการเก็บข้อมูล ได้แก่ แบบสอบถาม ประกอบด้วย 2 ส่วน คือ 1) ข้อมูลทั่วไป และ 2) พฤติกรรมการป้องกันโรคความดันโลหิตสูง โดยโปรแกรมฯ และแบบสอบถาม ผ่านการตรวจสอบความตรงเชิงเนื้อหาจากผู้ทรงคุณวุฒิ 5 ท่าน มีค่าความตรงเชิงเนื้อหา .92 และ .95 ตามลำดับ และแบบสอบถามมีค่าความเที่ยง .71 วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลด้วยสถิติพรรณนา และสถิติทีชนิดไม่อิสระและสถิติทีชนิดอิสระ ผลวิจัยพบว่า
1. หลังใช้โปรแกรมฯ กลุ่มทดลองมีคะแนนเฉลี่ยพฤติกรรมป้องกันโรคความดันโลหิตสูงโดยรวมสูงกว่าก่อนใช้โปรแกรมฯ และสูงกว่ากลุ่มเปรียบเทียบ อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ .01
2. หลังใช้โปรแกรมฯ กลุ่มทดลองมีค่าเฉลี่ยความดันโลหิตซิสโตลิกและระดับความดันโลหิตไดแอสโตลิคลดลงกว่าก่อนใช้โปรแกรมฯ และลดลงกว่ากลุ่มเปรียบเทียบ อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ .05
จากผลการศึกษานี้จึงควรนำโปรแกรมพัฒนาพฤติกรรมการป้องกันโรคความดันโลหิตสูงร่วมกับระบบสุขภาพทางไกลประยุกต์ใช้ในการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมป้องกันโรคความดันโลหิตสูงหรือโรคเรื้อรังอื่น ๆ ต่อไป
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Aekplakorn, W., Pakcharoen, H., & Sathiennoppakao, W. (2021). The Sixth Thai National Health Examination Survey, 2019-2020. Bangkok: Faculty of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University.
Bashshur, R. L., Howell, J. D., Krupinski, E. A., Harms, K. M., Bashshur, N., & Doarn, C. R. (2016). The empirical foundations of telemedicine interventions in primary care. Telemedicine and e-Health, 22(5), 342–375. doi.org/10.1089/tmj.2016.0045
Bunyarang, S. (2018). The Effect of a Behavior Modification Program for Hypertension Prevention in at Risk Groups in Phen District, Udon Thani Province (Master’s thesis). Bangkok: Sukhothai Thammathirat Open University. (in Thai)
Caplin, A., Chen, F. S., Beauchamp, M. R., & Puterman, E. (2021). The effects of exercise intensity on the cortisol response to a subsequent acute psychosocial stressor. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 131, 105336. doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2021.105336
Chanaman, P. (2024). The effects of self-management promotion program using telenursing on stroke prevention behaviors in uncontrolled hypertensive patients. Journal of Nursing and Health Sciences, 4(3), 33-46. (in Thai)
Department of Disease Control. (2019). Blood Pressure: Measure Early, Know Eearly, Preventable. Nonthaburi: Bureau of Non-Communicable Diseases. (in Thai)
Department of Disease Control. (2022). Department of Disease Control Advises Citizens to Pay Attention to Health and Measure Blood Pressure Regularly to Prevent Hypertension. Retrieved May 25, 2023, from https://ddc.moph.go.th/brc/news.php?news=25290 &deptcode=brc&news_views=388 (in Thai)
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A. G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences*. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 175–191.
Filippini, T., Malavolti, M., Whelton, P. K., Naska, A., Orsini, N., & Vinceti, M. (2021). Blood pressure effects of sodium reduction: Dose-response meta-analysis of experimental studies. Circulation, 143(16). doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.050371
Green, L. W., & Kreuter, M. W. (2005). Health Program Planning: An Educational and Ecological Approach (4th ed.). McGraw-Hill.
Hoffer-Hawlik, M., Moran, A. E., Zerihun, L., Usseglio, J., Cohn, J., & Gupta, R. (2021). Telemedicine interventions for hypertension management in low- and middle-income countries: A scoping review. PLOS ONE, 16(7), e0254222. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0254222
Loucks, E. B., Schuman-Olivier, Z., Saadeh, F., Scarpaci, M. M., Nardi, W. R., Gutman, R., et al. (2022).
Mindfulness-Based Blood Pressure Reduction: Evidence from the AHA Scientific Sessions 2022. American Heart Association. Retrieved October 7, 2024, from https://professional.heart.org/en/meetings/scientific-sessions
Mangsakoo, U. (2019). The effects of health behavior modification program for elderly with hypertension at Suwannaphum District, Roi Et Province. Thai Journal of Nursing, 68(3), 1-10. (in Thai)
Santos, E. de S. G., & Souza, O. F. de. (2021). Evidence of the association between sleep duration and blood pressure in adolescents: A systematic review. Revista Paulista de Pediatria, 39, e2019225. doi.org/10.1590/1984-0462/2021/39/2019225
Schultz, M. G., La Gerche, A., & Sharman, J. E. (2017). Blood pressure response to exercise and cardiovascular disease. Current Hypertension Reports, 19(11), 89. doi.org/10.1007/s11906-017-0787-1
Srisatidnarakul, B. (2010). Nursing Research Methodology (5th ed.). U & I Intermedia. (in Thai)
Thai Hypertension Society. (2019). Guidelines for hypertension treatment in general practice, 2019. Chiang Mai: Trick Think. (in Thai)
Udon Thani Provincial Public Health Office, Health Data Center. (2023). Data to support the Service Plan in the field of non-communicable diseases (NCDs: DM, HT, CVD). Retrieved October 7, 2024 from https://udn.hdc.moph.go.th/hdc/reports/page.php?cat_id= 1ed90bc32310b503b7ca9b32af425a
Whelton, P. K., Carey, R. M., Aronow, W. S., Casey, D. E., Collins, K. J., Himmelfarb, C. D., et al. (2018). guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 71(19), e127–e248. doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2017.11.006
World Health Organization. (2021). Hypertension. Retrieved October 7, 2024 from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2025 วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารเครือข่าย วิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการหรือเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและวิทยาลัยการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้







