ผลของโปรแกรมเสริมสร้างความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพผ่านทางแอปพลิเคชันไลน์ต่อความรอบรู้ ด้านสุขภาพในการปฏิบัติกิจกรรมทางกายและพฤติกรรมการปฏิบัติกิจกรรมทางกาย ของพนักงานองค์กรปกครองส่วนท้องถิ่น อำเภอเมืองราชบุรี จังหวัดราชบุรี
คำสำคัญ:
ความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพ, กิจกรรมทางกาย, แอปพลิเคชันไลน์, พนักงานองค์กรปกครองส่วนท้องถิ่นบทคัดย่อ
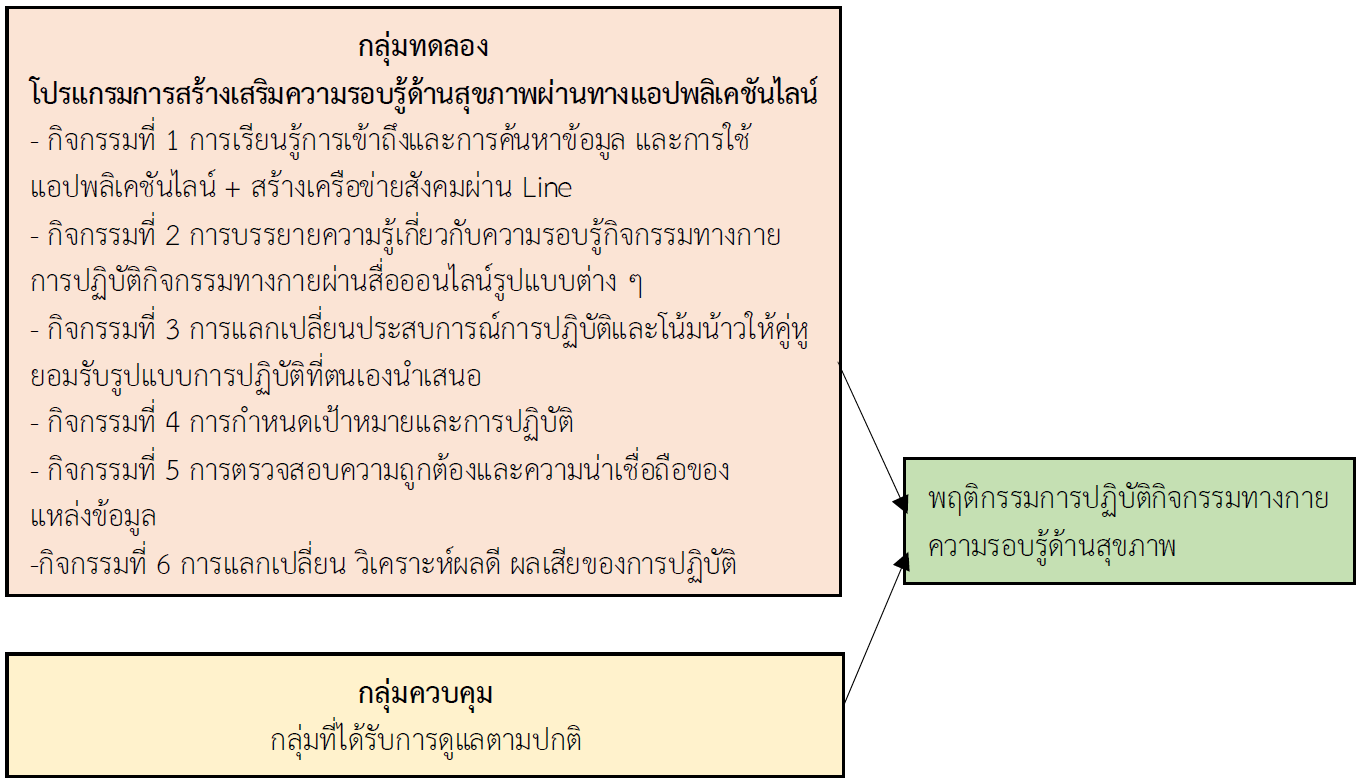
การวิจัยเชิงทดลองแบบสุ่มและมีกลุ่มควบคุม มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาผลของโปรแกรมเสริมสร้างความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพผ่านทางแอปพลิเคชันไลน์ต่อความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพในการปฏิบัติกิจกรรมทางกายและพฤติกรรมการปฏิบัติกิจกรรมทางกายของพนักงานองค์กรปกครองส่วนท้องถิ่น อำเภอเมืองราชบุรี จังหวัดราชบุรี โดยประยุกต์กรอบแนวคิดการเสริมสร้างความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพของกองสุขศึกษา กรมสนับสนุนบริการสุขภาพ กลุ่มตัวอย่าง คือ พนักงานองค์ปกครองส่วนท้องถิ่น จำนวน 114 คน สุ่มอย่างง่ายด้วยวิธีการจับฉลาก เป็นกลุ่มทดลอง 57 คน และกลุ่มควบคุม 57 คน กลุ่มทดลองได้รับโปรแกรมเสริมสร้างความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพผ่านทางแอปพลิเคชันไลน์เป็นระยะเวลา 8 สัปดาห์ ในขณะที่กลุ่มควบคุมไม่ได้โปรแกรมใด ดำเนินการเก็บข้อมูลโดยผู้วิจัยใช้แบบสอบถามข้อมูลส่วนบุคคล แบบประเมินความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพในการปฏิบัติกิจกรรมทางกาย และแบบสอบถามกิจกรรมทางกายระดับสากล ได้ค่าความตรงเชิงเนื้อหาเท่ากับ 1.0 และค่าความเชื่อมั่นเท่ากับ .977 และ .983 ตามลำดับ วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลด้วยสถิติเชิงพรรณนา สถิติ Paired t-test และสถิติ Independent t-test ผลการวิจัยพบว่า
1. หลังการทดลองกลุ่มทดลองมีค่าเฉลี่ยของคะแนนความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพในการปฏิบัติกิจกรรมทางกาย สูงกว่าก่อนการทดลองและสูงกว่ากลุ่มควบคุมอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ .05 (p-value < .05)
2. หลังการทดลองค่าเฉลี่ยพฤติกรรมการปฏิบัติกิจกรรมทางกายสูงกว่าก่อนการทดลองและสูงกว่ากลุ่มควบคุมอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ .05 (p-value < .05)
ควรนำโปรแกรมฯ ไปใช้เป็นแนวทางการดำเนินงานสำหรับบุคลากรทางสุขภาพ เช่น พยาบาลเวชปฏิบัติชุมชน ในการสร้างเสริมความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพเพื่อส่งเสริมกิจกรรมทางกายกลุ่มวัยทำงานผ่านทาง Social Media ที่สอดคล้องกับแนวคิดชีวิตวิถีถัดไป (Next Normal)
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Abdollahi, M., & Peyman, N. (2017). The Effect of an educational program based on health literacy strategies on physical activity in postpartum women. Journal of Midwifery & Reproductive Health, 5(4), 1059–1065. doi.org/10.22038/JMRH.2017.9252
Choojai, R., Boonsiri, C., & Patcheep, K. (2021). Effects of a health literacy enhancement program for COVID-19 prevention on health literacy and prevention behavior of COVID-19 among village health volunteers in Don Tako sub-district, Mueang district. The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health, 8(1), 252-262. (in Thai)
Glun-gumnird, N., & Nunthaitaweekul, P. (2023). Effects of self-efficacy promoting program combined with resistance exercise on pain and physical activity among patients with knee osteoarthritis. Thai Journal of Nursing, 72(4), 1–10. (in Thai)
Health Education Division, Ministry of Public Health. (2018). Guidelines for Promoting Health Literacy and Health Behaviors According to the National Health Act (3rd ed.). Bangkok: Sam Charoen Panich. (in Thai)
Ho, T. G., Hosseinzadeh, H., Rahman, B., & Sheikh, M. (2018). Health literacy and health-promoting behaviours among Australian-Singaporean communities living in Sydney metropolitan area. Proceedings of Singapore Healthcare, 27(2), 125–131. doi.org/10.1177/2010105817741906
Iawsawasdikul, R. (2016). Factors Related to the Exercise Behaviors of Personnel Under Phutthamonthon Subdistrict Municipality, Nakhon Pathom Province. A Dissertation Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for the Master of Public Health Degree in Faculty of Liberal Arts, Krirk University. (in Thai)
Inratsapong, W. (2023). The Effectiveness of a Self-efficacy Enhancement Program of Chronic disease patients with third- fourth stage chronic kidney disease in Siratana District, Sisaket Province. Journal of Health Consumer Protection (Online), 3(2), 50-62. (in Thai)
Kanbuala, W., Aiadsuy, N., & Deenan, A. (2023). The Effects of a health literacy promotion program on health literacy, food consumption behavior, exercise behavior and waist circumference of people with dyslipidemia. Journal of Prapokklao Hospital Clinical Medical Education Center, 40(2), 241-249. (in Thai)
Katewongsa, P., Widyastari, D. A., Haemathulin, N., Khanawapee, A., & Penmai, S. (2023). Recovery shape of physical activity after COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Sport and Health Science, 12(4), 501–512. doi.org/10.1016/j.jshs.2023.02.007
Kladthong, S., & Yamsakul, N. . (2021). The Effects of health literacy enhancement program according to 2 Aor. principles on health literacy, health behavior and blood sugar level of people with type 2 pre-diabetes mellitus. The Academic and Nursing Journal of Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Chakriraj, 1(2), 14–26. (in Thai)
Lee, I. M., Shiroma, E. J., Lobelo, F., Puska, P., Blair, S. N., Katzmarzyk, P. T., & Lancet Physical Activity Series Working Group. (2012). Effect of physical inactivity on major non-communicable diseases worldwide: an analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy. Lancet (London, England), 380(9838), 219–229. doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61031-9
Nutbeam, D. (2000). Health literacy as a public health goal: a challenge for contemporary health education and communication strategies into the 21st century. Health Promotion International, 15(3), 259-267. doi.org/10.1093/heapro/15.3.259
Physical Activity and Health Division, Department of Health. (2009). Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ). Bangkok: The War Veterans Organization of Thailand. (in Thai)
Pieasakran, T., Jiewpattanakul, Y., & Rerkluenrit, J. (2023). Effects of a health literacy exercise program on the exercise behaviors and health literacy of older adults with hypertension in the communities, Bangkok Metropolis. Nursing Science Journal of Thailand, 41(4), 44–55. (in Thai)
Polit, D. F., & Beck, C. T. (2021). Nursing Research: Generating and Assessing Evidence for Nursing Practice. (11th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer.
Regional Health Promotion Center 5 Ratchaburi. (2021). Report on the Survey of Health Behaviors, Literacy, and Environmental Factors Affecting the Health of the Working Population in Health Region 5, 2020. Retrieved January 23, 2023 from https://apps.hpc.go.th/dl/web/upFile/2021/01-5004-20210105135644/edcdbcbed5e894 c7d9e9de8a23183bf4.docx (in Thai)
Sookpool, A., Kingmala, C., Pangsuk, P., Yeanyoun, T., & Wongmun, W. (2020). Effectiveness of health literacy and health behavior development program for working people. Journal of Health Science of Thailand, 29(3), 419–429. (in Thai)
Thailand Physical Activity Knowledge Development Center. (2020). Home Physical Activity Guide. Retrieved January 21, 2023 from ttps://tpak.or.th/public/backend/print_media_file/82. (in Thai)
Thailand Physical Activity Knowledge Development Center. (2020). Regenerating Physical Activity in Thailand after COVID-19 pandemic. Retrieved January 21, 2023 from ttps://tpak.or.th/public/backend/print_media_file/81. (in Thai)
Tossanoot, P., & Posaen, R. (2023). The effectiveness of the behavior modification in dietary consumption and physical activities for diabetes prevention among overweight adults. Journal of Nursing and Health Science Research, 15(1), 219-235. (in Thai)
Wichainprapha, A., & Mekkamol, K. (2022). The effect of health literacy development program among primigravida on COVID-19 prevention behavior. Journal of Phrapokklao Nursing College, Chanthaburi, 33(2), 246–259. (in Thai)
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารเครือข่าย วิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการหรือเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและวิทยาลัยการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้







