ปัจจัยทำนายคุณภาพชีวิตของผู้สูงอายุจังหวัดนราธิวาส ภายใต้สถานการณ์ระบาดของโรคโควิด 19
คำสำคัญ:
ปัจจัยทำนาย, คุณภาพชีวิตของผู้สูงอายุ, โรคปอดอักเสบจากเชื้อไวรัสโคโรน่า 2019บทคัดย่อ
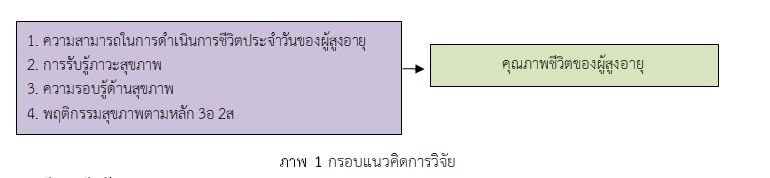
การวิจัยเชิงทำนายครั้งนี้เป็นการศึกษาปัจจัยทำนายคุณภาพชีวิตของผู้สูงอายุ จังหวัดนราธิวาสภายใต้สถานการณ์ระบาดของโรคโควิด 19 กลุ่มตัวอย่างเป็นผู้สูงอายุ จำนวน 142 คน ที่ได้จากการสุ่มตัวอย่างแบบหลายขั้นตอนในพื้นที่จังหวัดนราธิวาส เก็บข้อมูลโดยการสัมภาษณ์ตามแบบสอบถาม ตรวจสอบคุณภาพของเครื่องมือแบบสอบถามโดยผู้ทรงคุณวุฒิ จำนวน 3 ท่าน มีค่าดัชนีความสอดคล้องของวัตถุประสงค์รายข้อ (IOC) อยู่ระหว่าง .67-1.00 แบบสอบถามความสามารถในการดำเนินชีวิตประจำวัน การรับรู้ภาวะสุขภาพ ความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพ (ยกเว้นด้านความรู้ความเข้าใจทางสุขภาพ) และคุณภาพชีวิตของผู้สูงอายุ มีค่าสัมประสิทธิ์ความเชื่อมั่นแอลฟาของคอนบาคเท่ากับ .94, .95, .81, .81 และ .89 ตามลำดับ สำหรับแบบสอบถามความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพของผู้สูงอายุ ด้านความรู้ความเข้าใจทางสุขภาพ มีค่าความเชื่อมั่นด้วยวิธีการคูเดอร์ริชาร์ดสัน 20 เท่ากับ .81 วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลโดยสถิติเชิงบรรยายและการวิเคราะห์ถดถอยพหุคูณแบบขั้นตอน ผลการวิจัยพบว่า
1. ผู้สูงอายุมีความสามารถในการดำเนินชีวิตประจำวันและพฤติกรรมสุขภาพตามหลัก 3อ 2ส อยู่ในระดับดี (M = 19.53, SD = 1.70 และ M = 22.23, SD = 3.53 ตามลำดับ) คุณภาพชีวิตอยู่ในระดับปานกลาง (M = 93.61, SD = 21.11) ส่วนการรับรู้ภาวะสุขภาพและความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพมีคะแนนเฉลี่ยอยู่ในระดับไม่ดี (M = 108.37, SD = 30.31 และ M = 36.23, SD = 7.52 ตามลำดับ
2. การรับรู้ภาวะสุขภาพ ความสามารถในการดำเนินชีวิตประจำวัน และความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพ สามารถร่วมกันทำนายคุณภาพชีวิตของผู้สูงอายุจังหวัดนราธิวาสภายใต้สถานการณ์ระบาดของโรคโควิด 19 ได้ร้อยละ 24.10 (adjR2= .241; β = .450, .137 และ .060 ตามลำดับ)
ดังนั้น บุคลากรทางสุขภาพควรจัดกิจกรรมโครงการเพื่อพัฒนาการรับรู้ภาวะสุขภาพ ความสามารถในการดำเนินชีวิตประจำวัน และความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพ ซึ่งจะช่วยเพิ่มคุณภาพชีวิตของผู้สูงอายุภายใต้สถานการณ์การระบาดของโรคโควิด 19
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Boonsatean, W. & Reantippayasakul, O. (2020). Health Literacy: Situation and Impacts on Health Status of the Older Adults. APHEIT Journal of Nursing and Health, 2(1), 1-19. (in Thai)
Boonnarakorn, S., Chansangrat, N., Buamanee, N., Dangsri, P., Phenthai, S., & Atchariyawittaya, N. (2014). Health Leadership of the Elderly Muslims in the 3 Southern Border Provinces. National academic conference on Multidisciplinary on Cultural Diversit Towards the ASEAN Community. (17 July 2014 - 18 July 2014). (in Thai)
Chaimay, B. (2013). Sample Size Determination in Descriptive Study in Public Health. Thaksin Journal, 16(2). 9-18. (in Thai)
Cohen, J. (1977). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. New York: Academic Press.
Department of Disease Control. (2021). The report of COVID-19 situation in Narathiwat province Retrieved February 1, 2021 from: http://ntwo.moph.go.th/covid19/. (in Thai)
Department of Health Service Support. (2018). COVID-19 situation. Retrieved August 20, 2020 from https://hss.moph.go.th/show_topic.php?id=3601. (in Thai)
Department of Medical Services. (2015). Geriatric syndromes. Nonthaburi: Is August Company Limited. (in Thai)
Department of Medical Services, Ministry of Public Health. (2020). Guidelines for caring for the elderly during the COVID-19 outbreak. Retrieved August 20, 2020 from http://covid19.dms.go.th/. (in Thai)
Department of Mental Health. (2002). WHO Quality of Life Indicators, abbreviated set, Thai version. Retrieved August 2, 2022 from http://www.dmh.go.th/test/dowmload/files/whoqol.pdf. (in Thai)
Department of Older Persons. (2023). Elderly Statistic Data June 2023. Retrieved October 25, 2023 from https://www.dop.go.th/th/know/side/1/1/2387. (in Thai)
Ginggeaw, S. & Prasertsri, N. (2016). The Relationship between Health Literacy and Health Behaviors among Older Adults who have Multi-morbidity. Nursing Journal of the Ministry of Public Health, 25(3). 43-54. (in Thai)
Health Systems Research Institute. (1998). Definition of health promotion terminology. (Revised Edition). Nonthaburi: Health Systems Research Institute. (in Thai)
Judpoon, S. (2013). Social welfare management for developing quality of life of the elderly in ubdistrict Administrative Organization, Banlat district, Veridian E-Journal Silpakorn University Phetchaburi. 6(3), 510-519. (in Thai)
Kaewsuksai, R., Kongkun, P., Tongkoop, B., Samaair L., & Boonnarakorn, S. (2021). Relationships Between Knowledge, Perception, and the "New Normal Behaviors" for Preventing Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Infection among People in Narathiwat Province. The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health, 8(2), 67-79. (in Thai)
Kulsoontorn, K., Wingpat, K. & Bodeerat, C. (2021). Guidelines for Caring the Elderly During a COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Roi Kaensarn AcademiVol, 6(11). 288-302. (in Thai)
Narathiwat Public Health Office. (2020). The report of COVID-19 situations in Narathiwat province. Retrieved February 6, 2021 from http://ntwo.moph.go.th/covid19/. (in Thai)
Narathiwat Provincial Statistical Office. (2020). Narathiwat Provincial Statistical Report. Retrieved August 20, 2020 from http://narathiwat.nso.go.th/images/Statisticalinformationservice/ provincialstatisticalreport/2019 provincialstreport/2019 narathiwatstreportcompress.pdf. (in Thai)
Nilnate, W., Hengpraprom, S. & Hanvoravongchai, P. (2016). Level of Health Literacy in Thai Elders, Bangkok, Thailand. Journal of Health Research, 30(5). 315-321.
Noknoi, C. & Boripunt, W. (2017). The quality of life of elders in Songkhla province. Princess of Naradhiwas University Journal, 9(3), 94-110. (in Thai)
Prasartkul, P. (2018). (editor). Situation of the Thai elderly. Bangkok: Amarin Printing & Publishing. (in Thai)
Pradubmook, S, P., Theerasilp, U. & Phetchai, P. (2023). The Elderly’s Life Situations and Determinants of Elderly Violence: The Quantitative Survey in 5 Provinces. Journal of Roi Kaensarn Academi, 8(5), 472-490. (in Thai)
Prateepmanowong, J. (2019). The relationships between activities of daily living, exercise behaviour and quality of life in older persons with coronary artery disease. The Journal of Faculty of Nursing Burapha University, 27 (4). 66-76. (in Thai)
Punthasee, P. & Srisawad, K. (2020). Correlations between Health Belief and 3E 2S Health Behaviors of Elderly in Taejew Community Tungwatdorn Satorn Bangkok Thailand. Journal of Health and Health Management, 6(1), 45-57. (in Thai)
Srithanee, K. (2017). Relationship between Health Literacy and Quality of the Elderly’s Life at the Central Part of the North-East Thailand. Journal of Health Systems Research, 11(1). 26-36. (in Thai)
Suriart, C., Rutchanagul, P. & Thongbai, W. (2014). Health Perceptions, Health Behaviors and Health Service Needs among Inmates with Metabolic Disorders. Ramathibodi Nursing Journal, 20(3), 372-387. (in Thai)
Wongsawat, S. (2020). Knowledge of mind and spiritual care in COVID-19 pandemic. Department of Mental Health, Nonthaburi. Department of Mental Health. (in Thai)
Vanichbuncha, K. (2002). Principles of statistics. (7thed). Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Printing. (in Thai)
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2023 วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารเครือข่าย วิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการหรือเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและวิทยาลัยการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้







