ผลของโปรแกรมป้องกันภาวะเบาหวานขณะตั้งครรภ์ต่อความตั้งใจและ พฤติกรรมป้องกันภาวะเบาหวานขณะตั้งครรภ์ในหญิงตั้งครรภ์ที่มีภาวะน้ำหนักเกิน
คำสำคัญ:
หญิงตั้งครรภ์ที่มีภาวะน้ำหนักเกิน, ภาวะเบาหวานขณะตั้งครรภ์, ความตั้งใจในการป้องกันภาวะเบาหวานขณะตั้งครรภ์, พฤติกรรมป้องกันภาวะเบาหวานขณะตั้งครรภ์บทคัดย่อ
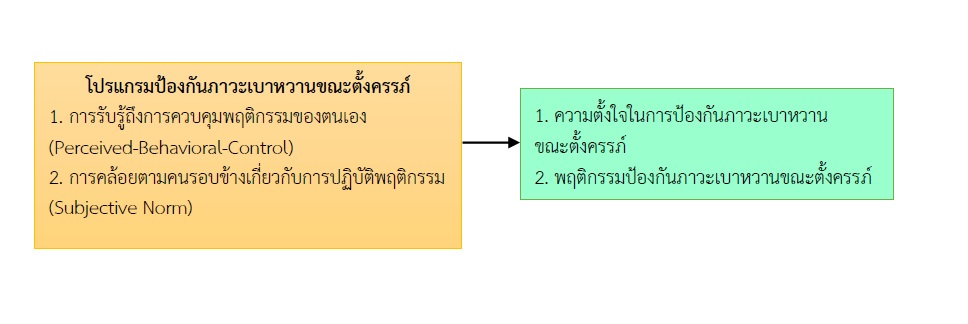
การวิจัยแบบกึ่งทดลองแบบ 2 กลุ่มวัดผลก่อนและหลังการทดลอง มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาผลของโปรแกรมป้องกันภาวะเบาหวานขณะตั้งครรภ์ต่อความตั้งใจและพฤติกรรมป้องกันภาวะเบาหวานขณะตั้งครรภ์ในหญิงตั้งครรภ์ที่มีภาวะน้ำหนักเกินก่อนการตั้งครรภ์ที่เข้ารับการฝากครรภ์ ณ แผนกฝากครรภ์ โรงพยาบาลชัยนาทนเรนทร ในช่วงเดือนธันวาคม พ.ศ. 2563 ถึง เดือนกรกฎาคม พ.ศ. 2564 ใช้วิธีสุ่มอย่างง่ายเพื่อเข้ากลุ่มทดลองและกลุ่มควบคุมกลุ่มละ 25 ราย ดำเนินโปรแกรมตามกรอบทฤษฎีการวางแผนพฤติกรรม เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูลโดยใช้แบบสอบถามความตั้งใจและแบบสอบถามพฤติกรรมป้องกันภาวะเบาหวานขณะตั้งครรภ์ มีค่าดัชนีความตรงตามเนื้อหาเท่ากับ 1.00 และค่าสัมประสิทธิ์ครอนบาคแอลฟ่า เท่ากับ .72 และ .82 ตามลำดับ วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลโดยใช้สถิติพรรณนา Chi-Square, Fisher’s Exact test, Mann-Whitney U, Independent t-test และ Dependent t-test ผลการวิจัยพบว่า
1. ภายหลังการทดลองกลุ่มทดลองมีคะแนนเฉลี่ยความความตั้งใจในการปฏิบัติตนเพื่อป้องกันภาวะเบาหวานขณะตั้งครรภ์สูงกว่ากลุ่มควบคุมอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ .001 (t48=7.53, p<.001)
2. ภายหลังการทดลองหญิงตั้งครรภ์มีคะแนนเฉลี่ยพฤติกรรมป้องกันภาวะเบาหวานขณะตั้งครรภ์สูงกว่ากลุ่มควบคุมอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ .001 (t48 =13.05, p <.001)
พยาบาลแผนกฝากครรภ์จึงควรนำโปรแกรมนี้ไปใช้เพื่อให้หญิงตั้งครรภ์เกิดความตั้งใจที่จะปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมป้องกันภาวะเบาหวานขณะตั้งครรภ์ไม่เกิดภาวะเบาหวานและภาวะแทรกซ้อนที่จะตามมาต่อทั้งมารดาและทารก
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Abdi, J., Eftekhar, H., Mahmoodi, M., Shojayzadeh, D., Sadeghi, R., & Saber, M. (2015). Effect of the Intervention Based on New Communication Technologies and the Social-Cognitive Theory on the Weight Control of the Employees with Overweight and Obesity. Journal of Research in Health Sciences, 15(4), 256–261.
Ajzen, I. (1991). Theory of Planed Behavior. Organizational Behavior & Human Decision Process, 50(2), 179-202.
Al-Hakmani, F. M., Al-Fadhil, F. A., Al-Balushi, L. H., Al-Harthy, N. A., Al-Bahri, Z. A., Al-Rawahi, N. A., et al. (2016). The Effect of Obesity on Pregnancy and Its Outcome in the Population of Oman, Seeb Province. Oman Medical Journal, 31(1), 12-17.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2020). Physical Activity and Exercise During Pregnancy and the Postpartum Period. Committee Opinion No. 804. Obstetrics & Gynecology, 135(4), 178-188.
American Diabetes Association. (2018). Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2018. Diabetes Care, 41(1), 13–27.
Antenatal Care Unit Jainad Narendra Hospital. (2019). Antenatal Registration. Chainat: Jainad Narendra hospital. (in Thai)
Bureau of Nutrition, Department of Health Ministry of Public Health. (2015). Guidelines for the Implementation of Nutritional Health Promotion in the Antenatal Clinic For Health Personnal. Bangkok: The War Veterans Organization of Thailand Under Royal Patronage of His majesty the King Printing Business Office. (in Thai)
Chairat, N. & Kala, S. (2022). Intention of Breastfeeding among Mothers with Cesarean Section: The Effects of a Nursing Program Based on the Planned Behavior Theory. The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health, 9(1), 121-134. (in Thai)
Garshasbi, A., Faghihzadeh, S., Naghizadeh, M. M. & Ghavam, M. (2008). Prevalence and Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Tehran. Journal Family Reprod Health, 2(2), 75-80.
Genova, M., Todorova-Ananieva, K. & Tzatchev, K. (2013). Impactof Body Mass Index on Insulinsensitivity/Resistancein Pregnant Women with and Without Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Acta Medica Bulgarica. 40(2), 60-67.
Glass, G. V. (1996). Primary, Secondary, and Meta-Analysis of Research. Educational Researcher, 5(10), 3-8.
International Diabetes Federation. (2017). The IDF Appropriate for Care and Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Retrieved November 3, 2022 from http://www.idf.org/wings.
International Weight Management in Pregnancy (i-WIP) Collaborative Group (2017). Effect of Diet and Physical Activity Based Interventions in Pregnancy on Gestational Weight Gain and Pregnancy Outcomes: Meta-Analysis of Individual Participant Data from Randomised Trials. The British Medical Journal (Clinical Research ed.), 358, j3119. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.j3119
Krungsaenmuang, T. & Wattananukulkiat, S. (2021). The Effects of a Health Behavior Promotion Program on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Among Pregnant Women with Potential Risks. Journal of Health and Nursing Education, 27(1), 106-121. (in Thai)
Lee, K. W., Ching, S. M., Ramachandran, V., Yee, A., Hoo, F. K. & Chia, Y. C.,et.al., (2018). Prevalence and Risk Factors of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Asia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomed Central Pregnancy and Childbirth, 18(1), 1-20.
Limruangrong, P., Boriboonhirunsarn, D., Puangsricharern, A. & Pinitlertsakun, O. (2016). Factors Influencing the Occurrence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnant Women with Abnormal. Journal of Nursing Science, 34(2), 58-69. (in Thai)
Malek, L., Umberger, W. J., Makrides, M. & ShaoJia, Z. (2017). Predicting Healthy Eating Intention and Adherence to Dietary Recommendations During Pregnancy in Australia Using the Theory of Planned Behaviour. Science Direct, 116(1), 431-441.
Polit, D. E. & Beck, C. T. (2006). Essentials of Nursing Research. (6th ed. ). Philadelphia: Lippincott.
Singwongsa, A. & Boriboonhirunsarn, D. (2016). Incidence and Associated Factors of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosed During 24-28 Weeks of Gestation. Thai Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 24(3), 184-192. (In Thai)
Sreepetch, S. & Kala, S. (2022). The Effects of a Nursing Program Applying the Theory of Planned Behavior on the Intention of Breastfeeding among Postpartum Teenage Mothers. The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health, 9(2), 26-39. (in Thai)
Sui, Z., Grivell, R. M. & Dodd, J. M. (2012). Antenatal Exercise to Improve Outcomes In Overweight or Obese Women: a Systematic Review. Acta Obstetricial et Gynecological Scandinavica, 91(5), 538-545.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2023 วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารเครือข่าย วิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการหรือเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและวิทยาลัยการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้







