ผลของการใช้แอปพลิเคชันฮักไตต่อความรอบรู้ทางด้านสุขภาพ ในผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 และโรคความดันโลหิตสูงที่เป็นโรคไตเรื้อรังระยะที่ 3 ร่วมด้วย กรณีศึกษาศูนย์แพทย์ชุมชนวัดหนองแวง พระอารามหลวง อำเภอเมือง จังหวัดขอนแก่น
คำสำคัญ:
แอปพลิเคชันฮักไต, ความรอบรู้ทางด้านสุขภาพ, กรณีศึกษาบทคัดย่อ
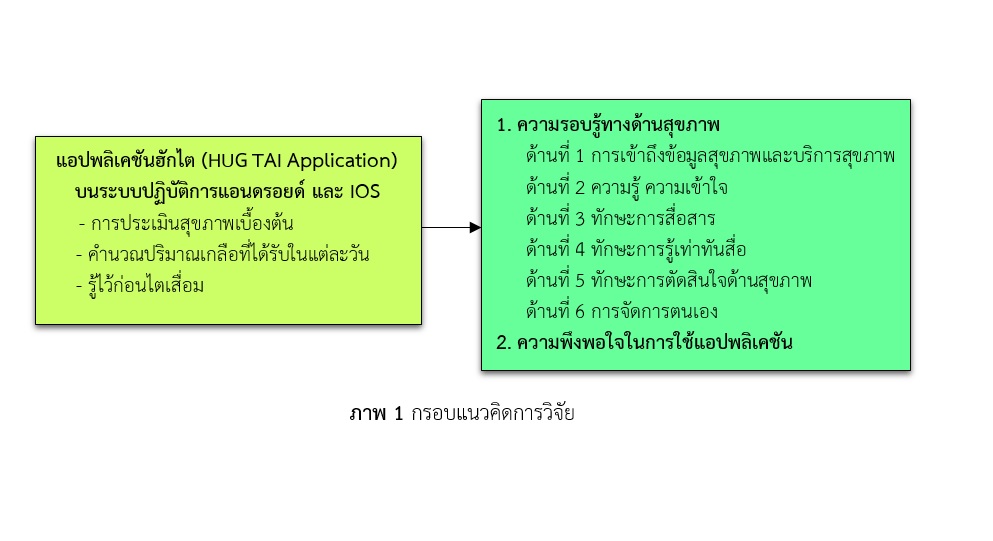
การวิจัยกึ่งทดลองแบบสองกลุ่มวัดก่อนและหลังการทดลองนี้ มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาเกี่ยวกับความรอบรู้ทางด้านสุขภาพจากการใช้แอปพลิเคชันฮักไตที่ผู้วิจัยสร้างขึ้น โดยใช้แบบประเมินความรอบรู้ทางด้านสุขภาพ และความพึงพอใจของผู้ใช้แอปพลิเคชั่น ในกลุ่มผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 และโรคความดันโลหิตสูงที่เป็นโรคไตเรื้อรังระยะที่ 3 ร่วมด้วย ศูนย์แพทย์ชุมชนวัดหนองแวงพระอารามหลวง อำเภอเมือง จังหวัดขอนแก่น กลุ่มตัวอย่างคัดเลือกแบบเฉพาะเจาะจง จำนวน 30 คน แบ่งเป็นกลุ่มทดลอง 15 คน กลุ่มควบคุม 15 คน โดยกลุ่มทดลองใช้แอพพลิเคชั่นฮักไตผ่านโทรศัพท์มือถือสามารถคำนวณปริมาณโซเดียม น้ำตาล และคำแนะนำการปฏิบัติตัวเพื่อชะลอการเสื่อมของไต เป็นเวลา 4 สัปดาห์ เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูลโดยใช้แบบประเมินความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพ ตรวจสอบคุณภาพของเครื่องมือโดยการหาค่าสัมประสิทธิ์อัลฟาของครอนบราค ได้ค่าความเที่ยงเท่ากับ 0.74 วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลโดยใช้ค่าร้อยละ ค่าเฉลี่ย ส่วนเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐาน สถิติ Paired t-test และสถิติ Independent t-test ผลการวิจัยพบว่า
1. ความรอบรู้ทางด้านสุขภาพภายหลังการใช้แอปพลิเคชันของกลุ่มทดลอง สูงกว่าก่อนการใช้แอปพลิเคชั่น อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ 0.05
2. ความรอบรู้ทางด้านสุขภาพภายหลังการใช้แอปพลิเคชันของกลุ่มทดลอง สูงกว่ากลุ่มควบคุมอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ 0.05
3. ความพึงพอใจหลังจากใช้แอปพลิเคชันอยู่ในระดับมาก (M=4.25, SD=0.74)
ควรจัดให้มีการนำแอปพลิเคชั่นไปใช้ในการดูแลผู้ป่วยและใช้สำหรับการส่งเสริมพฤติกรรมสุขภาพที่ดีของผู้ป่วยด้วยตนเอง โดยพัฒนาอย่างต่อเนื่องเพื่อให้เหมาะสมกับบริบททางสังคมและวัฒนธรรมในท้องถิ่น โดยมุ่งเน้นผู้ป่วยและครอบครัว สถานบริการสุขภาพ องค์กรและชุมชนในท้องถิ่น ให้มีความสามารถในการดูแลสุขภาพตนเองให้ดียิ่งขึ้นไป
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Apinya, T. (2018). Operating Manual for Implementation Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in Diabetes Patient and Hypertension. Nonthaburi: Bureau of Non Communicble Disease Ministry of Public Health. (in Thai)
Division of Non-Communicable Disease. (2018). Situation of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCD), Illness Statistics and Premature Death. 2018. Retrieved 5 October 2018 from http://thaincd.com/2016/media-detail.php?id=12986&gid=1-015-008 (in Thai)
Ginggaeaw, S., Prasertsri, N., & Promwong, W. (2019). The Roles of Community Nurse for Promoting Health Literacy in the Elderly with Chronic Illness. Journal of Nursing, Public Health, and Education, 20(1), 3-13. (in Thai)
Health Education Divition. (2018). Enhancing and Assessing Health Literacy and Health Behavior. Nontaburi: Ministry of Public Health.
Kidney Disease Association of Thailand. (2017). Recommendations for Care for Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Before Kidney Replacement Treatment, 2015. Bangkok: Kidney Disease Association of Thailand. (in Thai)
Kidney Disease Association of Thailand. (2016). Global Prevalence Tate of Diabetes from IDF. 2016. Retrieved 5 October 2016 from http://iregist.igenco.co.th/web/dmthai_old/ statistic/406 (in Thai)
Nutbeam, D. (2008). The Evolving Concept of Health Literacy. Social Science and Medicine, 67(12), 2072-2078.
Pannark, P., Moolsart, S., & Kaewprom, C. (2018). The Effectiveness of a Program for Health Literacy Development of the Patients with Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes at Bangwua District, Chachoengsao Province. Nursing Journal of the Ministry of Public Health, 27(3), 91-106. (in Thai)
Phongissaranuporn, S., Laipoonsawad, S., & Supachaipanichpong, P. (2018) Outputs of Self-Management Support Program for Delayed-Progression of Diabetes Nephropathy and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Damnoen Saduak Hospital. Region 4-5 Medical Journal, 37(2), 148-159. (in Thai)
Saedkong, P, Lunput, S., PhanomKaen, S., Mahem, K., & Pornpeng, D. (2019). Effect of Using Haktai Tool Innovative on Knowledge Believe and Health Behaviors in Chronic Kidney Disease. Journal of Nursing and Health Care, 36(4), 214-222. (in Thai)
Seesanea, S., Wattanakitkrileart, D., Charoenkitkarn, V., Dumavibhat, C., & Vanijja, V. (2018). The Effect of Mobile Application on Medication Adherence in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome after Hospitalization. Nursing Journal of the Ministry of Public Health, 28(1), (61-74). (in Thai)
Unaphak, P., & Rattanamanee, K. (2013). The Correlation Factors of Self-Care Behaviors to Prevent Complications among Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease at Somdetphraphutthalertla Hospital in Samutsongkhram Province. The Public Health Journal of Burapha University, 10(2), 44-54. (in Thai)
Wat Nong Wang Community Medical Center. (2018). Kidney Disease Patient Information at Nong Waeng Community Medical Center Khon Kaen Province. Khon Kaen: Wat Nong Wang Community Medical Center. (in Thai)
Winaiprasert, P., & Mamom, J. (2019). Development the Required Daily Nutrition Applications (NuTu-App) to Promote Nutrition Status in Patients with Pressure Ulcers. Thai Science and Technology Journal, 27(3), 485-498. (in Thai)
Wongnisanatakul, K. (2019). Health Literacy among Diabetic Patients at the Family Practice Center of Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya Hospital. Journal of Preventive Medicine Association of Thailand, 8(1), 49-61. (in Thai)
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารเครือข่าย วิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการหรือเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและวิทยาลัยการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้







