ปัจจัยที่มีอิทธิพลต่อการเกิดอุบัติเหตุจากการปฏิบัติงานของบุคลากรทันตสาธารณสุข ในโรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบลของจังหวัดยะลา
คำสำคัญ:
ความชุก, ปัจจัย, อุบัติเหตุจากการทำงาน, ทันตสาธารณสุข, โรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบลบทคัดย่อ
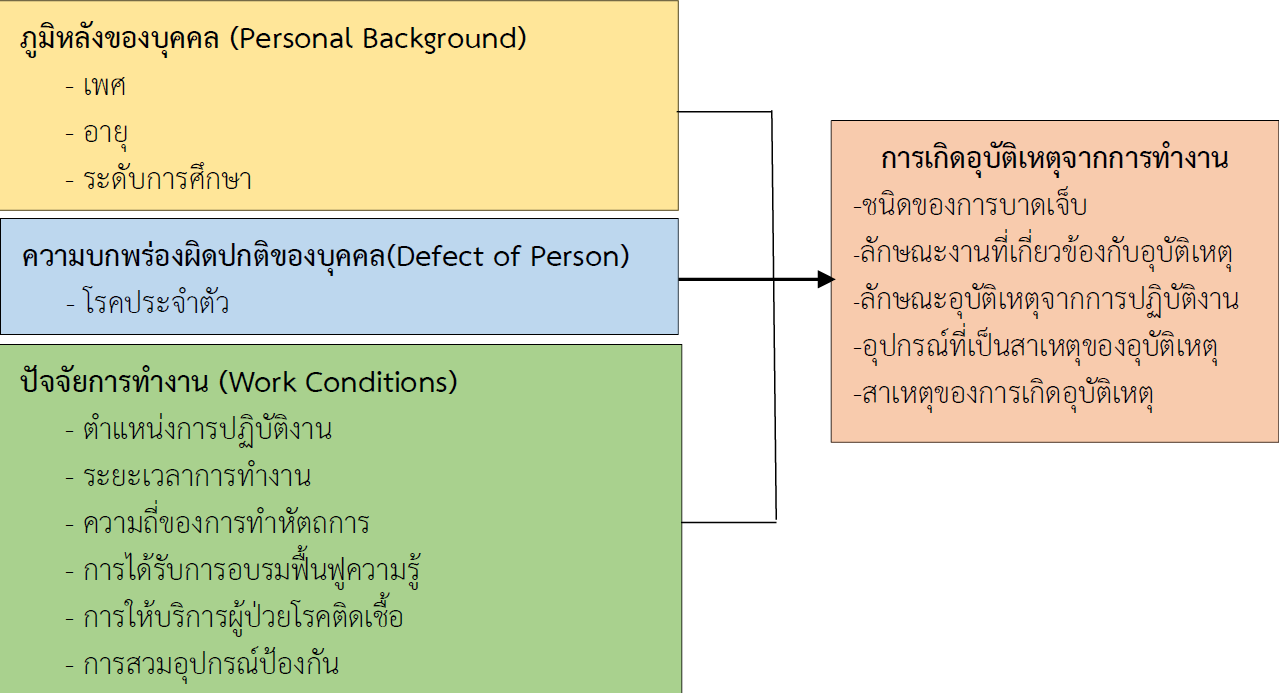
การวิจัยเชิงพรรณนาแบบภาพตัดขวางนี้ เพื่อศึกษาอัตราความชุกและปัจจัยเสี่ยงที่มีอิทธิพลต่อการเกิดอุบัติเหตุจากการทำงานของบุคลากรทันตสาธารณสุขในโรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบลของจังหวัดยะลา เก็บข้อมูลจากบุคลากรทันตสาธารณสุขที่ปฏิบัติงานในโรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบลของจังหวัดยะลา จำนวน 143 คน คัดเลือกโดยวิธีการสุ่มตัวอย่างอย่างง่าย วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลทั่วไปโดยใช้สถิติเชิงพรรณนา และวิเคราะห์ปัจจัยพยากรณ์โดยใช้ สถิติถดถอยพหุคูณ โดยมีการควบคุมตัวแปรกวน ได้แก่ เพศและอายุ ผลการวิจัยพบว่า
1. อัตราความชุกของการเกิดอุบัติเหตุถูกของมีคมและการสัมผัสเลือดและสารคัดหลั่ง คิดเป็นร้อยละ 38.46 โดยการถูกของมีคมบาด คิดเป็นร้อยละ 71.18 และการสัมผัสเลือดและสารคัดหลั่งพบร้อยละ 16.94 การขูดหินปูนพบการเกิดอุบัติเหตุร้อยละ 52.72
2. เมื่อควบคุมตัวแปรเพศและอายุ พบว่าปัจจัยเสี่ยงที่มีอิทธิพลกับการเกิดอุบัติเหตุอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ ได้แก่ ระดับการศึกษาต่ำกว่าระดับปริญญาตรี (AOR = 4.35, 95% CI = 1.88 – 10.06) และการสวมอุปกรณ์ป้องกันไม่เพียงพอ (AOR = 6.74, 95% CI = 1.69 – 26.86)
จากผลการศึกษาการลดการเกิดอุบัติเหตุจากการปฏิบัติงานด้านทันตกรรมควรมีการพัฒนาสมรรถนะของบุคลากรทันตสาธารณสุขโดยหน่วยงานควรมีการสนับสนุนให้บุคลากรได้รับการอบรมความรู้โดยเพราะด้านความปลอดภัยในการทำงาน และทักษะด้านการทำงาน รวมถึงการใช้อุปกรณ์ป้องกันส่วนบุคคลที่เพียงพอ เพื่อช่วยลดโอกาสเสี่ยงต่อการเกิดอุบัติเหตุจากการทำงานของบุคลากรทันตสาธารณสุข
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Aldakhil, L., Yenugadhati, N., Al-Seraihi, O., & Al-Zoughool, M. (2019). Prevalence and associated factors for needlestick and sharp injuries (NSIs) among dental assistants in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine, 24(1), 1-7.
Ardekani, A., Ayatollahi, J., Ayatollahi, F., Bahrololoomi, R., Ayatollahi, J., Ayatollahi, A., & Owlia, M. (2012). Occupational hazards to dental staff. Dental Research Journal, 9(1), 2-7.
Chanpanich, R., Singchungcha,i P., & Aree, P. (2022). Cost analysis of nursing activities in the COVID-19 cohort ward at a tertiary hospital. The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health. 10(3), 1-14.
Cheng, H. C., Su, C. Y., Yen, A. M. F., & Huang, C. F. (2012). Factors affecting occupational exposure to needlestick and sharps injuries among dentists in Taiwan: A nationwide survey. PLoS ONE, 7(4), 1-7.
Cleveland, J. L., Barker, L. K., Cuny, E. J., & Panlilio, A. L. (2007). Preventing percutaneous injuries among dental health care personnel. Journal of the American Dental Association, 138(2), 169 – 178.
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A. G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 175 – 191.
Heinrich, H. W. (1941). Industrial Accident Prevention: A Scientific Approach. (2nd Ed.). New York and London: McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc.
Iwamatsu-Kobayashi, Y., Watanabe, J., Kusama, T., Endo H., Ikeda, S., Tokuda, K, et al. (2022). A 19-year study of dental needlestick and sharps injuries in Japan. International Dental Journal, 73 (2023), 114 – 120.
Kheytui, W., Janaiem, W., Natthasetsakul, S & Tanan, A. (2020). Study of factors affecting incidence of patient’s blood or fluid contamination, needle stick or injury form sharp instrument in Dental Students at Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University. Mahidol R2R E-Journal, 7(1), 1–15. (in Thai)
Lee, J. J., Kok, S. H., Cheng, S. J., Lin, L. D., & Lin, C. P. (2014). Needlestick and sharps injuries among dental healthcare workers at a university hospital. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association, 113(4), 227 – 233.
Macintyre, C. R., Seale, H., Yang, P., Zhang, Y., Shi, W., Almatroudi, A., et al. (2014). Quantifying the risk of respiratory infection in healthcare workers performing high-risk procedures. Epidemiology and Infection, 142, 1802 – 1808.
Matsumoto, H., Sunakawa, M., Suda, H., & Izumi, Y. (2019). Analysis of factors related to needle-stick and sharps injuries at a dental specialty university hospital and possible prevention methods. Journal of Oral Science, 61(1), 164 – 170.
Ministry of Public health. (2019). Number of Patients Who Attended Dental Health Clinic in Yala Province (HDC data) in 2019. Retrieved October 12, 2020 from https://hdcservice.moph.go.th/ hdc/reports/report.php?source=dental/dental_1.php&cat_id=fc73b811eb6d9206e7e5baf8ad20d7b9&id=cba4cc41872398d244dde8e2604c1fda
Paul, T., Omar, R., & Maktabi, A. (2000). Self-reported needlestick injuries in dental health care workers at Armed Forces Hospital Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Military Medicine, 165(3), 208 – 210.
Shah, S. M., Merchant, A. T., & Dosman, J. A. (2006). Percutaneous injuries among dental professionals in Washington State. BMC public health, 6, 269. doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-6-269
Suwannakarn, T. (2015). Prevalence and Factor Associated with Sharp Injuries among Hospital Workers in a Private Hospital, Songkhla Province. A Dissertation Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for the Degree of Master of Science in Occupational Medicine, Prince of Songkhla University. Retrieved March 12, 2020 from https://core.ac.uk/ download/pdf/154815143.pdf (in Thai)
Verbeek, J. H., Rajamaki, B., Ijaz, S., Sauni, R., Toomey, E., Blackwood, B., et al. (2020). Personal protective equipment for preventing highly infectious diseases due to exposure to contaminated body fluids in healthcare staff. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, 4(4), CD011621. doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011621.pub4
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารเครือข่าย วิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการหรือเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและวิทยาลัยการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้







