ปัจจัยทำนายพฤติกรรมการหลีกเลี่ยงการได้รับบุหรี่มือสองของนักศึกษา ในมหาวิทยาลัย
คำสำคัญ:
ควันบุหรี่มือสอง, ความสามารถ, โอกาส, แรงจูงใจบทคัดย่อ
การศึกษาความสัมพันธ์เชิงทำนายนี้ มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาระดับพฤติกรรมหลีกเลี่ยงการได้รับควันบุหรี่มือสองของนักศึกษา และศึกษาปัจจัยพยากรณ์พฤติกรรมหลีกเลี่ยงการได้รับควันบุหรี่มือสองของนักศึกษาในมหาวิทยาลัยเขตดุสิต กรุงเทพมหานคร 147 คน เครื่องมือที่ใช้ได้แก่แบบสอบถามที่ผู้วิจัยสร้างขึ้นตามแนวคิดวงล้อจากวงล้อการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรม (The Behavior Chang Wheel) ผ่านการตรวจสอบความตรงตามเนื้อหาโดยผู้ทรงคุณวุฒิ 3 ท่าน มีค่าดัชนีความตรงตามเนื้อหาอยู่ระหว่าง .83 - 1.00 ค่าความเชื่อมั่นอยู่ระหว่าง .79-.92 วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลทั่วไปด้วยสถิติเชิงพรรณนา และวิเคราะห์ถดถอยทางพหุคูณแบบลำดับขั้น ผลการวิจัยพบว่า
1. ระดับพฤติกรรมการหลีกเลี่ยงการได้รับบุหรี่มือสองในภาพรวมอยู่ในระดับปานกลาง (M=14.88, SD=5.90)
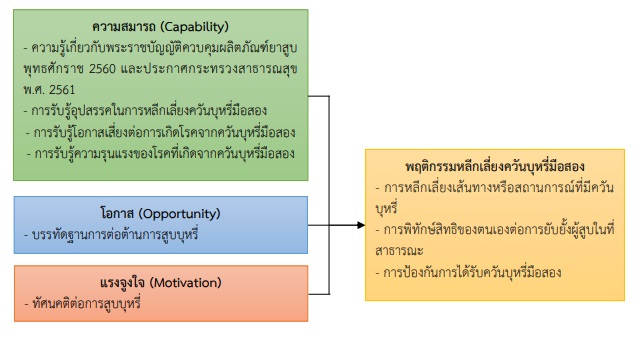
2. ปัจจัยทำนายพฤติกรรมการหลีกเลี่ยงการได้รับบุหรี่มือสองพฤติกรรมการหลีกเลี่ยงการได้รับบุหรี่มือสอง ตามองค์ประกอบของ ความสามารถ โอกาส และแรงจูงใจ ประกอบไปด้วยตัวแปรทั้ง 6 ตัวโดยเรียงจากตัวแปรที่มีอิทธิพลสูงที่สุด ได้แก่ ความรู้เกี่ยวกับพระราชบัญญัติควบคุมผลิตภัณฑ์ยาสูบพุทธศักราช ฯ (b=.332) การรับรู้ความรุนแรงของบุหรี่มือสอง (b=284) การต่อต้านการสูบบุหรี่ของคนรอบข้าง (b=.259) การรับรู้โอกาสเสี่ยงการเกิดโรคจากควันบุหรี่มือสอง (b =.246) ทัศนคติต่อการสูบบุหรี่ (b=-.169) และการรับรู้อุปสรรคในการหลีกเลี่ยงควันบุหรี่มือสอง (b=-.113) โดยสามารถร่วมอธิบายได้ ร้อยละ 86.3
หน่วยงานที่เกี่ยวข้องเช่นสถาบันการศึกษาควรดำเนินการเพื่อส่งเสริมความสามารถในการหลีกเลี่ยงควันบุหรี่มือสองเช่นการเพิ่มช่องทางการสื่อสารความรู้เกี่ยวกับเกี่ยวกับพระราชบัญญัติควบคุมผลิตภัณฑ์ยาสูบรวมไปถึงการรณรงค์ต่อต้านการสูบบุหรี่ในที่สาธารณะ มีนโยบายเพื่อการลดอุปสรรคในการหลีกเลี่ยงควันบุหรี่มือสอง รวมไปถึงการจูงใจให้นักศึกษาหลีกเลี่ยงควันบุหรี่มือสองโดยการพัฒนาการรับรู้เกี่ยวกับความรุนแรง โอกาสเสี่ยงการเกิดโรคจากควันบุหรี่มือสอง
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Becker, M. H. & Maiman L. A. (1975). The Health Belief Model and and Sick Role Behavior, In the Health Belief Model and Personal Health Behavior. New Jersey: Chales B. Slack.
Altman, D. G., & Bland, J. M. (1995). Statistics Notes: the nNormal Distribution. BMJ; 310:298, doi: 10.1136/bmj.310.6975.298.
Best, J. W. (1977). Research in Education. (3 rd ed). New Jersey: Prentice hall Inc.
Cohen, J. (1977). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. New York: Academic.
Goode, Erich (2015), "The Sociology of Deviance", The Handbook of Deviance, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 1–29, doi:10.1002/9781118701386.
Junnual, N, & Seubsamran, P. (2016). The Situation of Smoking Behavior among Staff and Students at Ubon Ratchathani University: Smoke Free Ubon Ratchathani University Project. Journal of Science and Technology, Ubon Ratchathani University, 18(2), 1-10. (In Thai)
Lian, T. Y., & Dorotheo, U. (2016). The Tobacco Control Atlas: ASEAN Region. Third Edition. Bangkok, Thailand.
Michie, S., Atkins, L., & West, R. (2014). The Behaviour Change Wheel: A Guide to Designing Interventions (1 ed.). Great Britain: Silverback Publishing.
Nurapak, A., Sombhopcharoen, M., Temsirikunchai, L., & Kengganpanich, M. (2014). Factors Correlated with Assertive Behavior from Second Hand Smoke in Secondary School Students in Bangkok Metropolitan. Journal of Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Bangkok, 30(2), 37-47. (In Thai)
Phetphoom, C., Pyeamkleep, R., & Pongpreecha, B. (2018). Factors Affecting Avoidance Behavior of Secondhand Smoke among Students in the University. The Public Health Journal of Burapha University, 13(2), 89-101. (In Thai)
Sirichotiratana, N. (2016). Impact of Free Trade Agreements on Tobacco Control. Public Health & Health Laws Journal, 2(2), 225-242.
Susi, A. K., Ni Putu Ayu, L. P., Kadek, I. K., & Karina, A. S. (2019). Incidence and Mortality of Cancers Related to Secondhand Smoking in Southeast Asia Countries. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 20(3), 971-976. DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.3.971
Suthum, K., Boonshuyar, C. & Pacheun, O. (2019). Preventive Behaviors on Secondhand Smoke among Secondary School Pupils, Ratchaburi Province. Journal of Health Education, 42(2), 172-183. (In Thai)
Suwanwong, C., & Pimthong, S. (2017). Factors Affecting Smoking Prevention Behavior among Adolescents: Research Synthesis by Systematic Review. Journal of Behavioral Science, 24(1), 63-81. (In Thai)
Thongkanya, R., & Preechawong, S. (2014). Factors Predicting Second-Hand Smoke Avoidance Behavior in Chronic Illness Patients, Bangkok Metropolis. Journal of The Royal Thai Army Nurses, 15(2), 331-338. (In Thai)
Thrasher, J. F., Boado, M., Sebrie, E. M., & Bianco, E. (2009). Smoke-Free Policies and the Social Acceptability of Smoking in Uruguay and Mexico: Findings from the International Tobacco Control Policy Evaluation Project. Nicotine & Tobacco Research, 11(6), 591-99. (In Thai)
Usah, J., Gunvihok, T., Julasereeku, S., Haruhanpong, V. (2015). Meta Synthesis of Preventive Factors for Cigarette Smoking Among Thai Youths. Disease Control Journal, 41(4), 271-84. (In Thai)
Wang, W. L., Herting, J. R., & Tung, Y. Y. (2008). Adolescents’Avoidance of Secondhand Smoke Exposure: Model Testing. Western Journal of Nursing Research, 30(7), 836-851.
Wattanawilai, C., & Rakpuangchon, W. (2018). Smoking Motivation and Non-Smoking Intention among Boy Students with a Smoking Family Member. The Journal of Faculty of Nursing Burapha University, 26(1), 20-28. (In Thai)
World Health Organization. (2009). WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2009: Implementing Smoke-Free Environment. Geneva: World Health Organization.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2022 วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารเครือข่าย วิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการหรือเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและวิทยาลัยการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้







