Effects of Using Simulation Based Learning on Self-Confidence in Primary Medical Care among Nursing Students in Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Songkhla
Keywords:
Simulation Based Learning, Self-Confidence, Satisfaction, Primary Medical CareAbstract
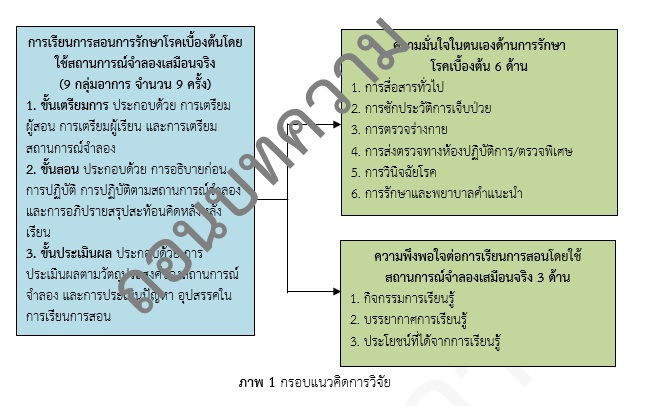
This one-group pre-test post-test quasi-experimental study aimed to compare self-confidence in primary medical care among nursing students before and after using simulation based learning and nursing students’ satisfaction, Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Songkhla, selected by purposive sampling. Research instrument were self-confidence and satisfaction satisfaction of simulation based learning. Population were 78 fourth year nursing students, academic year of 2021, Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Songkhla. Questionnaires, validated by a panel of 3 experts yielding IOC ranging from .67-1.00 and tested for reliability by Cronbach’s alpha coefficients yielding a value of .96 and .94 respectively. Data were analyzed using mean, standard deviation and t-test. Research results revealed as follows;
1. By comparison, mean score of self-confidence in primary medical care among nursing students, Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Songkhla after using simulation based learning was significantly higher than that of before (µ=4.18, σ=0.36 VS µ=3.78, σ=0.59) (p=.001).
2. Nursing students’ satisfaction, Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Songkhla of simulation based learning, overall, was at a high level (µ=4.44, σ=0.41). When considering each aspect, it was found that all aspects were at a high level. Aspect of benefit had the highest mean score (µ=4.46, σ=0.48) followed by aspect of leaning activity (µ=4.45, σ=0.46) and aspect of leaning atmosphere เรียนรู้ (µ=4.41, σ=0.48).
Therefore, Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Songkhla should adopt method of simulation based learning in further enhancing confidence in primary medical care and develop nursing students’ skill of primary medical care.
ถอนบทความเนื่องจาก :(ผู้นิพนธ์ขอถอนบทความเนื่องจากช่วงเวลาเก็บข้อมูลไม่สอดคล้องกันกับจริยธรรมวิจัย)
References
Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Songkhla. (2017). Bachelor of Nursing Science Program (Improve Curriculum for 2017). Songkhla: Boromarajonani College of Nursing. (In Thai)
Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Songkhla. (2021). Meeting Report Curriculum Management Committee No. 4/64. Songkhla: Boromarajonani College of Nursing. (In Thai)
Boromarajonani College of Nursing Songkhla. (2021). Course Syllabus: Primary Medical Care Practicum. Songkhla: Boromarajonani College of Nursing. (In Thai)
Buadong, D., Granger, J., Punyoo, J., & Jongaramraung, J. (2017). Satisfaction with and Self Confidence in Nursing Care for Pediatric Patients with Heart Failure among Nursing Students after Attending High Fidelity Simulation. Rama Nurse Journal, 26(3), 385-340. (In Thai)
Chubkhuntod, P., Thasanoh Elter, P., Gaewgoontol, N. & Potchana. R. (2020). Effects of Simulation Based Learning Model on Knowledge, Self-Efficacy and Abilities of Applying Nursing Process Skills during Intrapartum Care of Nursing Students. Journal of Health Science, 29(6), 1062-1072. (In Thai)
Kaewsawat, S., Aubdulla, O. & Keawhuai, N., (2020). Quasi-Experimental Research: Routine to Quasi-Experimental Research for Public Health Technical Officer. Health Education Professional Association, 35(1), 30-39. (In Thai)
Khammani, T. (2007). Pedagogical Sciences: Knowledge for effective Organization of Learning Process (14th Edition). Bangkok: Darn Sutha Press Company Limited. (In Thai)
Khumsuk, W. & Nillapun, M. (2021). Simulation-Based Learning. Journal of Council of Community Public Health, 3(1), 1-11. (In Thai)
Kowtragool, S. (2008). Educational Psychology (7th ed.). Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University. (In Thai)
Mahaprom, T., Chatrung, C., Noparoojjinda, Supawadee Peawnalaw, S., & Doungkeaw, J. (2020). Development of an Instructional Model Based-on Simulation-Based Learning in Nursing Care of Persons with Health Problems. Multidisciplinary Journal for Health, 1(2), 47-61. (In Thai)
Srisa-Ard, B. (2014). The Basic Research (9th ed.). Bangkok: Suveriyasarn. (In Thai)
Suwannakeeree, W., Jullmusi, O. & Tangkawanich, T. (2016). Simulation-Based Learning Management for Nursing Students. Journal of Nursing Science Chulalongkorn University, 28(2), 1-14. (In Thai)
Suwannakeeree, W., Jullmusi, O., Inkaew, T., Tangkawanich, T. & Rueangram. S. (2017). Satisfaction and Self-Confidence in Critical Care Nursing of Nursing Students Learning with Simulation-Based Learning. Journal of Nursing and Health Sciences, 11(3), 167-177. (In Thai)
Thongmeekhaun, T., Sateuw, S. & Chuakompeng, A. (2017). Perception of Students and Preceptors towards Clinical Skills Regarding Basic Medical Treatment among Nursing Students, Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Songkhla. Nursing Journal of the Ministry of Public Health, 27(Special), 131-143. (In Thai)
Thongmeekhaun, T. & Sateuw, S. (2017). Primary Medical Care Learning about Dyspnea Syndrome among Nursing Students: The Effects of Seminar Teaching and Learning Method. Songkhla: Boromarajonani College of Nursing. (In Thai)
Thongmeekhaun, T. & Sateuw, S. (2018). Primary Medical Care Learning about Dyspnea Syndrome among Nursing Students: The Effects of Seminar Teaching and Learning Method. The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health, 5(1), 74-90. (In Thai)
Vorapongsathorn, S. (2015). The Research in Health education (3rd ed.). Bangkok: Vitoon Binding & Printing. (In Thai)
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Journal of Nursing and Education

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





