The Grow Approach: A Research on How a New Coaching Program for First–Line Nurse Managers Can Boost Performance of Newly Registered Nurses at Thung Song Hospital
Keywords:
Coaching Program, Grow approach, Newly Registered Nurses, Public HospitalsAbstract
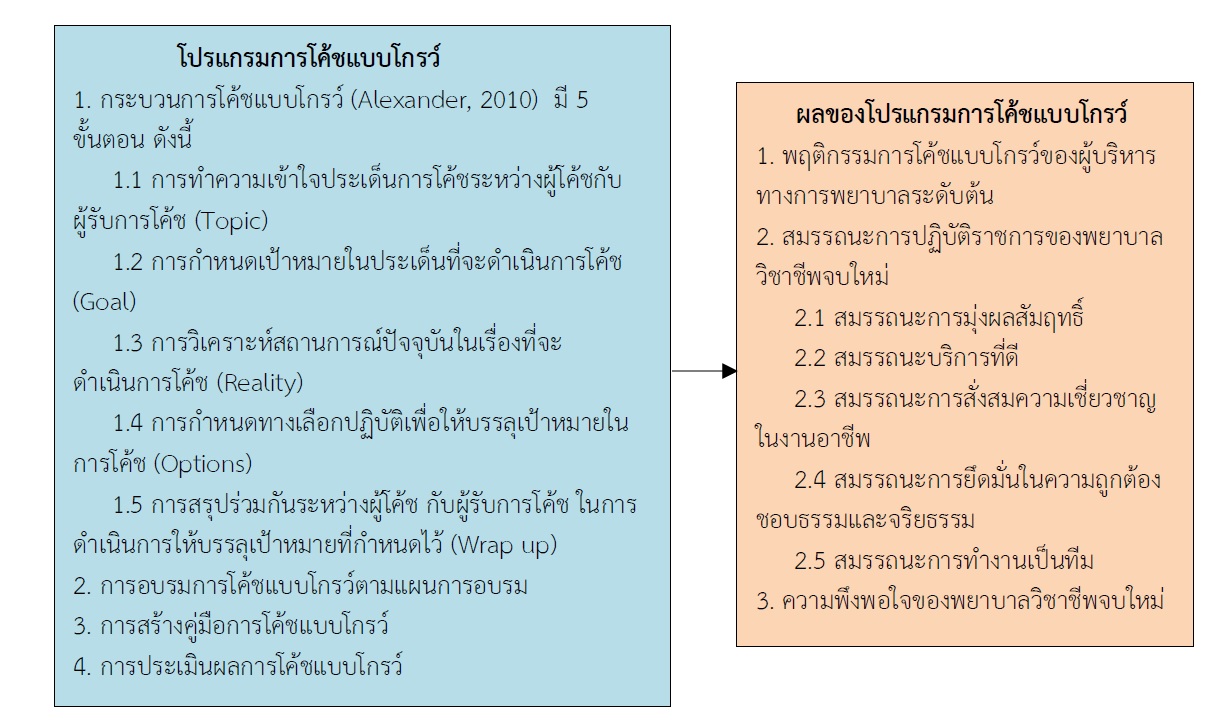
This one-group pre-posttest design quasi-experimental research, conducted at Thungsong hospital, aimed to: 1) compare the coaching behaviors of nursing administrators between before and after receiving a coaching program based on the Grow approach, 2) compare the competencies of new professional nurses between before and after using such coaching program, and 3) evaluate the satisfaction of new professional nurses towards the new coaching program. The purposive sample was divided in 3 groups: 1) 16 first-level nursing administrators or coaches who were head nurses and sub-head nurses, 2) 64 evaluators of new professional nurses, and 3) 16 newly professional nurses. The research tools were: 1) the Grow coaching program's manual and it's training plan, 2) a questionnaire on coaching behaviors of nursing administrators, 3) a questionnaire on competency of new professional nurses, and 4) a satisfaction questionnaire. All questionnaires were verified by five experts, yielding content validity index values of 0.97, 0.99, and 0.96, respectively, and Cronbach's alpha coefficients of 0.96, 0.91, and 0.92, respectively. Data were analyzed by descriptive statistics and Wilcoxon signed rank test.
The results showed as follows: 1) after using the program, coaching behaviors of nursing administrators were higher than before at the statistically significant level of < .001) ; 2) the performance of new registered nurses was also higher than before, and this, at the statistically significant level of <.001) ; and 3) the satisfaction of new registered nurses towards the quality of coaching was higher than before using the program, at the statistically significant level of p<.001.
Therefore, this approach can be used in order to develop professional nurses' skills, through coaching, in all departments and wards.
References
Alexander, G. (2010). Behavioral Coaching-The GROW Model In Passmore, Jonathan. Excellence in Coaching: the Industry Guide (2nded). Philadelphia: Kogan.
Gilmer, B. (1973). Applied Psychology. New York: Mc Graw-Hill.
Hawaharn, C. & Inthongpan, O. (2015). Research and Development of a Coaching Model to Develop Competence in Health Service Practice. Journal of Nursing Ministry Public Health, 25(1), 166-177.
Likert, R. (1976). The Human Organization: Its Management and Value. New York: McGraw Hill.
Medland, J. (2009). Coaching as a Successful Strategy for Advancing New Manager Competency and Performance. Journal of Nurses Staff, 25(3), 141-147.
Nirattipattanasai, K. (2013). Executive Coaching Executive Coaching. Retrieved December 30, 2021, from http://www.thecoach.in.th.
Office of the Civil Service Commission. (2020). Handbook for Evaluation of Government Performance. Retrieved November 3, 2020, from http://www.khuumuuekaarpraemin_phaaphrwmrabbbrihaarphlngaanaelarapraemin_phimphpii_52.pdf.
Office of the Civil Service Commission. (2009). Handbook of Competency Determination in Civil Service: Core Competency Handbook. Nonthaburi: Prachumchang Co., Ltd.
Promma, S. (2016). Coaching Skills Development Model of Nursing Leaders. (Ph.D. not published). Rajabhat Rajanagarindra University, Songkhla. (in Thai).
Ruangpisit, Y. (2015). The Development of Teaching System for Professional Nurses in Specialized Hospitals. One Under the Medical Department Ministry of Public Health (Nursing Degree Thesis. Master of Arts Not Published). Christian University, Nakhon Pathom. (in Thai).
Siriwan, S. (2017). Coaching to Develop Excellent Performance. Bangkok: HR
Sritrakul, R. (2015). Strategies for Nursing Supervision. Retrieved March 3, 2022 from http://www.nurse.kku.ac.th.
Thamapirat, N. & Uamtanee, A. (2017). Being a New Graduate Nurse who Works under the Supervision of a Nanny Nurse. Journal of the Royal Thai Army Nurses, 18(1-4), 32-40.
Tharaphaisansuk, O. (2018). The Effects of Supervision According to the Growth Coaching Model of Primary Nursing Administrators at Private Hospitals. Not Published). Christian University, Nakhon Pathom. (in Thai).
Thiangcharoen, P. (2012). The Effect of Using the Nurse Nanny Model on the Ability to Work. of New Registered Nurses as the Head of the Nursing Team Chachoengsao City Hospital. Chachoengsao Province. Not Published). Burapha University, Chonburi Province. (in Thai).
Tikkawi, J. (2016). How Good is Coaching?. Retrieved May 20, 2020. from https://www.bangkokbiznews.com/pr/detail/10054.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Journal of Nursing and Education

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





