The Effects of Enhancing Health Literacy Program on Health Literacy and Fall Prevention Behaviors among Caregivers of Older Adults at Risk in Trang Municipality
Keywords:
Enhancing Health Literacy Program, Health Literacy, Fall Prevention Behaviors, Older AdultsAbstract
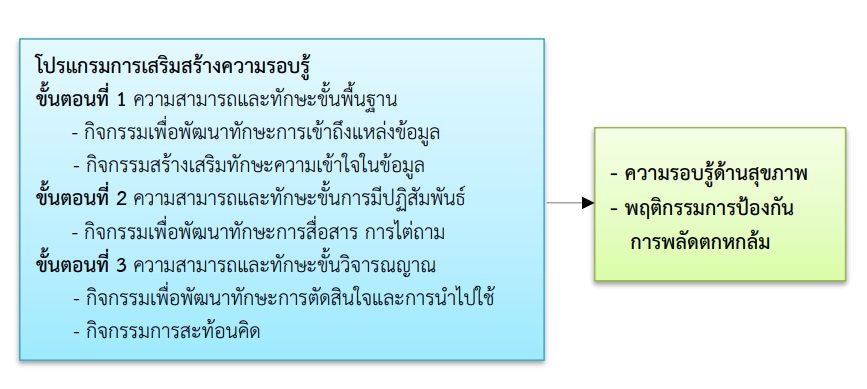
This quasi-experimental research, two-group pre-posttest design, aimed to study the effects of an enhancing health literacy program on health literacy and fall prevention behaviors among caregivers of older adults at risk. The sample was 58 caregivers in Trang Municipality, they were allocated to an experimental group (n=29) and a control group (n=29). Data were collected using a questionnaire regarding health literacy, and fall prevention behaviors. Three experts validated the research tools. The reliability of the questionnaire regarding the health literacy in the knowledge part was verified using KR-20, obtaining a value of 0.73. The rest of the questionnaire on health literacy in terms of obtaining, questioning, decision making, and applying, as well as fall prevention behaviors, were tested using Cronbach's alpha coefficient, yielding values of, 0.93 and 0.81, respectively. Data were analyzed by dependent t-test and independent t-test.
The results indicated that after receiving the enhancing health literacy program; 1) the experimental group had a higher mean score of the health literacy and the prevention behaviours (M=113.45, SD=15.25 and M=82.0, SD=9.07, respectively) than before receiving the program (M=96.45, SD=8.19 and M=76.83, SD=8.63, respectively) with statistically significant (t=7.28, p<.001 and t=14.31, p<.001, respectively), and 2) the experimental group had higher mean score of the health literacy and the prevention behaviors higher than (M=113.45, SD=15.25 and M=82.0, SD=9.07, respectively) the control group (M=96.83, SD=13.67 and M=76.03, SD=7.38, respectively) with statistically significant (t=4.37, p<.001 and t=2.75, p<.01, respectively)
The findings from this study can be used as a guideline for enhancing health literacy to prevention for falls, and apply to the level of health literacy of caregivers
References
Berkman, N. D., Sheridan, S. L., Donahue, K. E., Halpern, D. J., Crotty, K. (2011). Low Health Literacy and Health Outcomes: an Updated Systematic Review. Ann Intern Med. 19, 155(2), 97-107.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ:
Choeisuwan, V. (2018). Health Literacy: Concept and Application for Nursing Practice. Royal Thai Navy Medical Journal, 44(3), 183-197. (in Thai).
Daniel, S. (2014). Statistic Calculator: A-Priori Sample Size Calculator for Student t-test. Retrieved January 20, 2022 from http://danielsopercom/statcalc3/default.aspx.
European Health Literacy Consortium. (2012). Comparative Report on Health Literacy in Eight EU Member States [Internet]. The European Health Literacy Survey HLSEU. Retrieved February 24, 2022 from http: www.HEALTH-LITERACY.EU.
Foundation of Thai Gerontology Research and Development institute. (2020). Situation of the Thai Elderly 2020. Retrieved December 12, 2021 from https://thaitgri.org/?p=39772 file:///D:/Users/hp/Downloads/ThaiElderly_2563%20(2).pdf
Gladdar, S. F., Valerio, M. A., Garcia, C. M., & Hansen, L. (2012). Adolescent Health Literacy: the Importance of Credible Sources for Online Health Information. Journal of School Health, 82(1), 28-36.
Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Ministry of Public Health. (2019). Practice Guideline for Fall Prevention and Assessment in Older Adults. Retrieved November 14, 2020, from http://agingthai.dms.go.th/agingthai/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/book_9.pdf.
Jaemtim, N., Yuenyong, S., & Srisodsaluk, P. (2018). Effects of Preparation to Care for Elderly Program at Sanamchai Subdistrict Mung District Suphanburi Province. Nursing Journal of the Ministry of Public Health, 25(3), 108-119. (in Thai).
Kaeodumkoeng, K. (2019). Health Literacy: Process, Practice, Evaluation Tools. Bangkok: ID Oil Digital Printing Lt.d. (in Thai).
Kulapeng, W., Anothaisinthawee, T., Pantumongkol, W., Wisaiprom, J., & Tuntiweas, S. (2018). A Study on the Introduction of Community-based Preventive Interventions for Fall and Dementia in the Thai Elderly. Health Intervention and Technology Assessment Program, Ministry of Public Health. (in Thai)
Ministry of Public Health. (2019). Health Promotion and Dementia Prevention of Older Adults Manual for Health Personnel “Do Not Fall, Do Not Forget, Do Not Depress and Good Eats” Retrieved December 12, 2021 from http://203.157.212.7/ltc/document/m002.pdf.
Matsee, C., & Waratwichi, C. (2017). Promotion of Health Literacy: from Concept to Practice. Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Uttaradit Journal, 9(2), 96-111. (in Thai).
Noopud, P., Phrom-On, D., Woradet, S., & Chaimay, B. (2020). Prevalence of Fall Risk and Factors Associated with Fall Risk among Elderly People. Journal of Sports Science and Health, 21(1), 125-137. (in Thai).
Nutbeam, D. (2008). The Evolving Concept of Health Literacy. Social Science and Medicine, 67(12), 2072-2078.
Photihung, P. (2021). Relationship of Health Literacy to Health Promoting and Disease Prevention Behaviors in Thailand: A Systematic Review. Relationship of Health Literacy to Health Promoting and Disease Prevention Behaviors in Thailand: A Systematic Review. The Journal of Faculty of Nursing Burapha University, 29(3), 115-130. (in Thai).
Pinarad, K., Sitipongsakul, S., Patthananurak, S., Nualkale, A, Worauon, S. (2019). Development of Elderly Caregiver with Public Conciousness Model. Retrieved December 25, 2020 from https://oldweb.western.ac.th/media/attachments/2019/02/09/mind.pdf
Polit, D. F., & Beck, C. T. (2012). Nursing Research: Generating and Assessing Evidence for Nursing Practice. (9th ed.). Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins.
Pongaumpai, P., Hoontrakul, S., & Roojanavech, S. (2018). The Effects of Family Empowerment Program on Fall Prevention Capabilities of the Elderly. Royal Thai Navy Medical Journal, 45(2), 311-327. (in Thai).
Public Health Office of Trang. (2020). The Report of Chronic Patient Data 2019. Retrieved December 20, 2021 from: http:// tro.moph.go.th/provis/main/index.php.
Santwanpas, N., Srijaranai, S., Radabutr, M., Pragodpol, P., Chawajaroenpan, W., & Waisurasing, L. (2019). The Development of the Health Literacy on Fall Preventions for Older People in Community Health Region 4. Journal of The Police Nurse, 11(1), 95-106. (in Thai).
Sarapun, A., Sirisopon, N., Kainaka, P., Onsiri, S., Outayanik, B., Threrawachjareanchai, S., & Sukomol, N. (2017). Factors Related to a Fall Prevention Behaviors of Elderly. Journal of The Royal Thai Army Nurses, 18(Special), 215-222. (in Thai).
Simplee, S., & Banchonhattakit, P. (2019). Effects of Health Literacy Promoting Programs and Exercise by Applying Maneewach Exercise for Preventing Fall in Older Adult in Buriram Province. Journal of Health Education, 42(2), 149-159. (in Thai).
Strategy and Planning Division, Ministry of Public Health. (2020). Public Health Statistic. Retrieved December 20, 2020 from http://www.35.190.29.12/uploads/files/1662820210118045737.pdf.
Tasuwanin, T., & Tappakit, K. (2017). Effects of a Falling Prevention Program for Elderly. Journal of Nursing and Health Care, 35(3), 186-195. (in Thai).
World Health Organization. (2014). The Health Literacy Toolkit. Retrieved May 12, 2022. from http://www.searo.who.int/entity/ health promotion/documents/hl_tookit/en
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Journal of Nursing and Education

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





