การศึกษาความชุกและปัจจัยที่มีอิทธิพลต่อโรคหลอดเลือดดำเรื้อรังของพยาบาลโรงพยาบาลชลบุรี
คำสำคัญ:
โรคหลอดเลือดดำเรื้อรัง, พยาบาล, อาการทางคลินิกบทคัดย่อ
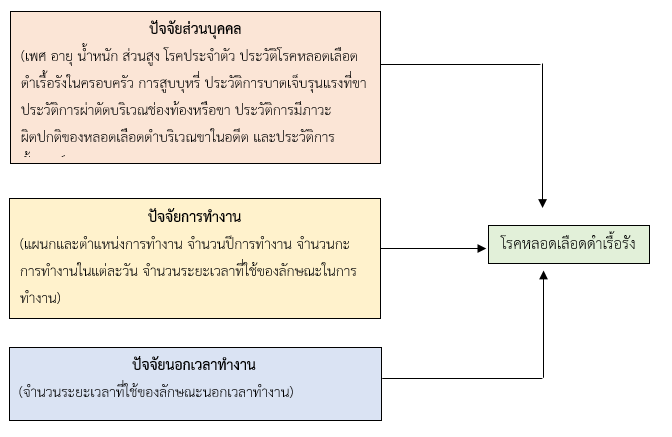
การวิจัยเชิงพรรณนาชนิดภาคตัดขวางมีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อสำรวจความชุกและวิเคราะห์ปัจจัยที่มีอิทธิพลต่อการเกิดโรคหลอดเลือดดำเรื้อรังของพยาบาลวิชาชีพโรงพยาบาลชลบุรี จำนวน 145 คน เครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการวิจัย คือ แบบสอบถามและการตรวจร่างกายเพื่อหาลักษณะผิดปกติของขาที่เข้าได้กับโรคหลอดเลือดดำเรื้อรัง นำข้อมูลมาจำแนกระดับอาการทางคลินิก (CEAP Classification) วิเคราะห์สถิติเชิงพรรณนาและสถิติเชิงอนุมาณด้วย Logistic Regression Analysis ผลวิจัยพบว่า
1. กลุ่มตัวอย่างมีช่วงอายุ 22 ถึง 59 ปี มีความชุกของการเกิดโรคหลอดเลือดดำเรื้อรัง (C0-C6) เท่ากับร้อยละ 66
2. อายุ และประวัติโรคหลอดเลือดดำในครอบครัวเป็นปัจจัยที่มีอิทธิพลต่อการเกิดโรคหลอดเลือดดำเรื้อรังอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ กล่าวคือ เมื่ออายุเพิ่มขึ้น 1 ปี จะมีความเสี่ยงต่อการเกิดโรคหลอดเลือดดำเรื้อรังเพิ่มขึ้นร้อยละ 7 และผู้ที่มีประวัติโรคหลอดเลือดดำในครอบครัวจะมีความเสี่ยงต่อการเกิดโรคหลอดเลือดดำเรื้อรังเพิ่มขึ้น 10 เท่าเมื่อเทียบกับผู้ที่ไม่มีประวัติโรคหลอดเลือดดำในครอบครัว
ดังนั้นเพื่อป้องกันการเกิดโรคหรือชะลอการดำเนินไปของโรค ควรหลีกเลี่ยงการนั่งไขว้ขาเป็นระยะเวลานาน การยกขาสูงเหนือระดับหัวใจ กระดกข้อเท้า การใส่ถุงน่องรัดขา และการสังเกตผิวหนังบริเวณขาเป็นประจำทุกวัน เพื่อลดอุบัติการณ์ของการเกิดโรคหลอดเลือดดำเรื้อรังในพยาบาลวิชาชีพในอนาคต
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Anwar Muzaffar, Georgiadis Kyrillos, Shalhoub Joseph, Lim Chung , Gohel Manjit, Davies Alun (2012). A Review of
Familial, Genetic, and Congenital Aspects of Primary Varicose Vein Disease. Circulation: Cardiovascular Genetics,
(4), 460-466.
Bahk Wook, Kim Hyunjoo, Jung Kyunghee, Jung Chul, Lee Inseok. (2012). Relationship Between Prolonged Standing
and Symptoms of Varicose Veins and Nocturnal Leg Cramps among Women and Men. Ergonomics, 55(2), 133-139.
Jennifer Beebe-Dimmer, John Pfeifer, Jennifer Engle, David Schottenfeld. (2005). The Epidemiology of Chronic Venous
Insufficiency and Varicose Veins. Ann Epidemiol, 15(3), 175-184.
Berti-Hearn Linda, Elliott Brenda. (2019). Chronic Venous Insufficiency: A Review for Nurses. Nursing2022, 49(12), 24-
Cires-Drouet Rafael, Fangyang Liu, Rosenberger Sarah, Startzel Matthew, Kidwell Margaret, Yokemick John et al.,
(2020). High Prevalence of Chronic Venous Disease among Health Care Workers in the United States. J Vasc Surg
Venous Lymphat Disord, 8(2), 224-230.
Dindelli Moreno, Parazzini Fabio, Basellini Aldo, Emanuela Rabaiotti, Giuseppe Corsi, Augusto Ferrari. (1993). Risk
Factors for Varicose Disease Before and During Pregnancy. Angiology, 44(5), 361-367.
Eberhardt Robert, Raffetto Joseph (2014). Chronic Venous Insufficiency. Circulation, 130(4), 333-346.
Gloviczki Peter, Comerota Anthony , Dalsing Michael, Eklof Bo, Gillespie David, Gloviczki Monika et al., (2011). The
Care of Patients with Varicose Veins and Associated Chronic Venous Diseases: Clinical Practice Guidelines of the
Society for Vascular Surgery and the American Venous Forum. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 53(5), 2S-48S.
Gourgou Sophie, Dedieu Florence, Sancho-Garnier Helene. (2002). Lower Limb Venous Insufficiency and Tobacco
Smoking: a Case-Control Study. American Journal of Epidemiology, 155(11), 1007-1015.
Hugo Partsch. (2012). "The Natural Progression of Chronic Venous Disorder: An Overview of Available Information
from Longitudinal Studies. In Amanda C. Shepherd, Tristan R. Lane, Alun H. Davies" Phlebolymphology (Vol. 19).
(pp. 138-147). France: Les Laboratoires Servier.
Kontosic Ivica, Vukelic Mihovil, Drescik Ivan, Mesaros-Kanjski Elika, Materljan Eris, Jonjic Anto. (2000). Work
Conditions as Risk Factors for Varicose Veins of the Lower Extremities in Certain Professions of the Working
Population of Rijeka. Acta Medica Okayama, 54(1), 33-38.
Krejcie Robert, Morgan Daryle (1970). Determining Sample Size for Research Activities. Educational and Psychological
Measurement, 30(3), 607-610.
Scott Thayer, LaMorte Wayne, Gorin Daniel, James Menzoian. (1995). Risk factors for Chronic Venous Insufficiency: a
Dual Case-Control Study. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 22(5), 622-628.
Vuylsteke Marc, Colman Roos, Thomis Sarah, Guillaume Genevieve, Quickenborne Damien, Staelens Ivan. (2018). An
Epidemiological Survey of Venous Disease among General Practitioner Attendees in Different Geographical
Regions on the Globe: the Final Results of the Vein Consult Program. Angiology, 69(9), 779-785.
Yun Myeong, Kim Young, Kang Dong, Kim Jong, Ha Won, Jung Kap. et al., (2018). A Study on Prevalence and Risk
Factors for Varicose Veins in Nurses at a University Hospital. Saf Health Work, 9(1), 79-83.
Zolotukhin Igor, Seliverstov Evgeny, Shevtsov Yuri, Avakiants Ilona, Nikishkov Aleksey, Tatarintsev Andrey et al.,
(2017). Prevalence and Risk Factors for Chronic Venous Disease in the General Russian Population. Eur J Vasc
Endovasc Surg, 54(6), 752-758.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2022 วารสารการพยาบาลและการศึกษา

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





