The Effects of a Self-Efficacy Enhancement Program on Caregivers’ Language Development Promotion Behaviors for Preschool Children
Keywords:
Self-Efficacy, Language Development, Caregivers of Preschool ChildrenAbstract
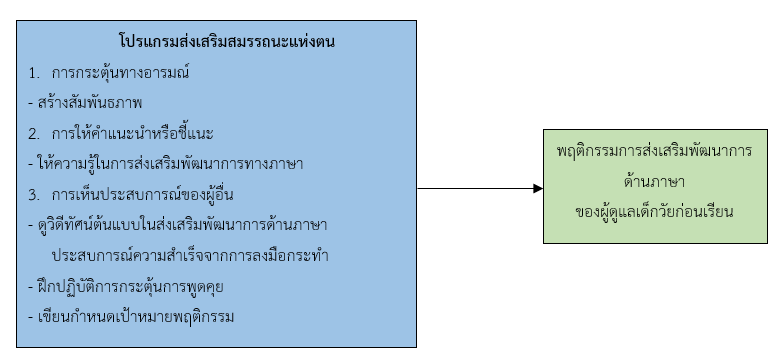
This two-group pretest–posttest design quasi-experimental research aimed to examine the effects of a self-efficacy enhancement program on caregivers’ competencies for language development promotion behaviors among preschool children. The sample consisted of 52 primary caregivers of child development centers in Ratchaburi Municipality. Participants were selected by simple random sampling and divided into an experimental (n = 27) and a control group (n = 25). All preschool children in child development centers were aged between 2 years and 3 years and 11 months. Data were collected from December 2023 to February 2024. The research instruments were 1) a general information questionnaire, 2) a language development promotion behavior questionnaire (CVI = .97 ; Cronbach’s alpha coefficient = .82), as well as 3) the self-efficacy enhancement program, consisting of an implementation plan (CVI = .96), storybooks, model videos, and a language development promotion manual (CVI = 1.00). Data were analyzed using chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, independent t-test, and paired t-test. The results showed as follows.
1. Caregivers in the experimental group had significantly higher overall language development-promoting behavior scores than those in the control group (p-value < .05). However, no significant differences were observed in behaviors related to receptive language (p-value = .055) and expressive language (p-value = .129) between the two groups.
2. Caregivers in the experimental group demonstrated significantly higher posttest scores compared with their pretest scores (p-value < .05).
These results suggest that nurses may apply this program for caregivers of preschool children to enhance their confidence and ability in effectively promoting children’s language development.
References
Albarran, A., & Reich, S. (2014). Using baby books to increase new mothers' self-efficacy and improve toddler language development. Infant Mental Health Journal, 23(4), 374-387. doi:10.1002/ icd.1832
American Academy of Pediatrics. (2016). Media and young minds. Pediatrics, 138(5), 1-6. doi:10.1542/ peds.2016-2591
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The Exercise of Control. New York, NY, US: W H Freeman/Times Books/ Henry Holt & Co.
Barani, M., Bilal, M., Rahdar, A., Arshad, R., Kumar, A., Hamishekar, H., et al. (2021). Nanodiagnosis and nanotreatment of colorectal cancer: An overview. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 23(1), 18. doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05129-6
Best, J. W. (1977). Research in education (3rd ed.). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall. Burns, N., & Grove, S. K. (2001) The Practice of Nursing Research, Conduct, Critique, and Utilization. 4th Edition, W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia.
Chumprasert, T., Wirunphanich, W., & Wattanasit, P. (2019). The relationship between the use of electronic media and the development of children aged 2-5 years in local government-operated child development centers, Songkhla Province. Southern Region College of Nursing and Public Health Network Journal, 6(2), 91–104.
Group of Academic Support and Research, Health Promotion Department, Department of Health. (2018). Factors affecting early childhood development in Thailand. CG Tool Co., Ltd.
Grove, S. K., Burns, N., & Gray, J. (2012). The Practice of Nursing Research: Appraisal, Synthesis, and Generation of Evidence (7th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders.
Hsieh, R.-L., Hsueh, Y.-M., Huang, H.-Y., Lin, M.-I., Tseng, W.-C., & Lee, W.-C. (2013). Quality of life and impact of children with unclassified developmental delays. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health, 49.
Koshy, B., Srinivasan, M., Bose, A., John, S., Mohan, V. R., Roshan, R., et al. (2021). Developmental trends in early childhood and their predictors from an Indian birth cohort. BMC Public Health, 21(1), 1-8.
Marrus, N., & Hall, L. (2017). Intellectual disability and language disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am, 26(3), 539-554. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2017.03.001
Mouton, B., Loop, L., Stiévenart, M., & Roskam, I. (2018). Confident parents for easier children: A parental self-efficacy program to improve young children’s behavior. Education Sciences, 8(3), 134.
National Institute for Child and Family Development. (2017). Annual Report 2017, National Institute for Child and Family Development. Department of Health, Ministry of Public Health: CG Tool Co., Ltd.
Pitiphat, A., Phokphatjapubet, S., Kamsripol, C., & Ruengworapoon, S. (2018). Factors associated with the promotion of growth and development behaviors of caregivers of toddlers. Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Bangkok Journal, 34(3), 1–10.
Pongpetchdit, B., & Attavee, B. (2020). Factors affecting early childhood development in Thailand: The 5th Public Health Center. Kue Karun Journal, 27(1), 59–70.
Radesky, J. S., Weeks, H. M., Ball, R., Schaller, A., Yeo, S., Durnez, J., et al. (2020). Young children’s use of smartphones and tablets. Pediatrics, 146(1), e20193518. doi.org/10.1542/peds.2019-3518
Srisatitnarakun, B. (2010). Research Methodology in Nursing Science (5Th Ed.). Bangkok, Thailand: U & I Inter Media.
Stievenart, M., & Martinez Perez, T. (2021). How can parental self-efficacy support children’s early language development? Review of preliminary research and future perspectives. European Journal of Developmental Psychology, 18(2), 199-213. doi:10.1080/17405629.2020.1776102
Sujaritpong, S., Rungpairawan, R., Hunsakunachai, T., Benjasuwanthep, B., Fuefue, A., Chuthapisit, J., et al. (2018). Textbook of Child Development and Behavior (Vol. 4). Bangkok: The Developmental and Behavioral Pediatric Society of Thailand.
Thisara, P., Phonmak, J., Sikhao, P., & Silapawitthayatorn, B. (2017). Predictive factors of parental behaviors in promoting early childhood development in Phayao Province. Journal of Nursing and Health Care, 35(2), 169–176.
Thongluang, P., Younak, R., & Tangkavanich, T. (2017). The effects of a self-efficacy enhancement program on early childhood development promotion. Journal of Nursing and Health, 11(3), 92–101.
TohYuso, N., & Maksingh, W. (2020). The effect of a self-efficacy enhancement program for mothers on promoting the development of children aged 0-5 years. Graduate School Journal of Mahamakut Buddhist University, 18(2), 195–208.
Wang , L., Liang, W., Zhang, S., Jonsson, L., Li, M., Yu, C., et al. (2019). Are infant/toddler developmental delays a problem across rural China?. Journal of Comparative Economics, 47(2), 458-469. doi:10.1016/j.jce.2019.02.003
World Health Organization. (2016). Investing in Early Childhood Development Essential to Helping More Children and Communities Thrive, New Lancet Series finds. Retrieved November 3, 2024 from https://www. who.int/news/item/05-10-2016-investing-in-early-childhood-development-essential-to-helping-more-children-and-communities-thrive-new-lancet-series-finds
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Nursing and Education

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





