ผลของโปรแกรมการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมการบริโภคอาหารที่ประยุกต์ทฤษฏี ทรานส์ทิโอเรทิคอลในผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่ไม่สามารถควบคุมระดับนํ้าตาลในเลือดได้ ในจังหวัดชลบุรี
คำสำคัญ:
ผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ไม่สามารถควบคุมระดับนํ้าตาลในเลือดได้, โปรแกรมการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมการบริโภคอาหาร, ทฤษฏีทรานส์ทิโอเรทิคอลบทคัดย่อ
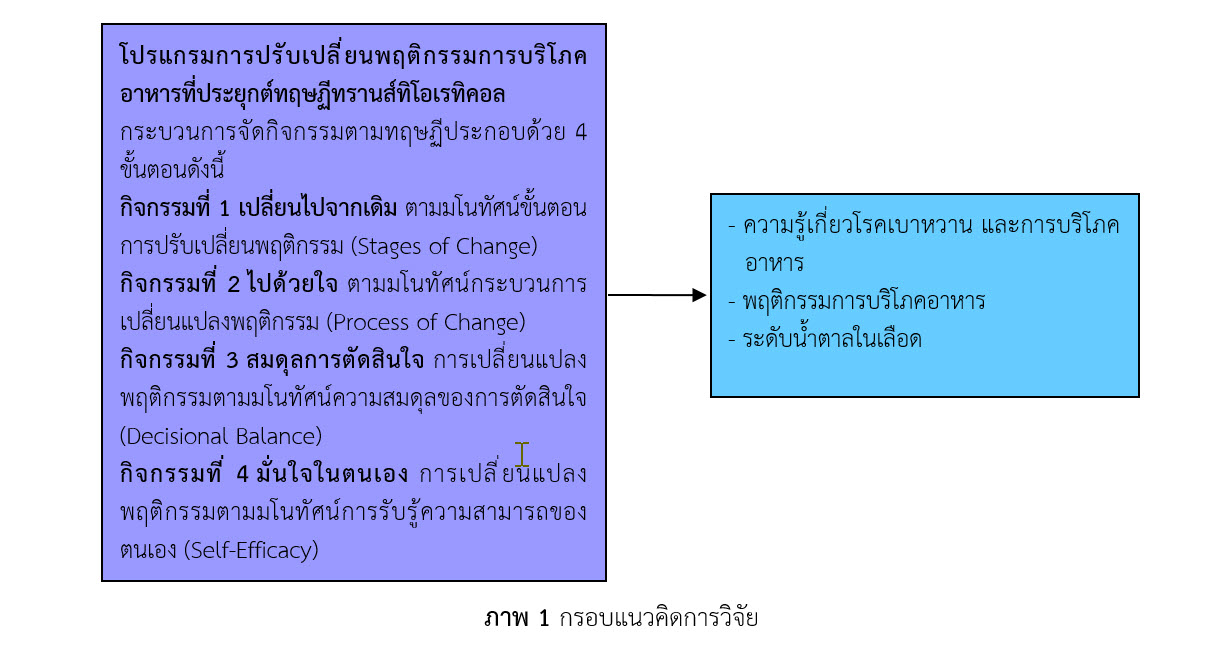
การวิจัยกึ่งทดลองแบบเปรียบเทียบสองกลุ่มระหว่างกลุ่มทดลองและกลุ่มควบคุม มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาผลของโปรแกรมการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมการบริโภคอาหารที่ประยุกต์ใช้ทฤษฏีทรานส์ทิโอเรทิคอลในผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่ไม่สามารถควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดได้ จำนวน 70 คน แบ่งเป็นกลุ่มละ 35 คนได้จากการสุ่มอย่างอย่างง่ายในพื้นที่จังหวัดชลบุรี โดยดำเนินกิจกรรมตามโปรแกรมฯ ประกอบด้วย 4 กิจกรรม ได้แก่ 1) ขั้นตอนการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรม (Stages of Change) 2) กระบวนการเปลี่ยนแปลงพฤติกรรม (Process of Change) 3) สมดุลการตัดสินใจ (Decisional Balance) และ 4 การรับรู้ความสามารถของตนเอง (Self-Efficacy) เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูลและวัดระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดก่อนและหลังการได้รับโปรแกรมฯ เป็นระยะเวลา 4 สัปดาห์ ด้วยแบบสอบถามข้อมูลทั่วไป แบบสอบถามความรู้เรื่องโรคเบาหวานที่มีค่าความเชื่อมั่นจากการวิเคราะห์คูเดอร์ริชาร์ดสัน 20 เท่ากับ .64 และพฤติกรรมการบริโภคอาหารที่มีค่าความเชื่อมั่นสัมประสิทธิ์แอลฟาของครอนบราคเท่ากับ .72 วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลโดยสถิติเชิงพรรณนา สถิติ Paired t- test และสถิติ Independent t- test ผลการวิจัยพบว่า
หลังจากได้รับโปรแกรมฯ กลุ่มทดลองมีความรู้เพิ่มสูงขึ้นกว่าก่อนได้รับโปรแกรมฯ และสูงกว่ากลุ่มควบคุมอย่างมีนัยสําคัญทางสถิติ (p<.05) โดยพฤติกรรมการบริโภคอาหารของกลุ่มผู้ป่วยที่ได้รับโปรแกรมฯ ดีกว่ากลุ่มผู้ป่วยที่ไม่ได้รับโปรแกรมฯ นอกจากนี้ ยังพบว่า ระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานที่ได้รับโปรแกรมฯ มีค่าเฉลี่ยลดลง เมื่อเปรียบเทียบกับกลุ่มควบคุมอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ (M=132.46, SD=35.46 และ M=172.60, SD=62.12, ตามลำดับ, p<.05)
การศึกษานี้แสดงให้เห็นว่า โปรแกรมการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมการบริโภคอาหารที่ประยุกต์ใช้ทฤษฏีทรานส์ทิโอเรทิคอลสามารถเพิ่มความรู้เกี่ยวกับโรคเบาหวานและการบริโภคอาหาร ปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมการบริโภคอาหารให้ดีขึ้น และยังช่วยลดระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดของผู้ป่วยได้ เป็นประโยชน์ต่อการนำไปประยุกต์ใช้ในการส่งเสริมและควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดของผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่ไม่สามารถควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดได้ต่อไป
เอกสารอ้างอิง
จุฑามาส จันทร์ฉาย และคณะ. (2555). โปรแกรมการเรียนรู้เรื่องเบาหวานและการจัดการตนเองของผู้ ที่เป็ นโรคเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 จังหวัดประจวบคีรีขันธ์. วารสารสาธารณสุขมหาวิทยาลัยบูรพา, 7(2), 77.
จุรีพร คงประเสริฐ. (2558). คู่มือปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมใน NCD คุณภาพ. นนทบุรี: โรงพิมพ์ชุมชน สหกรณ์การเกษตรแห่งประเทศไทย จํากัด
โชติกา สัตนาโค และจุฬาภรณ์ โสตะ. (2560). ผลของโปรแกรมการจัดการตนเองเพื่อควบคุมระดับ นํ้าตาลในเลือดของผู้ป่ วยโรคเบาหวานชนิดที่2ที่มีระดับนํ้าตาลในเลือดสูง. วารสารการ พยาบาลและการศึกษา, 10(4), 32.
ประกาย จิโรจน์กุล. (2556). แนวคิด ทฤษฎีการสร้างเสริมสุขภาพ และการนํามาใช้. นนทบุรี: โครงการสวัสดิการ สถาบันพระบรมราชชนก.
ปราณี สาวงศ์นาม. (2553). การปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมการบริโภคอาหารของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิด ที่ 2 ที่ควบคุมระดับนํ้าตาลในเลือดไม่ได้โดยกระบวนการเรียนรู้ แบบมีส่วนร่วม ศูนย์สุขภาพชุมชนโรงพยาบาลศรี ธาตุ. (วิทยาปริญญาพยาบาลศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต). มหาวิทยาลัยขอนแก่น.
สมาคมโรคเบาหวานแห่งประเทศไทย ในพระราชูปถัมภ์สมเด็จพระเทพรัตนราชสุดาฯ สยามบรมราชกุมารี,
สมาคมต่อมไร้ท่อแห่งประเทศไทย, กรมการแพทย์ กระทรวงสาธารณสุข, และสำนักงานหลักประกัน
สุขภาพแห่งชาติ. (2560). แนวทางเวชปฏิบัติสำหรับโรคเบาหวาน 2560. ปทุมธานี: บริษัท ร่มเย็น มีเดีย จำกัด.
สุวรรณี สร้อยสงค์, อังคณา เรือนก้อน, ขวัญสุวีย์ อภิจัทรเมธากุล, และนิลุมล นันตา. (2560). พฤติกรรมการดูแลเองตามการรับรู้ของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่ควบคุมระดับนํ้าตาลในเลือดไม่ได้. วารสารวิทยาลัยพยาบาลพระปกเกล้า จันทบุรี, 28(2), 100.
สุวัฒน์ แก่นทราย. (2559). ปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อการควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ในเขตรับผิดชอบโรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบลบ้านยางหลวงเหนือ ตำบลกุดจิก อำเภอเมือง จังหวัดหนองบัวลำภู. การประชุมวิชาการและการนำเสนอผลงานวิจัยระดับชาติ ราชธานีวิชาการ ครั้งที่ 1 หัวข้อ สร้างเสริมสหวิทยาการผสมผสานวัฒนธรรมไทย ก้าวอย่างมั่นใจเข้าสู่ AC; 29 กรกฎาคม 2559; ณ มหาวิทยาลัยราชธานี จังหวัด อุบลราชธานี.
Best, J. W. (1977). Research in Education 3rded. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey. Prentice-Hall.
Bloom, B., Engelhart, M., Furst, E., Hill, W. & Krathwohl, D. (1956). Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: The Classification of Educational Goals. Handbook I: Cognitive domain. New York and Toronto: Longmans, Green.
Lwanga, S. K. & Lemeshow, S. (1991). Sample Size Determination in Health Studies: a Practical Manual. Macmillan: World Health Organization.
World Health Organization. (2017). The Top 10 Causes of Death. Retrieved March 12, 2017, from http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
- บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารสภาการสาธารณสุขชุมชน ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
- บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารสภาการสาธารณสุขชุมชน


