The effectiveness of behavior modification programs to promote healthy behaviors by 3 in. To 2 in. In populations at risk of diabetes and high blood pressure. in Public health Center Bannongri,Ban Lueak Subdistrict, Photharam District, Ratchaburi Provinc
Keywords:
behavior modification program, the behavior 3. 2.Abstract
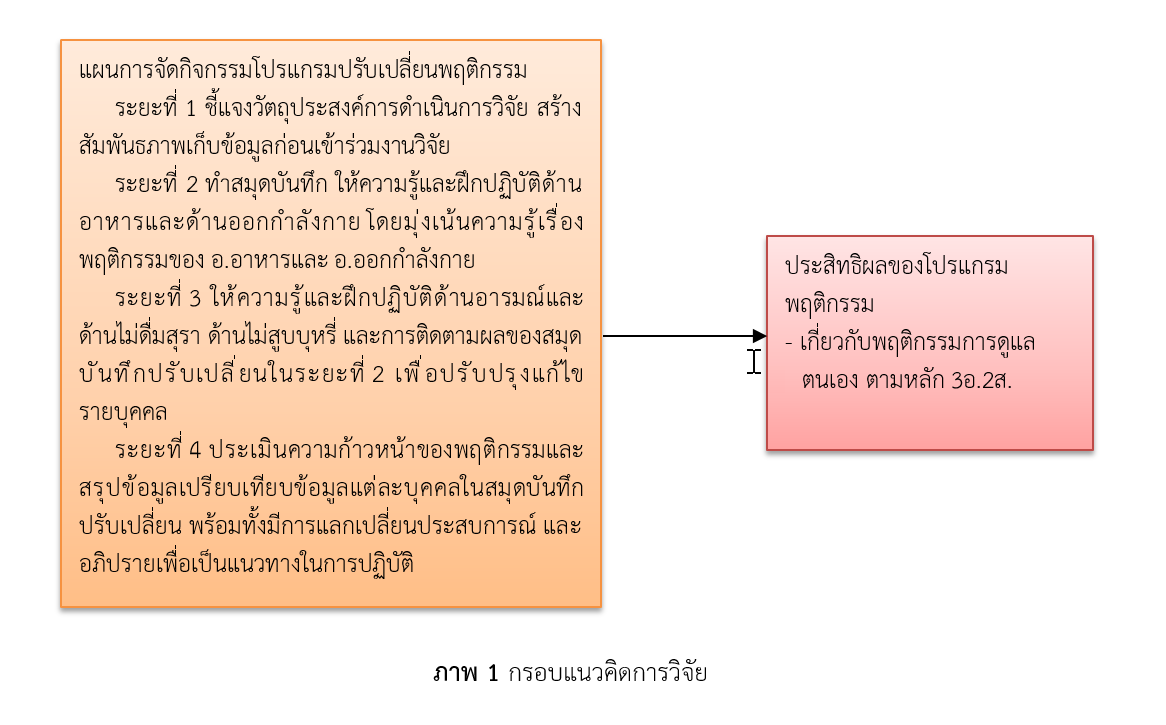
This research This study was the first research laboratory. (Pre-experimental Research) It aims to promote healthy behaviors by 3 Rd. 2. The population at risk of diabetes and high blood pressure. The Health Promotion Hospital Tambon Nong Ri. Choose Ban Photharam Ratchaburi. To promote healthy behaviors and by 3 in. To 2 in. Of the population at risk of diabetes and high blood pressure before and after the use of behavior modification. The sample was taken from the risk of diabetes and high blood pressure. Between April 1, 2561 to May 1, 2561 a total of 30 cases.
The tools used in this research. 1. The instruments used in the trial. Behavior modification program is to reduce tummy. 2. The instrument used to collect data contains personal information and behavioral risk groups with diabetes and high blood pressure and promote healthy behavior by 3 in. To 2 in. In populations at risk of diabetes and high blood pressure. The researchers collected data before and after the introduction of a health promotion program applied to populations at risk of diabetes and high blood pressure. To promote healthy behavior by 3 Rd. 2. The statistics used in this study Descriptive statistics include percentage (Percentage) Average (Mean) and standard deviation (Standard Deviation) statistics and reference pair t-test.
The results showed that the average score of health promoting behaviors by 3 in. To 2 in. In populations at risk of diabetes and high blood pressure. A pre-trial and post-trial 2.14 equals 3.13. When the average health promotion by 3 in. To 2 in. In populations at risk of diabetes and high blood pressure before and after the experiment. Comparison The average rating of 3 based health promotion. 2. After the trial was higher than before the experiment. The highly statistically significant (p <0.05).
References
กลุ่มบริหารยุทธศาสตร์ สำนักโรคไม่ติดต่อ กรมควบคุมโรค.(2555). รายงานสรุปข้อมูลการประชุมเชิงปฏิบัติการจัดทำข้อมูลโรคไม่ติดต่อระดับประเทศในการประชุม UN General Assemble High-Level Meeting on the Prevention and Control of Non Communicable Diseases. กรุงเทพฯ:บริษัท โอ-วิทย์ (ประเทศไทย) จำกัด.
กองทุนสนับสนุนการสร้างเสริมสุขภาพ. (2558). โครงการส่งเสริมการรณรงค์และขยายผล ศูนย์เรียนรู้องค์กรต้นแบบไร้พุงต้นแบบสำนักสร้างเสริมวิถีชีวิตสุขภาวะ.สำนักงานกองทุนสนับสนุนการสร้างเสริมสุขภาพ (สสส.). คู่มือลดพุงลดโรค.หน้า 1-10.
นวลนิตย์ ไชยเพชร อุดมศิลป์ แก้วกล่ำ, สิทธิพงษ์ สอนรัตน์ และยุวดี วิทยพันธ. (2560). ประสิทธิผลของโปรแกรมปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมสุขภาพต่อ พฤติกรรมสุขภาพของกลุ่มเสี่ยงโรคไม่ติดต่อเรื้อรังชุมชนโพหวาย ตำบลบางกุ้ง อำเภอเมือง จังหวัดสุราษฎร์ธานีNon Communicable Diseases (NCD’s) High Risk Patients: Effectiveness of a Health Behaviors Changing Programs on Health Behavior in Suratthani. วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้, 4(2), 45-59.
ปัญญา ไข่มุก. (2556). คณะกรรมการผู้ทรงคุณวุฒิ สำนักงานกองทุนสนับสนุนการสร้างเสริมสุขภาพ (สสส.) ผู้เชี่ยวชาญทางด้านกระดูก ข้อ และวิทยาศาสตร์การกีฬา สสส. เรื่อง ลดพุง ลดโรค ปี 2556.
รุจิรางค์ วรรณ์ธนาทัศน์. (2560). ประสิทธิผลของโปรแกรมการส่งเสริมการมีส่วนร่วมของเครือข่ายในการดูแลสุขภาพของผู้สูงอายุ และการรับรู้ความสามารถในการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรม 3อ. 2ส.ของผู้สูงอายุ จังหวัดนครปฐม. วารสารแพทย์เขต 4-5, 36(1), 2-11.
สิรีวัฒน์ อายุวัฒน์, อภิเชษฐ์ พูลทรัพย์ และนิดา มีทิพย์. (2560). การคัดกรองโรคความดันโลหิตสูงและโรคเบาหวานในประชาชน.วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้, 4(พิเศษ), 131-145.
สุพิชชา วงศ์จันทร์. (2557). อิทธิพลทางจิตสังคมและการกำกับตนเองที่มีผลต่อพฤติกรรมสุขภาพของผู้รับบริการที่มีภาวะอ้วนในเขตกรุงเทพมหานคร. วิทยานิพนธ์ ปริญญาวิทยาศาสตร์ดุษฎีบัณฑิต สาขาวิจัยพฤติกรรมศาสตร์ประยุกต์. มหาวิทยาลัยศรีนครินทรวิโรฒ, 1-28.
สำรวย กลยณี และศศิวรรณ ทัศนเอี่ยม .(2562). ผลของการประยุกต์ใช้หลัก 3อ. 2ส. ร่วมกับแรงสนับสนุนทางสังคมเพื่อลดความเสี่ยงต่อโรคเบาหวานและความดันโลหิตสูงของประชาชนกลุ่มเสี่ยงราใหม่. วารสารราชพฤกษ์ 17(2), 95-104.
วิชัย เทียนถาวร. (2556). ระบบเฝ้าระวัง ควบคุม ป้องกัน โรคเบาหวาน ความดันโลหิตสูงในประเทศไทย:นโยบายสู่การปฏิบัติ. (พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 3 ปรับปรุง). กรุงเทพฯ: ชุมนุมสหกรณ์การเกษตรแห่งประเทศไทยจำกัด.
อรรถพงศ์ เพ็ชร์สุวรรณ์. (2552). พฤติกรรมสุขภาพของประชาชนเกี่ยวกับโรคความดันโลหิตสูงและโรคเบาหวานกรณีศึกษา ผู้รับบริการทางการแพทย์เขตสถานีอนามัย อำเภอหนองจิก จังหวัดปัตตานี. วิทยานิพนธ์ ปริญญามหาบัณฑิต .วารสารการพยาบาล สุขภาพ และการศึกษา ปีที่ 1 ฉบับที่ 3 (ก.ย.–ธ.ค. 61). หน้า 11-16.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
- บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารสภาการสาธารณสุขชุมชน ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
- บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารสภาการสาธารณสุขชุมชน


