Factors Associated with Glomerular Filtration Rate among Diabetics and Hypertension with Reduced Glomerular Filtration Rate in Nong Ma Saeo Health Promoting Hospital, Mueang Amnat Charoen District, Amnat Charoen Province
Keywords:
Glomerular filtration rate, Dietary behavior, Diabetes, HypertensionAbstract
This cross-sectional research aimed to examine the factors associated with glomerular filtration rate in the patient of diabetics, and hypertension with reduced glomerular filtration rate in Nong Ma Saeo Health Promoting Hospital, Mueang Amnat Charoen District, Amnat Charoen Province.The calculated number of subjected recruited in this study was 69 subjects. However, the whole population (76 participants) who met the inclusion criteria and showed willingness to join in the study were all recruited in this study. Questionnaires with 0.75 reliability were used for data collection. The descriptive and inferential statistics with Spearman Rank Correlation Coefficient, and Pearson Product Moment Correlation Coefficient were used for data analysis.
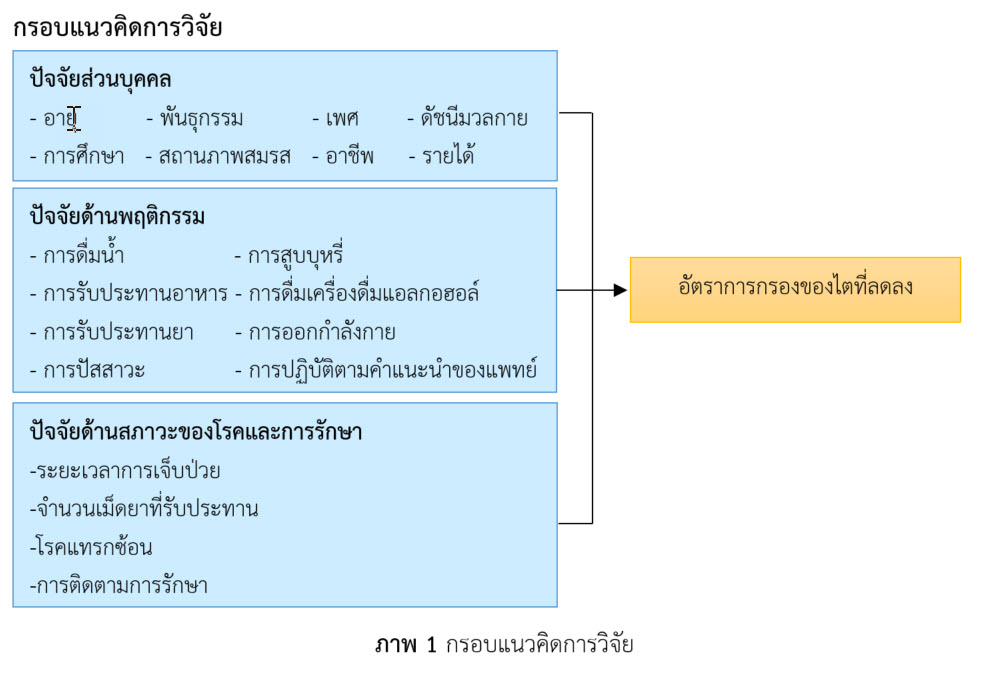
The results are as follows: the majority of participants were female (72.4%); the aged between 70–79 years old (30.3%); body mass index (BMI) between 25–29.9 (32.9%); married status (75.0%); held primary education (86.8%); working in agricultural areas (82.9%); monthly income from 500–1500 Baht (55.3%); having parents or siblings with first-degree diabetics and hypertension 55.3% and 43.4%, respectively. The factors that associated with glomerular filtration rate in the patients of diabetics and hypertension with statistic significance were as follows: genetics (rs = 0.294, p-value = 0.010), eating behaviors (r = 0.189, p-value = 0.017), and quantity of taken pills (rs = 0.106, p-value = 0.032). To prevent the renal deterioration, therefore, encouraging eating behavior and increasing medication adherence should be strengthened by health practitioners working in the multidisciplinary teams.
References
กวิศรา สอนพูด, ลัฆวี ปิยะบัณฑิตกุล .(2563). การดูแลสุขภาพเพื่อชะลอไตเสื่อมของผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานความดันโลหิตสูงแลประชาชนในชุมชนแห่งหนึ่ง จังหวัดศรีสะเกษ. วารสารพยาบาลสงขานครินทร์, 40(1), 101-114.
ณิชชาภัทร ยอดแคล้ว, พรนภา ศุกรเวทย์ศิริ. (2562). ความชุกและปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับการเกิดโรคไตเรื้อรังในผู้ป่วย เบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่เข้ารับการรักษาที่ศูนย์สุขภาพชุมชนเมือง จังหวัดขอนแก่น. สำนักงานป้องกันควบคุมโรคที่ 7 ขอนแก่น, 26(2), 24-33.
ประเสริฐ ธนกิจจารุ. (2558). สถานการณ์ปัจจุบันของโรคไตเรื้อรังในประเทศไทย. วารสารกรมการแพทย์, 40 (กันยายน-ตุลาคม), 6-17.
เพ็ญพร ทวีบุตร, พัชราพร เกิดมงคล และขวัญใจ อำนาจสัตย์ซื่อ. (2560). ผลของโปรแกรมการพยาบาลระบบสนับสนุนและให้ความรู้ในผู้ป่วยโรคเรื้อรังที่มีภาวะไตเรื้อรังระยะเริ่มต้น. วารสารพยาบาลสาธารณสุข, 31(1), 129-146.
ภราดร ล้อธรรมมา และศศิธร ชิดนายี. (2559). พฤติกรรมเสี่ยงต่อการเกิดโรคไตเสื่อมของนักศึกษาพยาบาล วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี อุตรดิตถ์. วารสารวิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี อุตรดิตถ์, 8(1), 59-66.
วีนัส สาระจรัส, แอนนา สุมะโน. (2561). ผลของกระบวนการสนับสนุนการจัดการตนเองต่อการชะลอไตเสื่อมในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานที่มีภาวะไตเรื้อรัง โรงพยาบาลแหลมฉบัง ชลบุรี. วารสารสาธารณสุขและวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ, 1(3), 13-23.
ศศิธร ดวนพล, ธีรศักดิ์ พาจันทร์ และพิทยา ศรีเมือง. (2563). ความชุกและปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับการเกิดโรคไตเรื้อรังในผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานและความดันโลหิตสูง โรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบลบ้านข่าใหญ่ อำเภอจตุรพักตรพิมาน จังหวัดร้อยเอ็ด. วารสารศูนย์อนามัยที่ 9, 14(34), 145-155.
สำนักงานกองทุนสนับสนุนการสร้างเสริมสุขภาพ. (2563). โรคไตวายเรื้อรัง มหันตภัยเงียบ. (อินเทอร์เน็ต) สืบค้นจาก https://www.thaihealth.or.th/Content/ 2425120.html เมื่อวันที่ 5 สิงหาคม 2563.
สำนักงานประชาสัมพันธ์จังหวัดอำนาจเจริญ. (2562). มูลนิธิชลลดา มอบเครื่องฟอกไตและอุปกรณ์ฟอกไต ให้แก่โรงพยาบาลอำนาจเจริญ. สืบค้นเมื่อ 5 สิงหาคม 2563 จาก https://thainews.prd.go.th/th/news/ detail/TCATG190224074352962
Philip Kam-Tao Li, Guillermo Garcai-Garcia, Siu-Fai Lui, et (2020). Kidney Health for Everyone Everywhere -From Prevention to Detection and Equitable Access to Care. Nefrologia, 40(2), 133-141.
Zhang, Q. L., & Rothenbacher, D. (2008). Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease in Populationbased Studies: Systematic Review. BMC Public Health, 8(1), 117.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
- บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารสภาการสาธารณสุขชุมชน ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
- บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารสภาการสาธารณสุขชุมชน


