การพัฒนาระบบการดูแลผู้ป่วยโรคความดันโลหิตสูงที่ควบคุมความดันโลหิตไม่ได้ โรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบล อำเภอบ่อพลอย จังหวัดกาญจนบุรี
คำสำคัญ:
ระบบการดูแลผู้ป่วย โรคความดันโลหิตสูง การดูแลตนเอง ควบคุมความดันโลหิตไม่ได้บทคัดย่อ
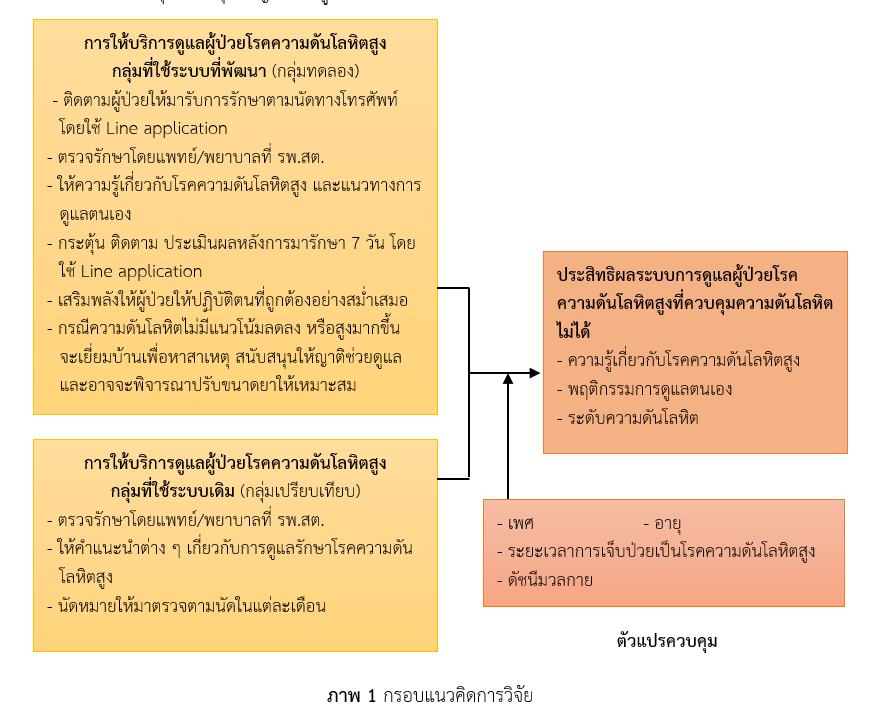
การวิจัยและพัฒนานี้ มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อพัฒนาระบบการดูแลผู้ป่วยโรคความดันโลหิตสูงที่ควบคุมความดันโลหิตไม่ได้ ศึกษาประสิทธิผลระบบการดูแลผู้ป่วย และความพึงพอใจต่อระบบการดูแลผู้ป่วยโรคความดันโลหิตสูงที่ได้พัฒนาขึ้น ของโรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพ (รพ.สต.) อำเภอบ่อพลอย จังหวัดกาญจนบุรี กลุ่มตัวอย่างเป็นผู้ป่วยโรคความดันโลหิตสูงชนิดไม่ทราบสาเหตุ ที่ไม่สามารถควบคุมระดับความดันโลหิตได้ ไม่มีโรคแทรกซ้อนจากโรคความดันโลหิตสูง และยินยอมที่จะร่วมมือในการวิจัย จำนวน 80 คน แบ่งเป็นกลุ่มที่ใช้ระบบที่พัฒนา และกลุ่มที่ใช้ระบบเดิม (ให้การตรวจรักษา แล้วให้คำแนะนำต่าง ๆ ตามสภาพปัญหาของผู้ป่วย ให้ยาไปรับประทาน และการนัดหมายให้มาตรวจตามนัด) กลุ่มละ 40 คน เครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการศึกษาคือ ระบบการดูแลผู้ป่วยโรคความดันโลหิตสูง แบบสอบถาม แบบทดสอบก่อนหลัง และแบบบันทึกระดับความดันโลหิต วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลโดยใช้สถิติเชิงพรรณนา Independent t-test และ Paired sample t-test พบผลการศึกษา ดังนี้
ระบบที่พัฒนา คือ ติดตามผู้ป่วยให้มาตรวจตามนัดด้วย Line application ให้ความรู้และประเมินพฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเอง ให้ยา ให้คำแนะนำในการดูแลตนเอง และมีการติดตามทาง Line application โดยเจ้าหน้าที่ รพ.สต. หลังจากการมารักษา 7 วัน ในช่วง 2 เดือนแรก ในเดือนที่ 3 หากผู้ป่วยยังไม่สามารถควบคุมระดับความดันโลหิตได้ ก็ทำการเยี่ยมบ้านเพื่อหาสาเหตุและส่งเสริมให้ญาติช่วยดูแล และพิจารณาปรับยาให้เหมาะสม ผลการใช้ระบบที่พัฒนา พบว่า หลังการใช้ระบบดังกล่าว ทำให้ผู้ป่วยโรคความดันโลหิตสูงที่ควบคุมความดันโลหิตไม่ได้มีความรู้เกี่ยวกับโรคความดันโลหิตสูง พฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเองดีขึ้น และมีระดับความดันโลหิตลดลง (ทั้งค่า Systolic และ Diastolic blood pressure) อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ (p-value < 0.001) เมื่อเปรียบเทียบหลังการใช้ระบบที่พัฒนา กับการใช้ระบบเดิม พบว่า กลุ่มที่ใช้ระบบที่พัฒนามีความรู้เกี่ยวกับโรคความดันโลหิตสูง พฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเอง ดีกว่ากลุ่มที่ใช้ระบบเดิม และมีระดับความดันโลหิตลดลงมากกว่ากลุ่มที่ใช้ระบบเดิม (ทั้งค่า Systolic และ Diastolic blood pressure) อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ (p-value < 0.001) ทั้งนี้ ผู้ใช้ระบบการดูแลผู้ป่วยโรคความดันโลหิตสูงที่พัฒนา มีความพึงพอใจมาก ร้อยละ 97.5
จากผลการวิจัยดังกล่าว แสดงให้เห็นว่าระบบการดูแลผู้ป่วยโรคความดันโลหิตสูงที่ได้พัฒนานี้ มีประสิทธิผลที่ดี ผู้ป่วยมีความพึงพอใจเป็นส่วนใหญ่ จึงควรนำระบบนี้ไปใช้ที่ รพ.สต.อื่น ต่อไป
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Binibbroheng, J., Niyomdecha, S., Nualpakdee, A. (2012). Efficacy of Behavior Program with Telephone Follow-Up for Hypertension Patients. Research Report. (in Thai).
Blood Pressure Association of Thailand. (2015). Guidelines for the Treatment of Hypertension in General Practice 2012, Revised Version 2015. Retrieved April 12, 2020 Available from: http://www. pharcpa.com/files/
Bo Phloi District Public Health Office. (2019). Statistics of Non-Communicable Disease Patients in Bo Phloi District, Kanchanaburi Province. Report paper.
Burbank, P. M., Reibe, D., C. A. & Nigg, C. (2002). Exercise and Older Adults: Changing Behavior with the Transtheoretical Model. Orthopedic Nursing, 21(4), 51-63.
Center for Continuing Pharmaceutical Education. (2020). The 1st Academic Conference of Pharmacy Society of Thailand 2020, on "High Blood Pressure: What to Know and Need to Know". Retrieved August 2, 2020 Available from: https://ccpe.pharmacy council.org/ index.php?option =seminar_detail& subpage=seminar_detail&id=3115
Department of Disease Control. (2011). Risk Behavior Survey, Non-Communicable Diseases and Injuries. Retrieved April 12, 2020 Available from: http://thaincd.com/information statistic/injureddata. Php
Dey, K. P., & Hariharan, S. (2006). Integrated Approach to Healthcare Quality Management: A Case Study. The TQM Magazine, 18(6), 583-605.
Jone, H. (2013). Changes in Diabetes Self-Care Behaviors Make a Difference in Glycemic Control : the Diabetes Stages of Change (DiSC) Study. Diabetes Care, 26, 732-737.
Kanchanaburi Public Health Office. (2019). Hypertension Patients Report. Kanchanaburi: kanchanaburi Public Health Office.
La-ongphon, B. (1990). The Relationship Between Perceived Self-Efficacy and Outcome Expectancy, and Health Practices in Patients with Opened Fracture of Lower Extremities After Receiving External Fixator. Master of Nursing Science Thesis in Adult Nursing, Prince of Songkla University.
Orem. D. E. (1995). Nursing Concepts of Practice. In K. M. Renpenning & S. G.Taylor (Eds.), (5th ed). St.Louis: Mosby Year Book.
Panatoop, S. (2019). The Caring System Development of Miss Appointment Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Research report. (in Thai).
Prochaska, J. O. Johnson, S. & Lee, P. (2009). The Transtheoretical Model of Behavior Change. in Shumaker, S A., Ockkrne, J. K. and Riekert, K. A. (ed), The Handbook of Health Behavior Change, 3rd ed. New York: Springer.
Puangpetch L. (2009). Self-Care Behavirors and Complications of Patients with Hypertentionospital. Region 6 Medical J, 23, 141-51.
Supimol, W. (2014). Health Behavior. Chon Buri: Faculty of Public Health, Burapha University.
Thai Hypertension Society. (2019). 2019 Thai Guidelines on The Treatment of Hypertension. Chiang Mai: trickthink
Thai Hypertension Society. (2020). 18th Annual Symposium, Thai Hypertension Society. Retrieved September 12, 2020 Available from: http://thaihypertension.org/files/452_1. Thai% 20Hypertension%20Conference%202020.pdf
Voraharn, A. (2018). The Self Care Model Development of Diabetes Mellitus Patients at Lao Khwan Hospital. Research Report. (in Thai).
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
- บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารสภาการสาธารณสุขชุมชน ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการ ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
- บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารสภาการสาธารณสุขชุมชน


