Social Media Use and Its Influence on Nursing Students’ Health Status: A Study at Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Sunpasitthiprasong
Keywords:
social media, health status, nursing studentsAbstract
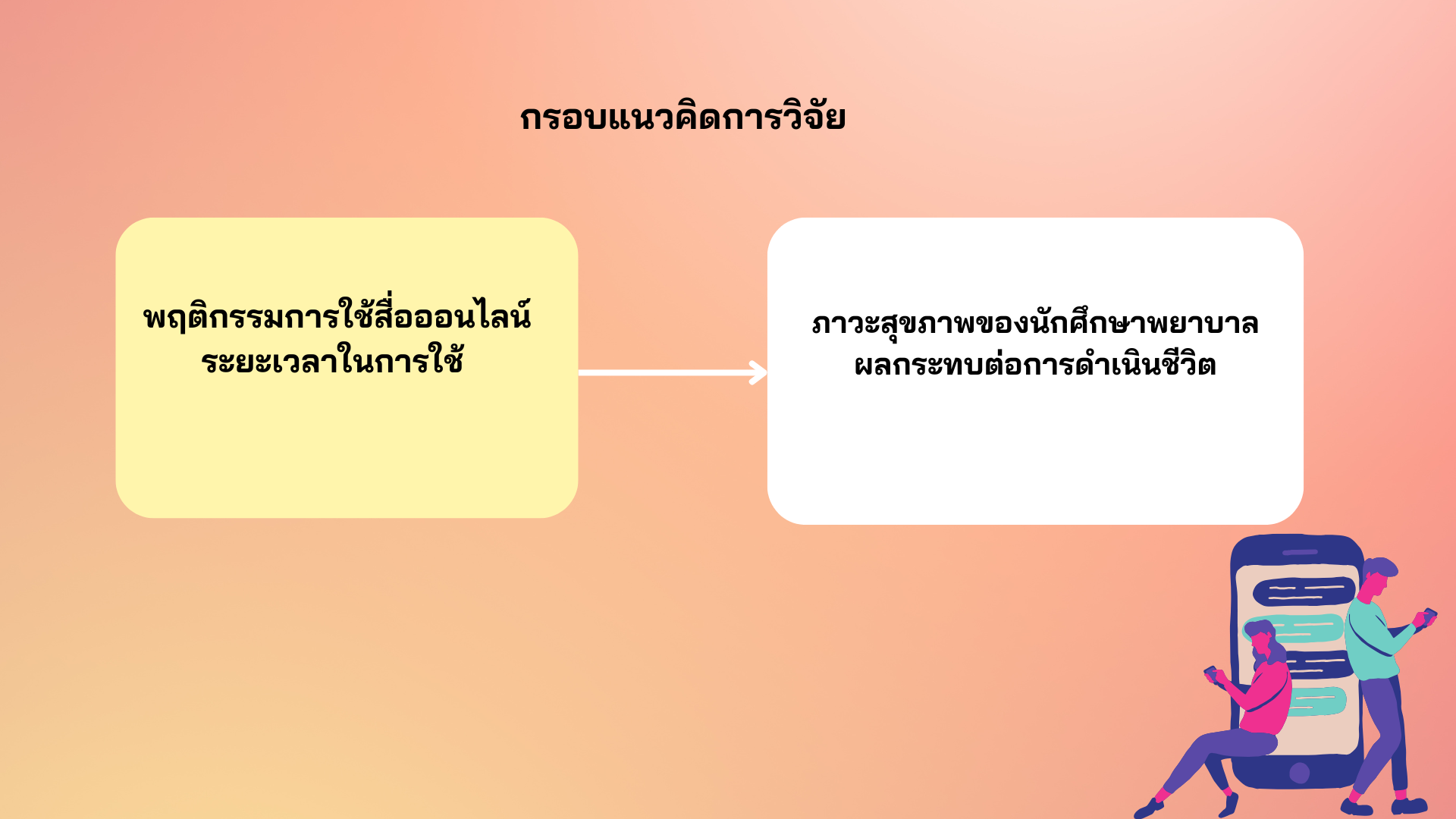
Social media has become an integral part of nursing students’ lives and serves as an easily accessible learning resource for students. Understanding students' behavior in using social media can help educators manage teaching and support students in using social media more effectively and safely. This study aimed to explore social media usage behavior and its relationship with the health status of nursing students at Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Sunpasitthiprasong. A cross-sectional survey was conducted with 270 first to fourth year nursing students, selected through multi-stage random sampling. Data were collected using two validated questionnaires that assessed social media use and health status. The instruments’ reliability coefficients were 0.87 and 0.78, respectively. Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics and chi-square tests.
Results: Most students used social media in excess of 6 hours daily (53%). The most frequently used platforms were Instagram (100%), Line (99.6%), TikTok (96.7%), Facebook (96.7%), and YouTube (94.6%), with students having at least three hours a day usage time. They used social media for recreational purposes, such as listening to music and watching movies, as well as searching for learning content. Social media usage was significantly associated with physical symptoms such as back pain (p = .019), headaches (p = .015), numbness in the fingertips (p = .024), irritability (p = .003) and difficulty concentrating (p= .010). Over half of the participants reported that these symptoms negatively affected their daily lives, particularly their sleep quality (71.5%), academic focus (66.3%), social interactions (56.7%), and engagement in preferred activities (53.7%). The findings suggested that excessive social media usage has measurable negative impacts on students’ physical and mental health. Providing education and encouraging students to shorten the duration of social media use during each session may help reduce the negative impacts of social media on students' physical and mental well-being. Educators can utilize popular types of social media among students as a channel to distribute instructional materials, making them easily accessible and widespread.
References
สำนักงานสถิติแห่งชาติ. การสำรวจการมีการใช้เทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศและการสื่อสารในครัวเรือน [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. 2567 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 8 ธ.ค. 2567]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: https://www.nso.go.th/nsoweb/storage/survey_detail/2024/20240531072624_48392.pdf
สถาบันราชานุกูล. กรมสุขภาพจิต พบเด็กวัยรุ่นติดเกม-ป่วยทางจิตเวชเพิ่มสูงขึ้น 1.5 เท่าในรอบ 3 ปี แนวโน้มอายุน้อยลง เตือนพ่อแม่เฝ้าระวัง ลูกหลานเสพติดเกมประเภท“โมบ้า”ย้ำชัดไม่ใช่กีฬาทางสมอง หวั่นสมองติดเกม เลิกยาก [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2566 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 8 ธ.ค. 2567]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: https://th.rajanukul.go.th/preview-3169.html
อังคณา ศิริอำพันธ์กุล. ภาวะซึมเศร้ากับพฤติกรรมการใช้สื่อโซเชียล. วารสารปัญญาภิวัฒน์ 2561;10:327-37.
Oluwatosin E, Ajewumi V, Magbagbeola O, Kalu C, Ike RA, Okunjolu F, et al. The impact of social media on mental health and well-being. World J Adv Res Rev 2024;24:3027. doi: 10.30574/wjarr.2024.24.1.3027.
พัชริดา บํารุงศรี, จันจิรา ตราสุวรรณ, สุภาพร รัตนรัตน, อภิสรา ทาระการ, ณัฐธิดา ชํานาญกิจ, ณัฐปภัสร์ พงศ์ทองเมือง, และคณะ. พฤติกรรมการใช้สื่อสังคมออนไลน์ของนักศึกษาคณะพยาบาลศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏสุราษฎร์ธานี [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2567 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 10 ธ.ค. 2567]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: https://publication.npru.ac.th/jspui/bitstream/123456789/1389/1/npru_134.pdf
ลักขนา ชอบเสียง, เชาวลิต ศรีเสริม, พรธิรา บุญฉวี, จุฑามาศ ทองประสาน, ณัฐพงษ์ ศรีชาติ. การรับรู้และการจัดการตนเองเมื่อถูกกลั่นแกล้งบนสังคมออนไลน์ของนักศึกษาหลักสูตรพยาบาล วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี สรรพสิทธิประสงค์. วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี สรรพสิทธิประสงค์ 2564;5:22-33.
Berdida DJE. Resilience and academic motivation's mediation effects in nursing students' academic stress and self-directed learning: A multicenter cross-sectional study. Nurse Educ Pract 2023;103639. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2023.103639.
Blumler JG, Katz E. The Uses of Mass Communications: Current Perspectives on Gratifications Research. Sage Annual Reviews of Communication Research Volume III. SAGE Publications, Inc; 1974.
Pouwels JL, Valkenburg PM, Beyens I, van Driel II, Keijsers L. Social media use and friendship closeness in adolescents' daily lives: An experience sampling study. Dev Psychol 2021;57:309-23. doi: 10.1037/dev0001148.
ทรงฤทธิ์ ทองมีขวัญ, สกุลตลา แซ่เตียว, วรินทร์ลดา จันทวีเมือง, ทิพย์สุคนธ์ กิจรุ่งโรจน์, จินตวีร์พร แป้นแก้ว. พฤติกรรมการใช้สื่อออนไลน์ของนักศึกษา วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี สงขลา. วารสารพยาบาลศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยสยาม 2563;21:67-77.
Simpson MC, Sawatzky J-V. Clinical placement anxiety in undergraduate nursing students: A concept analysis. Nurse Educ Today 2020;87:104329
Tang K, Hilton C, Yunita R, Walvinson R, Paerin. Association between social media and mental health changes among gen-z in Batam, Indonesia: A cross-sectional study. cmhp [Internet]. 2024 [cited 2024Dec.25];7:12-5. Available from: https://cmhp.lenterakaji.org/index.php/cmhp/article/view/160
Sherman LE, Payton AA, Hernandez LM, Greenfield PM, Dapretto M. The power of the like in adolescence: effects of peer influence on neural and behavioral responses to social media. Psychol Sci 2016;27:1027-35. doi: 10.1177/0956797616645673.
European Union News. Study shows links between social media use, unhealthy lifestyles and teenage wellbeing [Internet]. 2024 [cited 2024 Nov 27]. Available from: https://go-gale-com.ep.bib.mdh.se/ps/i.do?p=ITOF&u=malard&id=GALE%7CA811484470&v=2.1&it=r
พนัส เชื้อประเสริฐศักดิ์, ปรียานุช วุฒิชูประดิษฐ์, สุพัฒน์ ชูประดิษฐ์. โปรแกรมส่งเสริมสุขภาพจิตต่อภาวการณ์ติดสื่ออนไลน์ ของนักศึกษามหาวิทยาลัย. วารสารวิจัยสหวิทยาการ บัณฑิตศึกษา 2565;1:287-95.
Amy F. Does social media use really cause teenage depression? This is Local London [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2024 Nov 27]. Available from: https://www.thisislocallondon.co.uk/young-reporter/18105479
Aryuwat P, Asp M, Lövenmark A, Radabutr M, Holmgren J. An integrative review of resilience among nursing students in the context of nursing education. Nurs Open 2023;10:2793-818. doi: 10.1002/nop2.1559.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Boromarajonani College of Nursing Sunpasitthiprasong

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี สรรพสิทธิประสงค์ ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับวิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี สรรพสิทธิประสงค์ และคณาจารย์ท่านอื่นๆ ในวิทยาลัยพยาบาลฯ ความรับผิดชอบเกี่ยวกับบทความแต่ละเรื่องผู้เขียนจะรับผิดชอบของตนเอง


