Effects of a Self-Management Program on Self-Management Behaviors for Slowing the Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy among Diabetic Patients at Fang Hospital, Chiang Mai Province
Keywords:
self-management program, diabetes, diabetic nephropathyAbstract
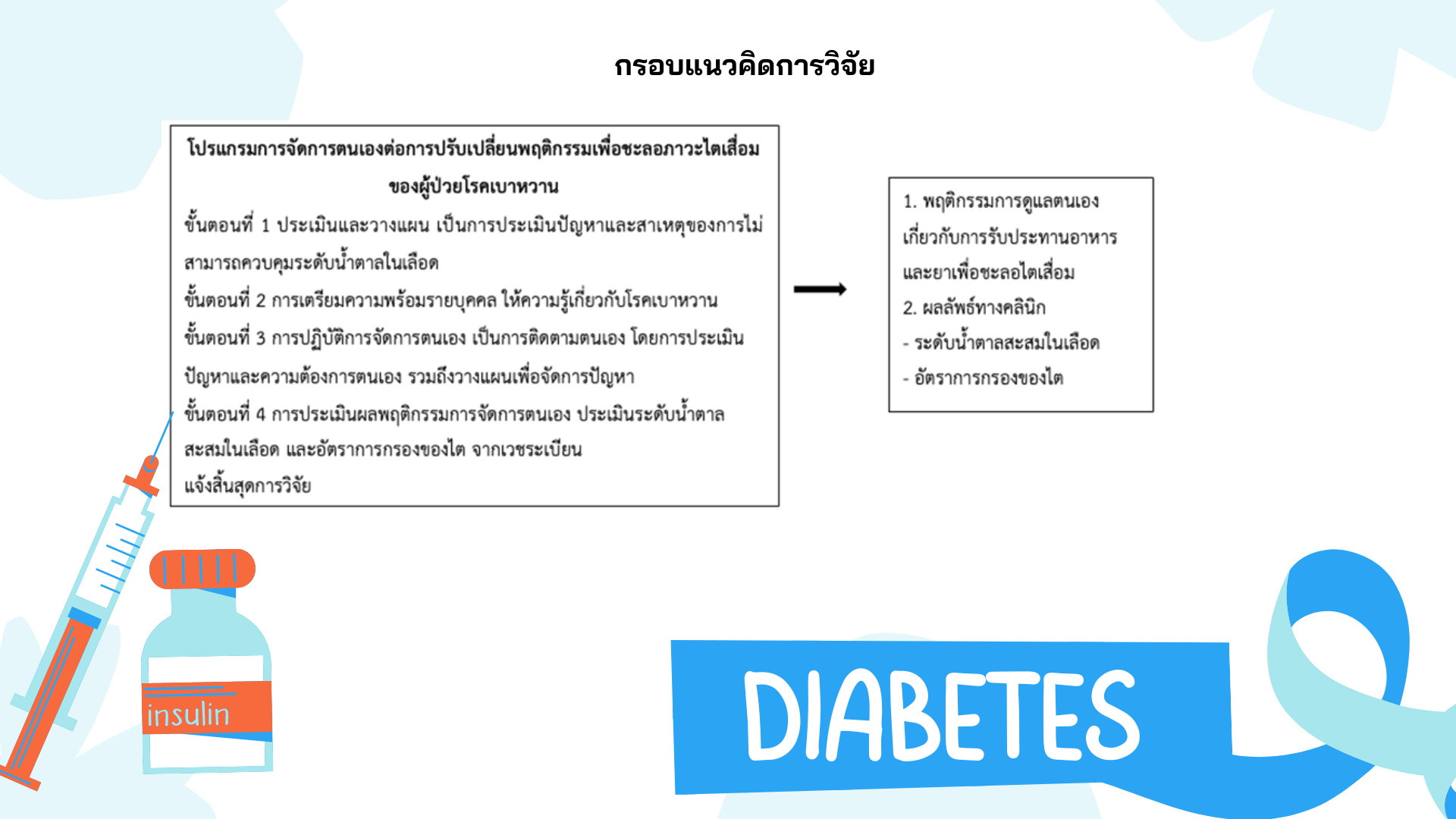
Diabetic patients who are unable to control their blood sugar levels can experience kidney blood vessels impairment, resulting in reduced filtration rates and eventually kidney failure. If patients are unable to self-manage and delay the progression of kidney disease, it can ultimately result in the need for kidney replacement therapy ultimately. The objectives of this two-group pretest-posttest quasi-experimental design research were: 1) to compare the average scores of self-manage behaviors, and 2) to compare the clinical outcomes of diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease between the experimental and control groups. The sample consisted of type 2 diabetes patients receiving treatment at Fang Hospital, Chiang Mai. A purposive sampling method was used to recruit the participants into experimental and control groups, 30 for each group. Research tools included a personal data questionnaire, a self-management program for behavior changing to delay the progression of chronic kidney disease in diabetic patients, an assessment questionnaire for blood sugar control behaviors in diet control and medication. The content validity index of the last two research tools were 1.0, and their reliability coefficients, measured with Cronbach's alpha, were .73 and .78, respectively. Personal data were analyzed using descriptive statistics. ANCOVA was used to compare the average scores of blood sugar control behaviors in diet and medication between the experimental and control groups.
The results revealed that after participating in the program, the experimental group had higher mean scores of self-manage (blood sugar control behaviors regarding diet and medication), higher estimated glomerular filtration rate and lower blood sugar level than the control group, statistical significance at p-value <.001. Therefore, the self-management program for behavior changing can delay the progression of chronic kidney disease in diabetic patients.
References
กองโรคไม่ติดต่อ กรมควบคุมโรค. รณรงค์วันเบาหวานโลกปี 2563 หนุนบทบาทพยาบาลร่วมสร้างพลังแห่งการเปลี่ยนแปลงโรคเบาหวาน [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. 2563 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 13 พ.ย. 2565]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: https://ddc.moph.go.th/brc/news.php?news=15591&deptcode=brc
กองโรคไม่ติดต่อ สำนักสื่อสารความเสี่ยงฯ กรมควบคุมโรค. กรมควบคุมโรค เผยสถานการณ์โรคเบาหวานทั่วโลก มีผู้ป่วยแล้ว 537 ล้านคน มีส่วนทำให้เสียชีวิต สูงถึง 6.7 ล้านคน หรือเสียชีวิต 1 ราย ในทุกๆ 5 วินาที [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. 2565 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 13 พ.ย. 2565]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: https://pr.moph.go.th/?url=pr/detail/2/02/181256/
พุทธรักษ์ ดีสิน, ศุภศิลป์ ดีรักษา. ความชุกและปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับโรคแทรกซ้อนในผู้ใหญ่ที่เป็นโรคเบาหวานชนิดที่ สอง โรงพยาบาลท่าคันโทจังหวัดกาฬสินธุ์. วารสารวิจัยและพัฒนาระบบสุขภาพ 2563;13:36-41.
สุรัตน์ อนันทสุข. โปรแกรมการพัฒนาพฤติกรรมสุขภาพเพื่อชะลอภาวะไตเสื่อมในผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานชนิดไม่พึ่งอินซูลิน ในโรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพ ตำบลบางพูน อำเภอเมืองปทุมธานี จังหวัดปทุมธานี [วิทยานิพนธ์ปริญญาคหกรรมศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต]. ปทุมธานี: มหาวิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีราชมงคลธัญบุรี; 2564.
นิตยา สิตะเสน, กีรดา ไกรนุวัตร, รักชนก คชไกร. ความชุกและปัจจัยทำนายการเกิดโรคไตจากเบาหวานในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ในศูนย์บริการสาธารณสุข กรุงเทพมหานคร. วารสารพยาบาลศาสตร์ 2563;38:31-43.
บดินทร์ จักรแก้ว. ความชุกและปัจจัยเสี่ยงของการเกิดภาวะไตวายเรื้อรังในผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานชนิดที่2 ในอำเภอเขตกึ่งเมืองของจังหวัดเชียงใหม่. วารสารสาธารณสุขล้านนา 2565;18:16-30.
จิรวัฒน์ สีตื้อ. ความชุกของโรคไตวายเรื้อรังและปัจจัยเสี่ยงที่สัมพันธ์กับการทำงานของไตลดลงของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ในศูนย์สุขภาพชุมชนเขตเมืองร่องซ้อ จังหวัดแพร่. วารสารการแพทย์และวิทยาศาสตร์คลินิก โรงพยาบาลแพร่ 2562;27:1-15.
กมลทิพย์ วิจิตรสุนทรกุล. ระบาดวิทยาและการทบทวนมาตรการป้องกันโรคไตเรื้อรัง. นนทบุรี. กองโรคไม่ติดต่อ กรมควบคุมโรค. 2565.
ธีรศักดิ์ พาจันทร์, กฤชกันทร สุวรรณพันธ์, บุญสัน อนารัตน์, นิรันดร์ ถาละคร. ปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับการควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 อำเภอท่าบ่อ จังหวัดหนองคาย. วารสารศูนย์อนามัยที่ 9 2565;16:285-98.
วิทยา เลิกสายเพ็ง. ปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อการควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดของผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานในเขตรับผิดชอบโรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบลหนองปิ้งไก่ ตำบลนาบ่อคำ อำเภอเมืองกำแพงเพชร จังหวัดกำแพงเพชร. วารสารวิจัยและวิชาการสาธารณสุขจังหวัดพิจิตร 2564;2:1-10.
กานต์ชนก สุทธิผล. ปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อการคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่2 ศูนย์สุขภาพชุมชนประชานุเคราะห์โรงพยาบาลราชบุรี. มหาราชนครศรีธรรมราชเวชสาร 2565;5:1-11.
ชลาภัทร คำพิมาน และพัฒนชัย รัชอินทร์. ผลของโปรแกรมปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมชะลอไตเสื่อม ของผู้ป่วยเบาหวาน ความดัน โลหิตสูง ที่มีภาวะไตเสื่อมระยะที่ 1 ถึง 3 ตำบลดงขวาง อำเภอเมือง จังหวัดนครพนม. วารสารโรงพยาบาลนครพนม 2560;4:42-9.
กนกวรรณ ด้วงกลัด, ปัญญรัตน์ ลาภวงศ์วัฒนา, ณัฐกมล ชาญสาธิตพร. โปรแกรมการส่งเสริมการจัดการตนเองในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่ควบคุมไม่ได้. วารสารวิจัยสุขภาพและการพยาบาล 2563;36:66-83.
Kanfer FH, Gaelick-Buys L. Self management methods. New York: Pergamon Press;1991.
สาวิตรี นามพะธาย. ผลของโปรแกรมการจัดการโรคเบาหวานด้วยตนเองต่อพฤติกรรมการควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือด และค่าน้ำตาลเฉลี่ยสะสมในเลือดของผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่ควบคุมไม่ได้ [วิทยานิพนธ์ปริญญาพยาบาลศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต]. นครปฐม: มหาวิทยาลัยคริสเตียน; 2561.
พนิดา รัตนศรี. ผลของโปรแกรมสนับสนุนการจัดการตนเองเพื่อชะลอไตเสื่อมต่อพฤติกรรมการจัดการตนเองและผลลัพธ์ทางคลินิกในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ของโรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบลสำราญ. วารสารสำนักงานสาธารณสุข จังหวัดขอนแก่น 2565;4:210-224.
งานสารสนเทศ โรงพยาบาลฝาง. รายงานข้อมูล. HosXp. 2566.
สุพัตรา พงษ์อิศรานุพร, ศศรส หลายพูนสวัสดิ์, ประทุน สุภชัยพานิชพงศ์. ผลของโปรแกรมสนับสนุนการจัดการตนเองเพื่อชะลอไตเสื่อมต่อพฤติกรรมการจัดการตนเอง และผลลัพธ์ทางคลินิกในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 โรงพยาบาลดำเนินสะดวก. วารสารแพทย์เขต 4-5 2561;37:148-59.
ประเสริฐ บุญเกิด. แบบทดสอบสภาพสมองเบื้องต้นฉบับภาษาไทย Mental State Examination T10 (MSET10). สมาคมโรคสมองเสื่อมแห่งประเทศไทย สารจากนายก 2561;10:1-4
ศิริลักษณ์ ถุงทอง, เพลินพิศ ฐานิวัฒนานนท์. ผลของโปรแกรมสนับสนุนการจัดการตนเองเพื่อ ชะลอไตเสื่อมจากเบาหวานต่อพฤติรรมการจัดการตนเองและผลลัพธ์ทางคลินิกในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่ไม่สามารถควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดได้. วารสารสงขลานครินทร์ 2558;35:67-84.
ราชวิทยาลัยอายุรแพทย์แห่งประเทศไทย ในพระบรมราชูปถัมภ์. แนวทางเวชปฏิบัติสำหรับโรคเบาหวาน 2566. กรุงเทพฯ: ศรีเมืองการพิมพ์; 2566.
Hisni D, Soewondo P, Dahlia D, Ayubi D. Concept analysis of self-management in patient with diabetes nephropathy. Journal Endurance 2023; 28:363-8.
Naber T, Purohit S. Chronic Kidney Disease: Role of Diet for a Reduction in the Severity of the Disease. Nutrients 2021;13:1-16.
Lambrinou E, Hansen T B, Beulens J W. Lifestyle factors, self-management and patient empowerment in diabetes care. European journal of preventive cardiology 2019;26:55-63.
Swanson V, Maltinsky W. Motivational and behavior change approaches for improving diabetes management. Practical Diabetes 2019;36:121-5.
Sayeed KA, Qayyum A, Jamshed F, Gill U, Usama SM, Asghar K, Tahir A, Siddiqui A. Impact of diabetes-related self-management on glycemic control in type II diabetes mellitus. Cureus 2020;12:e7845.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Boromarajonani College of Nursing Sunpasitthiprasong

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี สรรพสิทธิประสงค์ ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับวิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี สรรพสิทธิประสงค์ และคณาจารย์ท่านอื่นๆ ในวิทยาลัยพยาบาลฯ ความรับผิดชอบเกี่ยวกับบทความแต่ละเรื่องผู้เขียนจะรับผิดชอบของตนเอง


