The Effectiveness of a Fall Prevention Program with Participation of Family on Fall Prevention Behavior for Older Adults Living in the Community
Keywords:
fall prevention, family involvement, older adultsAbstract
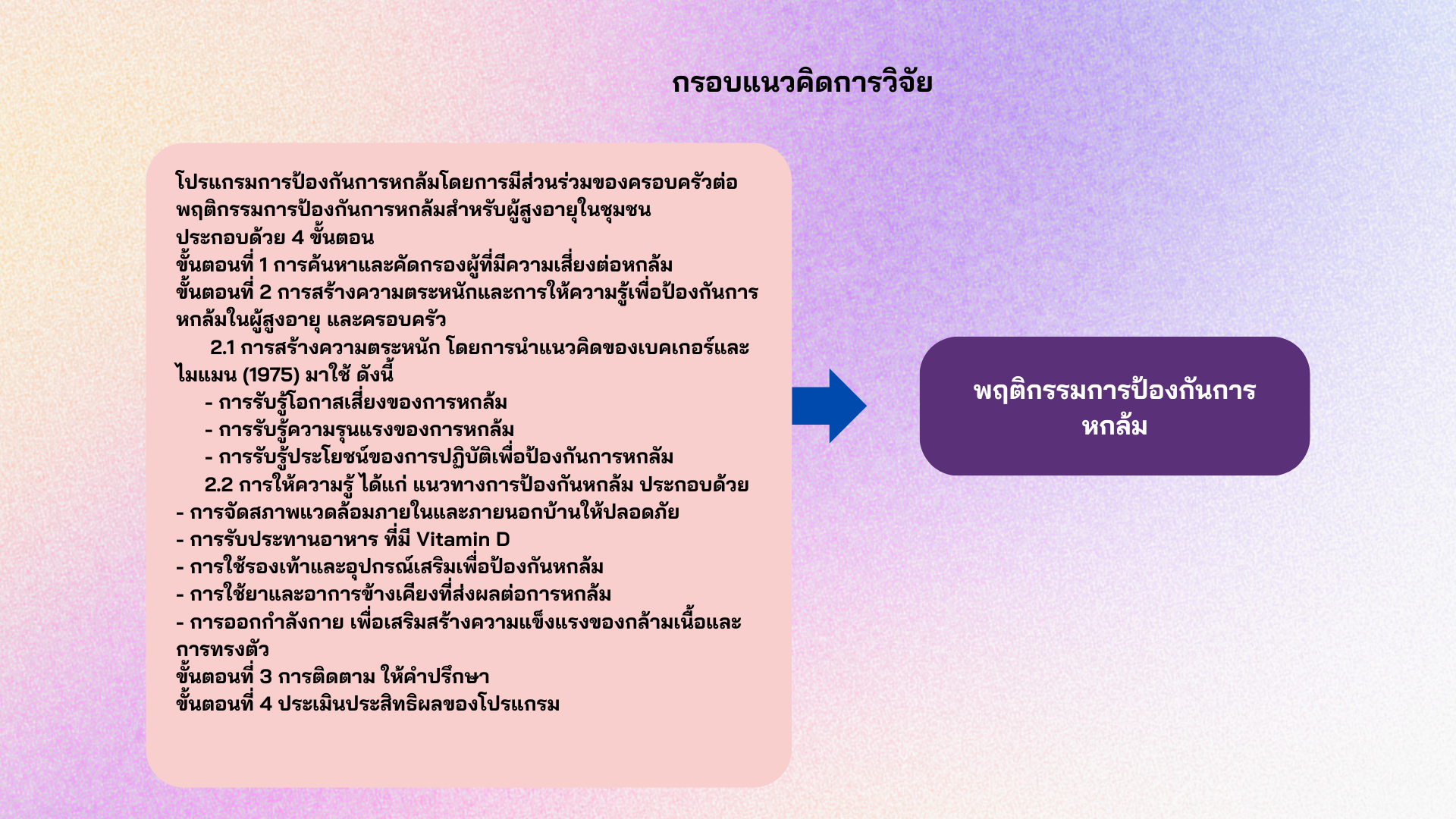
Falls in older adults are a major problem affecting the well-being of older adults. Preventing falls can reduce incidence and severity of falls and injuries. This quasi-experimental research using a two-group, pretest-posttest design, aimed to compare fall prevention behaviors in older adults in relation to the involvement of their families. The subjects were older adults who were specifically selected from the Ban Pho Sub-district, Mueang District, Trang Province. The study involved 46 participants who were divided into two groups: an experimental group of 23 individuals who received a fall prevention program with family involvement, and a control group of 23 individuals who followed their regular routine care. The research instruments consisted of the following: 1) the fall prevention program with family involvement that applied Health Belief Model theory, 2) a personal data questionnaire, and 3) a fall prevention behavior assessment for older adults in the community. Three qualified experts verified their content validity indexes of 0.98. The Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of the fall prevention behavior assessment was 0.82. Data were analyzed using percentages, means, standard deviations, and paired t-test statistics.
The majority of the sample group were female (87%), with no problems with walking or balancing (87%). The control and experimental groups had an average age of 66 and 65 years, respectively, and had no differences in general characteristics. The mean difference in fall prevention behavior scores before and after the experiment were 0.81 (Mean=0.81, SD.=.620) and 1.94 (Mean=1.94, SD=.059), respectively. After the completion of the program, the mean values for fall prevention behavior among the older adults in the experimental group was significantly higher than that of the control group (p<.01) and they had significantly higher mean scores than before receiving the program (p<.01). In conclusion, the fall prevention programs for the older adults with the involvement of families helped increase fall prevention behavior. Therefore, families, caregivers, and relevant organizations responsible for older individuals in communities should implement fall prevention programs with the involvement of families. The program aimed to raise awareness about risk factors, severity, and preventive measures against falls. This effort could contribute to preserving older adults 's overall well-being.
References
กรมกิจการผู้สูงอายุ กระทรวงพัฒนาสังคมและความมั่นคงของมนุษย์. สถิติผู้สูงอายุ [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2567 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 2567 ก.พ. 20]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: https://www.dop.go.th/th/know/side/1/1/2449
Eliopoulos C. Gerontological Nursing. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2018.
วีรศักดิ์ เมืองไพศาล. สถานการณ์โรคและการดูแลสุขภาพในผู้สูงอายุ. ใน: วีรศักดิ์ เมืองไพศาล, บรรณาธิการ. พฤฒาวิทยาและเวชศาสตร์ผู้สูงอายุสำหรับการดูแลผู้ป่วยสูงอายุขั้นต้น. นนทบุรี: ภาพพิมพ์; 2560. หน้า 21-29.
World Health Organization. WHO global report on falls prevention in older age [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2014 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 2022 มี.ค. 3]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: https://extranet.who.int/agefriendlyworld/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/WHo-Global-report-on-falls-prevention-in-older-age.pdf
นิพา ศรีช้าง, ลวิตรา กำวี. การพยากรณ์การพลัดตกหกล้มของผู้สูงอายุ (อายุ 60 ปีขึ้นไป) ในประเทศไทย ปี พ.ศ. 2560-2564 [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2567 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 2566 ม.ค. 10]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: http://www.thaincd.com/document/file/violence/
สำนักโรคไม่ติดต่อ กรมควบคุมโรค กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. รายงานสรุปผลการประเมินความรอบรู้การป้องกันการพลัดตกหกล้มของผู้สูงอายุ ปีงบประมาณ 2566 [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2566 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 2566 ม.ค. 10]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: https://ddc.moph.go.th/dip/news.php?news=37140&deptcode=
ละออม สร้อยแสง, จริยาวัตร คมพยัคฆ์, กนกพร นทีธนสมบัติ. การศึกษาแนวทางการป้องกันการหกล้มในผู้สูงอายุชุมชนมิตรภาพพัฒนา. วารสารพยาบาลทหารบก 2557;15:123-29.
วรรณพร บุญเปล่ง, วดีรัตน์ ศรีวงศ์วรรณ, พัฒนา เศรษฐวัชราวนิช. อัตราและปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับการหกล้มของผู้สูงอายุ: ชุมชนริมแม่น้ำเจ้าพระยา จังหวัดนนทบุรี. วารสารพยาบาลศาสตร์ 2558;33:74-86.
ผ่องพรรณ อรุณแสง. การพยาบาลปัญหาสำคัญของผู้สูงอายุ: การนำใช้. พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 4. ขอนแก่น: คณะพยาบาลศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยขอนแก่น; 2560.
ภาวดี วิมลพันธ์ุ, ขนิษฐา พิศฉลาด. ผลของโปรแกรมป้องกันการพลัดตกหกล้มต่อการพลัดตกหกล้มในผู้สูงอายุ. วารสารพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข 2557;23:98-109.
นารีรัตน์ จิตรมนตรี. การป้องกันการหกล้มและกระดูกหักที่บ้านและสถานดูแลระยะยาวด้วยสหวิชาชีพ. ใน: วีรศักดิ์ เมืองไพศาล, บรรณาธิการ. ประเด็นสำคัญในทางปฏิบัติสำหรับการดูแลผู้สูงอายุระยะยาว. กรุงเทพมหานคร: บริษัท ภาพพิมพ์จำกัด; 2564. หน้า 89-97.
สถาบันเวชศาสตร์สมเด็จพระสังฆราชญาณสังวรเพื่อผู้สูงอายุ กรมการแพทย์ กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. แนวทางเวชปฏิบัติการป้องกันและประเมินการหกล้มในผู้สูงอายุ. นนทบุรี: สินทวีการพิมพ์; 2562.
Kittipimpanon K, Amnatsatsue K, Kerdmongkol P, Jarupat Maruo S, Nityasuddhi D. Development and Evaluation of a Community-based Fall Prevention Program for Elderly Thais. Pac Rim Int J Nurs Res 2012;16:222-35.
วิทยา วาโย, นารีรัตน์ จิตรมนตรี, วิราพรรณ วิโรจน์รัตน์. ผลของโปรแกรมป้องกันการหกล้มแบบสหปัจจัยต่อพฤติกรรมการป้องกันการหกล้มของผู้สูงอายุในชุมชน. วารสารการพยาบาลและการดูแลสุขภาพ 2560;35:25-33.
บุศรินทร์ ผัดวัง, ถาวร ล่อกา. การติดตามผลลัพธ์ระยะยาวในการสนับสนุนการจัดการดูแลตนเองต่อระดับน้ำตาลในกระแสเลือดและระดับความดันโลหิตในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานและความดันโลหิตสูง: กรณีศึกษา บ้านฮ่องห้า ตำบลน้ำโจ้ อำเภอแม่ทะ จังหวัดลำปาง. วารสารวิจัยทางวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ. 2558;943-51.
Ojo EO, Thiamwong L. Effect of Nurse-Led fall prevention programs for older adults: A systematic review. Pac Rim Int J Nurs Res Thail 2022;26:417-31.
คณะทำงานแผนยุทธศาสตร์พัฒนาจังหวัดด้านสังคมและการพัฒนาคุณภาพชีวิต จังหวัดตรัง. แผนพัฒนาคุณภาพชีวิตรองรับสังคมสูงวัย จังหวัดตรัง ปี 2566-2570 [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2566 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 2566 ม.ค. 10]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: http://trang.nfe.go.th/UserFiles/Pdf/2023/140623.pdf
สถิติประชากรทางการทะเบียนราษฎร์ สำนักบริหารการทะเบียน กรมการปกครอง [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2566 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 2566 ม.ค. 10]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: https://stat.bora.dopa.go.th/stat/statnew/statMONTH/statmonth/#/mainpage
สถิติประชากรผู้สูงอายุ โรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบลบ้านโพธิ์ อำเภอเมือง จังหวัดตรัง. มีนาคม 2565. เอกสารอัดสำเนา.
Becker MH, Maiman LM. Sociobehavioral Determinants of Compliance with Health and Medical Care Recommendations. Med Care 1975;13:10-24.
Cohen's Standards for Small, Medium, and Large Effect Sizes [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2566 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 2566 มิ.ย. 16]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: https://core.ecu.edu/wuenschk/docs30/EffectSizeConventions.pdf
ธีรภัทร อัตวินิจตระการ, ชวนนท์ อิ่มอาบ. ประสิทธิผลของโปรแกรมการเตรียมความพร้อมและป้องกันการหกล้มในผู้สูงอายุ. วารสารแพทย์เขต 4-5 2562;38:288-98.
ฐิติมา ทาสุวรรณกิจ, กรรณิการ์ เทพกิจ. ผลของโปรแกรมการป้องกันการพลัดตกหกล้มในผู้สูงอายุ. วารสารการพยาบาลและการดูแลสุขภาพ 2560;38:186-95.
จรัญญา ส่งเสริม. ผลของโปรแกรมป้องกันพลัดตกหกล้มของผู้สูงอายุในชุมชน. วารสารโรงพยาบาลนครพนม 2564;8:73-83.
โสภิตตา แสวา. ผลของโปรแกรมป้องกันการพลัดตกหกล้มโดยประยุกต์ตามแบบแผนความเชื่อด้านสุขภาพร่วมกับแรงสนับสนุนทางสังคมต่อพฤติกรรมป้องกันการพลัดตกหกล้มของผู้สูงอายุในอำเภอเกาะจันทร์ จังหวัดชลบุรี. วิทยานิพนธ์หลักสูตรสาธารณสุขศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต, คณะสาธารณสุขศาสตร์, มหาวิทยาลัยบูรพา. 2565.
Mohammed RA, Nour-Eldein H, Abdel-Halim AW, Abdulmajeed AA. Effect of a fall prevention program for elderly persons attending a rural family medicine center, Egypt. J Public Health 2019;27:1-8.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Boromarajonani College of Nursing Sunpasitthiprasong

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี สรรพสิทธิประสงค์ ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับวิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี สรรพสิทธิประสงค์ และคณาจารย์ท่านอื่นๆ ในวิทยาลัยพยาบาลฯ ความรับผิดชอบเกี่ยวกับบทความแต่ละเรื่องผู้เขียนจะรับผิดชอบของตนเอง


