The Effects of Parental involvement Programs on Promoting Knowledge, Parental Attitudes, and the Fine Motor Development in Preschool Children
Keywords:
development, fine motor, preschool age, parental involvementAbstract
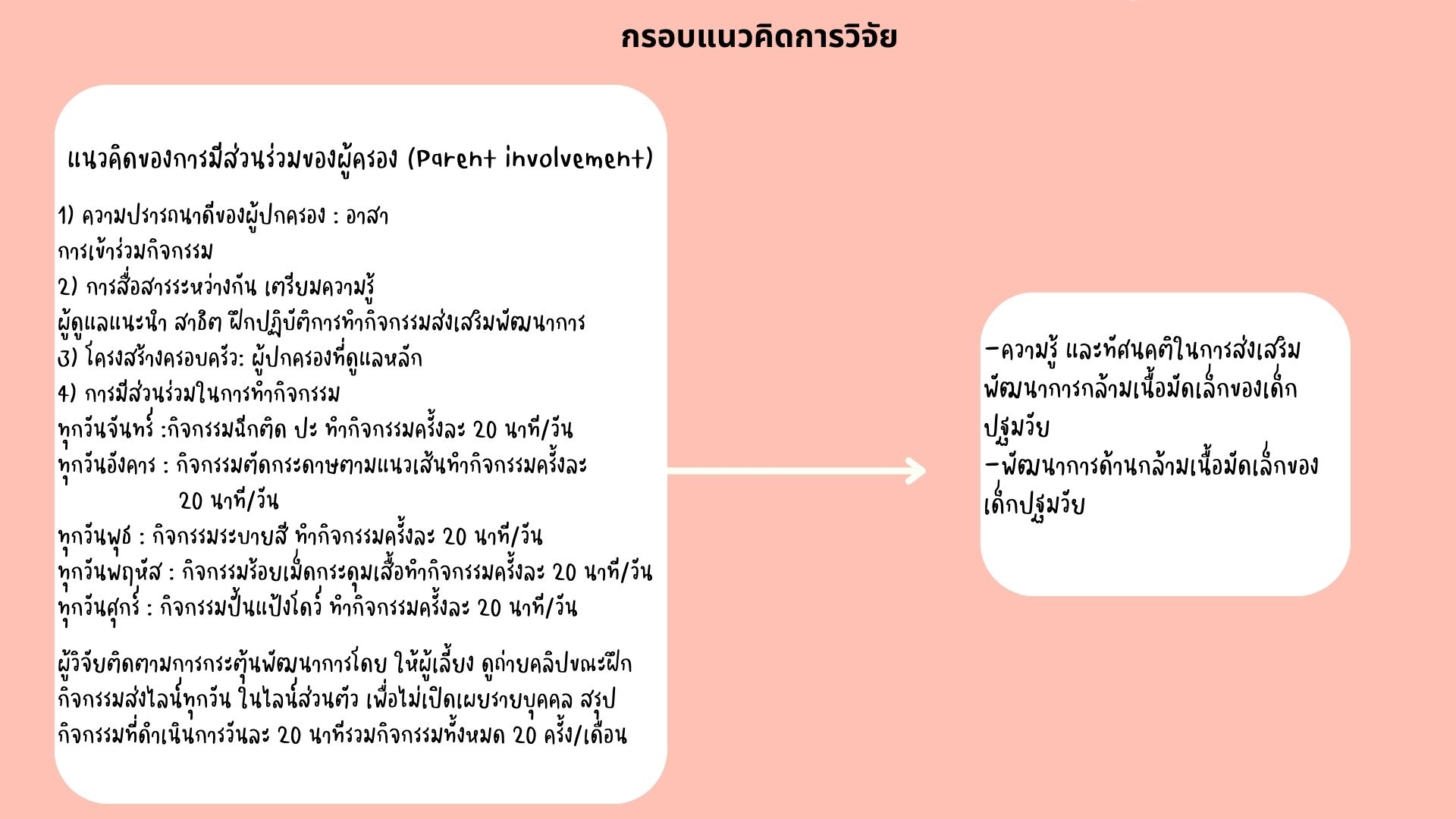
Delayed development in fine motor skills is often observed in preschool children, affecting their learning, behavior, and intellectual abilities. While fine motor skills are typically promoted in classrooms, continuity at home is often lacking. This quasi-experimental study aimed to compare the knowledge, attitudes of parents, and the fine motor skills development of preschool children before and after participating in a program. The sample group consisted of 20 children aged 4-5 years, identified with suspected delayed fine motor skills development through assessment of the Developmental Surveillance and Promotion Manual (DSPM). Parental consent was obtained for participation. The program comprised five activities, each lasting 20 minutes, conducted at home within one month. The research tools included: 1) DSPM developmental assessment, 2) a program involving parental participation in promoting child development, 3) a general information questionnaire, 4) a test on parental knowledge of fine motor skills development, and 5) an attitude test on parental promotion of fine motor skills development. Data analysis included a paired t-test to compare knowledge scores, parental attitudes, and fine motor skills development before and after the program. The results revealed statistically significant increases in average knowledge scores, parental attitudes, and fine motor skills development after the program (p <.05). In conclusion, the program involving parental participation effectively increased knowledge and attitudes among parents and promoted fine motor skills development in preschool children.
References
คณะอนุกรรมการตรวจสอบและประเมินผล ภาคราชการกลุ่มกระทรวงคณะที่ 2. รายงานการพัฒนาเด็กปฐมวัย [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. 2562 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 3 มี.ค. 2566]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: https:// www.nesdc.go.th/ewt_w3c/ewt_dl_link.php?nid=10104
Franklin Q, Prows CA, Developmental and genetic influences on child health promotion [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. 2021 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 16 มี.ค. 2566]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: https:// repository.poltekkeskaltim.ac.id/638/1/Wong%E2%80%99s%20Essentials%20of%20Pediatric%20Nursing%20by%20Marilyn%20J.%20Hockenberry%20Cheryl%20C.%20Rodgers%20David%20M.%20Wilson%20(z-lib.org).pdf
ทองใบ สวัสดิ์ผล. การจัดประสบการณ์เพื่อพัฒนากล้ามเนื้อมัดเล็กที่ส่งผลต่อการเขียน ของเด็กปฐมวัยระดับชั้นอนุบาลปีที่ 3 โรงเรียนการกุศลวัดบ้านก่อ อำเภอศรีสมเด็จ จังหวัดร้อยเอ็ด [วิทยานิพนธ์ครุศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต]. มหาสารคาม: มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏมหาสารคาม; 2561.
สถาบันวิจัยประชากรและสังคม มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล. สุขภาพคนไทย 2561: พุทธศาสนากับการสร้างเสริมสุขภาวะ หนังสือและรายงานวิจัย [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. 2561 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 5 มิ.ย. 2566]. เข้าถึงได้จาก: https://ipsr.mahidol.ac.th/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/472-ThaiHealth2018-TH_compressed.pdf.
กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. คู่มือเฝ้าระวังและส่งเสริมพัฒนาการเด็กปฐมวัย (Developmental Surveillance and Promotion Manual: DSPM) นนทบุรี: โรงพิมพ์องค์การสงเคราะห์ทหารผ่านศึก; 2562.
ศิวิไล กระจับเงิน. การจัดประสบการณ์การเรียนรู้โดยใช้ชุดกิจกรรมศิลปะสร้างสรรค์ ด้วยการ ปั้นนูนเพื่อพัฒนากล้ามเนื้อมัดเล็กสำหรับเด็กปฐมวัย ชั้นอนุบาลปีที่ 1. วารสารเทคโนโลยีและสื่อสารการศึกษา คณะศึกษาศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหาสารคาม 2562;2:171-80.
อรทัย นามขาว, อนุกูล จินตรักษ์. การจัดกิจกรรมศิลปะสร้างสรรค์โดยใช้กระดาษเพื่อพัฒนากล้ามเนื้อมัดเล็กของเด็กปฐมวัยระดับชั้นอนุบาล 3. วารสารศึกษาศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหาสารคาม 2565;16:198-208.
นุชจณี อู่ทอง, อัฐณีญา สัจจะพัฒนกุล. การส่งเสริมพัฒนาการด้านกล้ามเนื้อมือมัดเล็กของเด็กปฐมวัย โดยใช้ชุดกิจกรรมการฉีก และการปะ. การประชุมวิชาการระดับชาติสำหรับนักศึกษาครั้งที่ 2: 15 มี.ค. 2565; มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏกำแพงเพชร; 2565.
Fan X, Chen M. Parental involvement and students' academic achievement: A meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review 2001;13:1-22.
Kovács K, Kovács KE, Bacskai K, Békési Z, Oláh ÁJ, Pusztai G. The effects and types of parental involvement in school-based sport and health programs still represent a knowledge gap: A systematic review. IJERPH 2022;19:128-59.
วณิตา ขวัญสำราญ. บทบาทของพยาบาลกับการมีส่วนร่วมของผู้ปกครองในการดูแลเด็กปากแหว่งเพดาน โหว่. วารสารคณะพยาบาลศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยบูรพา 2015;23:14-25.
พูนศิริ ฤทธิรอน, ดวงหทัย จันทร์เชื้อ, พัสตราภรณ์ แย้มเม่น, นิชนันท์ อินสา, อมรรัตน์ เนียมสวรรค์, รัชดาวรรณ บุญมีจิว และคณะ. ปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อพัฒนาการเด็กปฐมวัยไทยเขตสุขภาพที่ 2 พิษณุโลก. วารสาร วิจัยและพัฒนาระบบสุขภาพ 2021;14:42-56.
นัยนา ภูลม, จินตนา วัชสินธุ์, นุจรี ไชยมงคล. นิเวศวิทยาครอบครัว: ปัจจัยที่มีอิทธิพลต่อพัฒนาการเด็กวัย เตาะแตะ. วารสารสุขภาพและการศึกษาพยาบาล 2016;22:18-36.
สิทธิพงศ์ ปาปะกัง. บทบาทของผู้ปกครองในการประเมินพัฒนาการเด็กตามคู่มือ DSPM. วารสาร โรงพยาบาลมหาสารคาม. 2022;19:176-85.
มธุวดี อิงศิโรรัตน์. ความรู้และทัศนคติของผู้ปกครองเด็กกลุ่มอาการออทิซึมในโรงพยาบาล อุดรธานี. วารสารการแพทย์โรงพยาบาลอุดรธานี 2018;26:108-18.
สิทธิพรร์ สุนทร, วัชรินทร์ สุทธิศัย, พงษ์ศักดิ์ ซิมมอนด์ส, รัชนิดา ไสยรส, ภัณฑิลา น้อยเจริญ. แนวคิดและกระบวนทัศน์ในการกำหนดขนาดตัวอย่าง ด้วย G* Power. วารสารสหวิทยาการวิจัย 2562;8(ฉบับพิเศษ):29-39.
ปรารถนา กุศลโกมล, สุรสา จันทนา. การพัฒนาความสามารถในการใช้กล้ามเนื้อมัดเล็กของเด็กปฐมวัยด้วยกิจกรรมศิลปะสร้างสรรค์. วารสารพุทธสังคมวิทยาปริทรรศน์ 2565;7:155-64.
มนัสมีน เจะโนะ, รอฮานิ เจะอาแซ. ผลของโปรแกรมการกระตุ้นพัฒนาการอย่างมีส่วนร่วมของผู้ดูแลเด็ก ในศูนย์พัฒนาเด็กเล็กต่อพัฒนาการของเด็กอายุ 2-5 ปี. วารสารวิทยบริการ [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. 2562 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 1 เม.ย. 2566];30:80-8. เข้าถึงได้จากhttps://journal.oas.psu.ac.th/index.php/asj/article/view/1406
Caterine L, Preschool learning and teaching. New York: Harper and Row; 1972.
Amineh RJ, Asl HD. Review of constructivism and social constructivism. JSSAL [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2023 Mar 15];1:9-16. Available from: https://www.academia.edu/31113252/Review_of_Constructivism_and_Social_ConstruConstru
Breckler SJ, Wiggins EC. On defining attitude and attitude theory: Once more with feeling. In Attitude structure and function. Psychology Press; 2014. P.407-27.
Inson S, Aonkam Y, Ruangrith R. Effectiveness of development promotion and reinforce positive to improve discipline programs base on family participation to children aged 3-5 years. Academic Journal of Mahasarakham ProvincialPublic Health. Office 2021;5:143-60.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Boromarajajonani College of Nursing Sunpasitthiprasong

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี สรรพสิทธิประสงค์ ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับวิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี สรรพสิทธิประสงค์ และคณาจารย์ท่านอื่นๆ ในวิทยาลัยพยาบาลฯ ความรับผิดชอบเกี่ยวกับบทความแต่ละเรื่องผู้เขียนจะรับผิดชอบของตนเอง


