THE FACTORS INFLUENCING THE INTENTION TO QUIT SMOKING AMONG MILITARY STUDENTS IN THE ROYAL THAI ARMY
Keywords:
intention to quit smoking, social support, perceived self-efficacy, attitude towards smoking cessation, military studentsAbstract
The objective of this predictive study was to investigate smoking behaviors and the factors influencing the intention to quit smoking among military cadets in the Royal Thai Army. The sample included 481 military students enrolled in educational institutions affiliated with the Royal Thai Army during the 2022 academic year, all of whom were either current smokers or had a history of smoking. Simple random sampling was used to select participants. Data were collected through an online questionnaire comprising 48 items designed to assess factors affecting the intention to quit smoking. The index of item-objective congruence (IOC) was at .67 or higher, and the Cronbach's alpha coefficient was .907. Analysis of the data involved descriptive statistics and multiple linear regression analysis using the Enter method.
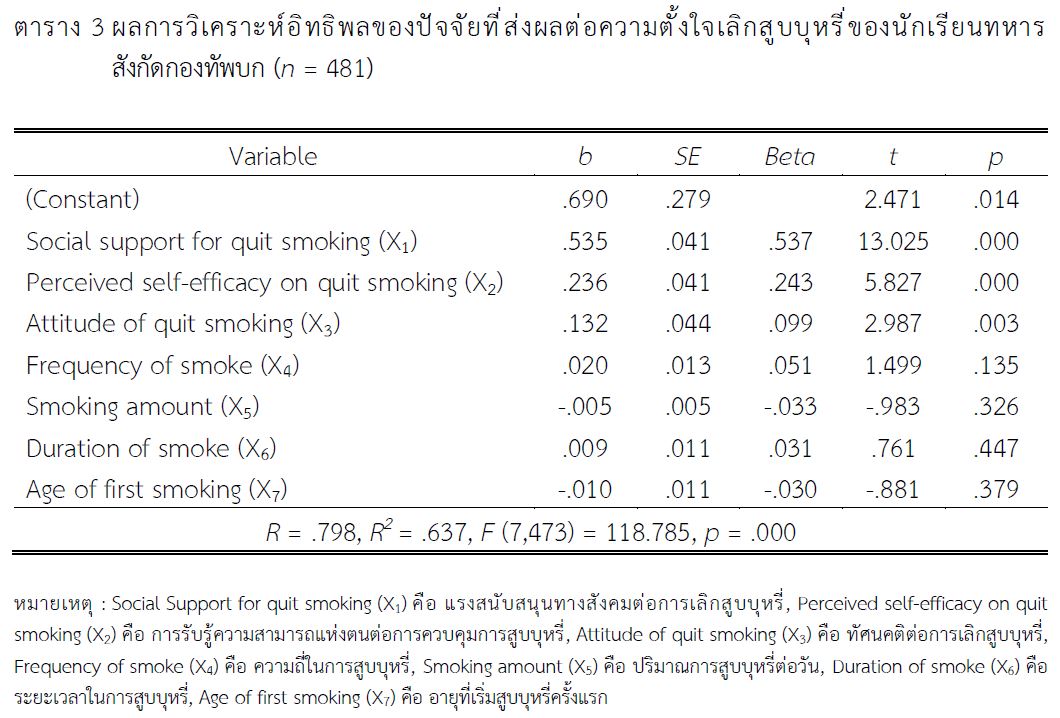
Findings revealed that 1) The respondents reported that an average age of initial smoking onset was between 16 and 18 years (49.50%, M = 17.02 years, SD = 2.38). Daily cigarette consumption ranged from 1 to 10 cigarettes (83.60%, M = 5.49 cigarettes/day, SD = 5.75), while smoking durations varied from 2 to 5 years (45.30%, M = 3.74 years, SD = 2.85). Curiosity was identified as the most common reason for smoking (45.70%). The types of cigarettes commonly used included traditional cigarettes alone (39.10%), a combination of traditional and e-cigarettes (34.30%), and solely e-cigarettes (22.90%). The majority of participants smoked on a daily basis (48.20%). Notably, military cadets exhibited high levels of awareness regarding their own attitudes and abilities, social support, and intention to quit smoking, and 2) The study found that variables such as age of first smoking, smoking quantity per day, frequency, duration, social support in smoking cessation, self-efficacy in smoking control, and attitude towards smoking cessation collectively accounted for 63.70 percent of the variance in smoking cessation intention among military cadets in the Royal Thai Army (R = .798, R2= .637, F (7,473) = 118.785, p = .000).
Recommendations include establishing smoking cessation clinics or organizing anti-smoking campaigns in schools, enhancing awareness regarding the adverse effects of e-cigarettes, and providing support resources for individuals seeking to quit smoking.
Downloads
References
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50, 179-211. https://doi.org/10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T
Boonpen, P., Mentara, P., & Boonpen, P. (2019). E-Cigarettes behavior and smoking cessation behavior of youth smoker in Higher Education Institute, Bangkok. Srinakharinwirot Research and Development (Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences), 11(22), 111-127.
Buddanoi, T., Chanaboon, S., & Kankhwao, B. (2019). Smoking behavior of secondary a casestudy of one school in Khonkean Municipality at Mung, Khonkaen. Journal of Health Science and Community Public Health, 2, 139-152.
Bunkerd, T., Keawsri, N., Authai, T., Laengtong, N., Sakhuntod, P., Ket-ngam, S., Jaiman, H., Wongsorn, A., & Chaitiang, N. (2022). Factors related to smoking behavior of people in Mae Ka Subdistrict, Phayao Province. UBRU Journal for Public Health Research, 11(1), 42–52.
Flay, B., & Petraitis, J. (1994). The theory of triadic influence: A new theory of health behavior with implications for preventive interventions. Advances in Medical Sociology, 4, 19-44.
Jinaphan, N. (2021). Factors associated with willingness to stop smoking of NCDs patients In the Sam Ngam district Phichit Province. Phichit Public Health Research And Academic Journal, 2(2), 8-19.
Kawsiso, M., Homsin, P., & Srisuriyawet, R. (2021). Predicting factors of multiple risk behaviors among male adolescents in Lopburi Province. Thai Red Cross Nursing Journal, 14(1), 140-155.
Lapyai, S. (2019). New tobacco products on social media and law enforcement on new tobacco products control. Public Health Policy and Laws Journal, 5(1), 13-29.
National Statistical Office. (2017). The smoking and drinking behavior survey 2017. Pimdeekarnpim.
Paha, K., & Prechawong, S. (2014). Attitudes, subjective norms, perceive behavioral control, and intention to quit smoking in Police Officers. Journal of The Police Nurses, 6(1), 157-169.
Parinyarux, P., Tajai, P., Chanwuthinun, A., & Ditsawanon, P. (2022). Influence of information on e-cigarette smoking behaviors and decisions. Disease Control Journal, 48(3), 539-550.
Punyakunlaset, S., Chansatitporn, N., & Vatanasomboo, P. (2019). Factors affecting level of intention to quit smoking among Police Officers in the Central Region, Thailand. Journal of Health Science, 28(6), 1029-1039.
Tobacco Control Research and Knowledge Management Center. (2021). Report on the situation of tobacco consumption in Thailand 2019. Sintaveekit.
Yangpaksee, P., Srithongphet, J., Chaiyakiat, C., Bundit, N., Chayakul, T., Eangchuan, N., . . . Kongyoo, S. (2019). Factors predicting the intention to quit smoking among military officers in Bangkok. Thai Journal of Nursing, 68(2), 9-16.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2021). WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic 2021: Addressing new and emerging products. Executive summary. Geneva.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 JOURNAL OF THE POLICE NURSES

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ผลงานที่ได้ตีพิมพ์แล้วจะเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารพยาบาลตำรวจ














