การพัฒนาระบบตอบสนองเร่งด่วนในการจัดการผู้ป่วยที่มีภาวะติดเชื้อและช็อกจากการติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือด
คำสำคัญ:
ระบบตอบสนองเร่งด่วน, ภาวะติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือด, ภาวะช็อกจากการติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือดบทคัดย่อ
การศึกษานี้เป็นการวิจัยและพัฒนา มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อพัฒนาระบบตอบสนองเร่งด่วนในการจัดการผู้ป่วยที่มีภาวะติดเชื้อและช็อกจากการติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือด โรงพยาบาลสมุทรปราการ และเปรียบเทียบผลลัพธ์ด้านบริการโรงพยาบาล ได้แก่ จำนวนวันนอน ค่ารักษาพยาบาล และอัตราการเสียชีวิตของผู้ป่วย ก่อนและหลังพัฒนาระบบตอบสนองเร่งด่วน ตัวอย่าง คือ ผู้ป่วยที่ได้รับการวินิจฉัยว่าเป็นภาวะติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือดหรือช็อกจากการติดเชื้อ
ในกระแสเลือด เข้ารับการรักษาผ่านหน่วยงานอุบัติเหตุและฉุกเฉิน โรงพยาบาลสมุทรปราการ จำนวน 134 คน เลือกตัวอย่างแบบเจาะจง แบ่งตัวอย่างออกเป็นกลุ่มควบคุม คือ ผู้ป่วยที่มีภาวะติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือดหรือช็อกจากการติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือด และได้รับการดูแลรักษา ก่อนมีระบบตอบสนองเร่งด่วนในการจัดการผู้ป่วยที่มีภาวะติดเชื้อและช็อกจากการติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือด จำนวน 67 คน และกลุ่มทดลอง คือ ผู้ป่วยที่มีภาวะติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือดหรือช็อกจากการติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือด และได้รับการดูแลรักษาผ่านระบบตอบสนองเร่งด่วนในการจัดการผู้ป่วยที่มีภาวะติดเชื้อและช็อกจากการติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือด จำนวน 67 คน เครื่องมือวิจัย ประกอบด้วย แนวทางการประเมิน คัดกรอง และการตอบสนองต่อผู้ป่วยที่มีภาวะติดเชื้อและช็อกจากการติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือด แนวปฏิบัติการจัดการผู้ป่วยที่มีภาวะติดเชื้อและช็อกจากการติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือด และแบบบันทึกข้อมูล วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลโดยใช้สถิติบรรยาย Chi-square test และ Mann-Whitney U test
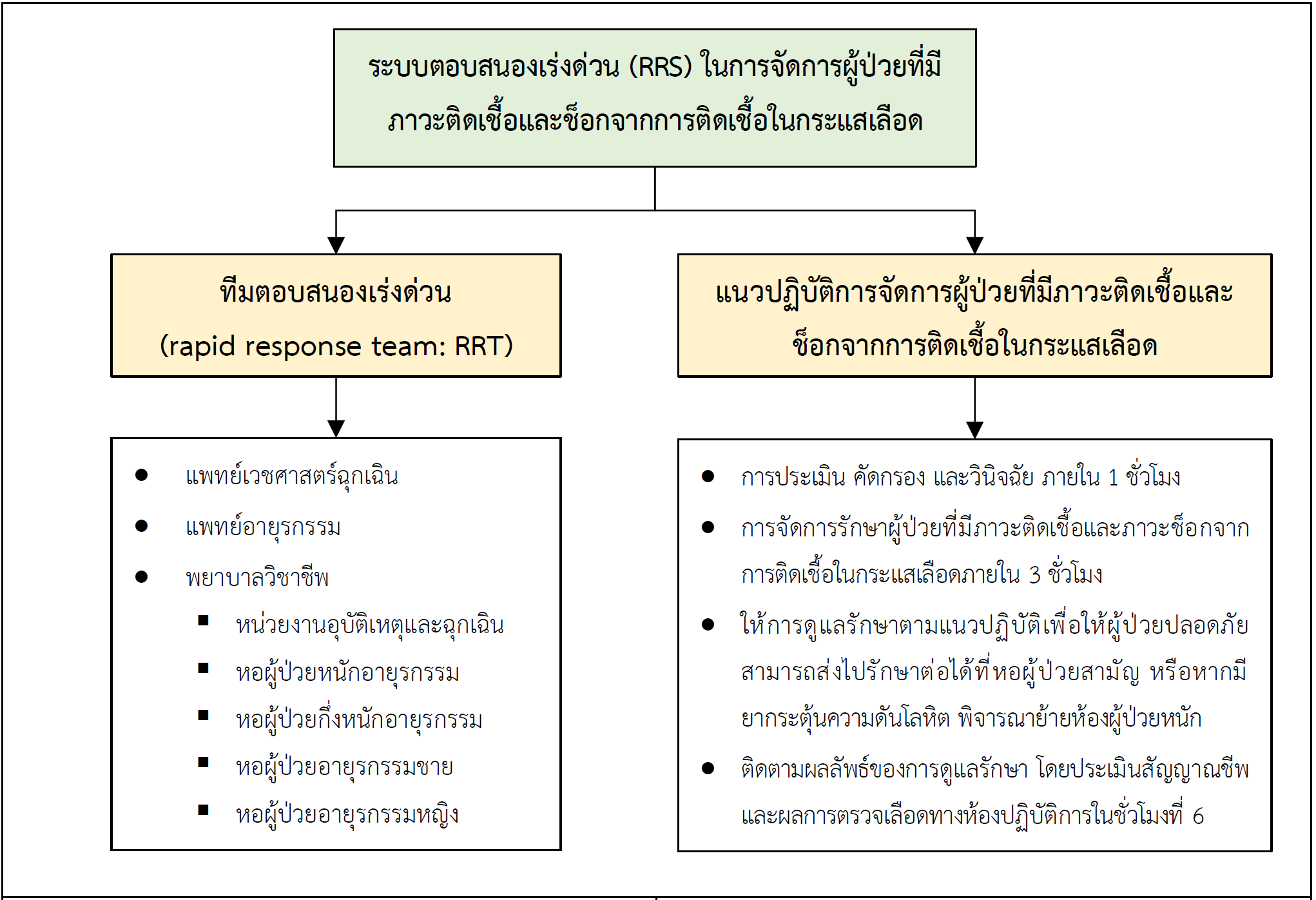
ผลการวิจัยพบว่า 1) ระบบตอบสนองเร่งด่วนในการจัดการผู้ป่วยที่มีภาวะติดเชื้อและช็อกจากการติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือด ประกอบด้วย ทีมตอบสนองเร่งด่วน และแนวปฏิบัติการจัดการผู้ป่วยที่มีภาวะติดเชื้อและช็อกจากการติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือด มีความเหมาะสมและมีความเป็นไปได้ในการนำไปใช้ทางคลินิกจนเกิดผลลัพธ์ตามที่คาดหวัง และ 2) จำนวนวันนอน ค่ารักษาพยาบาล และอัตราการเสียชีวิต ก่อนและหลังพัฒนาระบบตอบสนองเร่งด่วนในการจัดการผู้ป่วยที่มีภาวะติดเชื้อและช็อกจากการติดเชื้อในกระแสเลือด แตกต่างกันอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ .05
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Basodan, N., Al Mehmadi, A. E., Al Mehmadi, A. E., Aldawood, S. M., Hawsawi, A., Fatini, F., . . . Alzahrani, A. G. (2022). Septic shock: Management and outcomes. Cureus, 14(12), e32158.
Chawiwan, T., & Chintapanyakun, T. (2020). The effectiveness of utilization of the Ramathibodi Rapid Response system in premium wards at Somdech Phra Debaratana Medical Center. Nursing Journal of Ministry of Public Health, 30(3), 128-143.
Choi, S., Son, J., Oh, D. K., Huh, J. W., Lim, C. M., & Hong, S. B. (2021). Rapid response system improves sepsis bundle compliances and survival in hospital wards for 10 years. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(18), 4244.
Donabedian, A. (2003) An introduction to quality assurance in health care. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Dugar, S., Choudhary, C., & Duggal, A. (2020). Sepsis and septic shock: Guideline-based management. Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine, 87(1), 53–64.
Evans, L., Rhodes, A., Alhazzani, W., Antonelli, M., Coopersmith, C. M., French, C., . . . Levy, M. (2021). Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensive Care Medicine, 47(11), 1181–1247.
Fernando, S. M., Reardon, P. M., Rochwerg, B., Shapiro, N. I., Yealy, D. M., Seely, A. J. E., . . . Kyeremanteng, K. (2018). Sepsis-3 septic shock criteria and associated mortality among infected hospitalized patients assessed by a rapid response team. Chest, 154(2), 309–316.
Guirgis, F. W., Jones, L., Esma, R., Weiss, A., McCurdy, K., Ferreira, J., . . . Gray-Eurom, K. (2017). Managing sepsis: Electronic recognition, rapid response teams, and standardized care save lives. Journal of Critical Care, 40, 296–302.
Hyun, D. G., Lee, S. Y., Ahn, J. H., Huh, J. W., Hong, S. B., Koh, Y., . . . Korean Sepsis Alliance. (KSA) Investigators (2022). Mortality of patients with hospital-onset sepsis in hospitals with all-day and non-all-day rapid response teams: A prospective nationwide multicenter cohort study. Critical Care, 26(1), 280.
Institute of Medical Research & Technology Assessment. (2013). Appraisal of Guideline for Research & Evaluation II; AGREE II. Nonthaburi: Department of Medical Services, Ministry of Public Health.
Jones, D., & Ludikhuize, J. (2022). Improving outcomes from sepsis during rapid response team review. Australian Critical Care, 35(4), 332–333.
Jouffroy, R., Djossou, F., Neviere, R., Jaber, S., Vivien, B., Heming, N., & Gueye, P. (2024). The chain of survival and rehabilitation for sepsis: Concepts and proposals for healthcare trajectory optimization. Annals of Intensive Care, 14(1), 58.
Ju, T., Al-Mashat, M., Rivas, L., & Sarani, B. (2018). Sepsis rapid response teams. Critical Care Clinics, 34(2), 253–258.
Khanina, A., Cairns, K. A., McGloughlin, S., Orosz, J., Bingham, G., Dooley, M., & Cheng, A. C. (2020). Improving sepsis care for hospital inpatients using existing medical emergency response systems. Infection, Disease & Health, 25(2), 63–70.
Meyers, C. V., & Brandt. W. C. (2015). Implementation fidelity in education research: Designer and evaluator considerations. New York, NY: Routledge.
Public Health Strategies of the Ministry of Public Health. (2023). Public Health Statistics A.D. 2022. Nonthaburi: Ministry of Public Health.
Salvatierra, G. G., Bindler, R. C., & Daratha, K. B. (2016). Rapid response teams: Is it time to reframe the questions of rapid response team measurement? Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 48(6), 616-623.
Schramko, L., Paterson, T., & Anstey, M. H. (2022). Duration and management of sepsis-associated hypotension at rapid response team call-outs to patients subsequently admitted to the intensive care unit: A case series. Australian Critical Care, 35(4), 450–453.
Semanco, M., Wright, S., & Rich, R. L. (2022). Improving initial sepsis management through a nurse-driven Rapid Response Team protocol. Critical Care Nurse, 42(5), 51–57.
Singer, M., Deutschman, C. S., Seymour, C. W., Shankar-Hari, M., Annane, D., Bauer, M., . . . Angus, D. C. (2016). The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA, 315(8), 801–810.
Soukup S. M. (2000). The Center for advanced nursing practice evidence-based practice model: promoting the scholarship of practice. The Nursing Clinics of North America, 35(2), 301–309.
Sprogis, S. K., Currey, J., Jones, D., & Considine, J. (2021). Use of the pre-medical emergency team tier of rapid response systems: A scoping Review. Intensive & Critical Care Nursing, 65, 103041.
Sriwilai, W. (2024). Emergency nursing care for patients with septic shock. Journal of The Police Nurses and Health Science, 16(1), 237–249.
Thompson, K., Venkatesh, B., & Finfer, S. (2019). Sepsis and septic shock: Current approaches to management. Internal Medicine Journal, 49(2), 160–170.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 วารสารพยาบาลตำรวจและวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ผลงานที่ได้ตีพิมพ์แล้วจะเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารพยาบาลตำรวจ














