ผลของโปรแกรมการทรงตัวขณะเคลื่อนไหวโดยใช้ Magic Animal Way ต่อการทรงตัวของเด็กวัยเรียนที่มีความบกพร่องด้านร่างกาย
คำสำคัญ:
เด็กวัยเรียน, ความบกพร่องทางร่างกาย, การทรงตัวขณะเคลื่อนไหว, Magic Animal Wayบทคัดย่อ
การวิจัยครั้งนี้เป็นการวิจัยกึ่งทดลอง แบบกลุ่มเดียววัดก่อนและหลังการทดลอง มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อเปรียบเทียบผลของโปรแกรมการทรงตัวขณะเคลื่อนไหวโดยใช้ Magic Animal Way ต่อการทรงตัวของเด็กวัยเรียนที่มีความบกพร่องด้านร่างกาย ตัวอย่างเป็นเด็กวัยเรียนที่มีความบกพร่องด้านร่างกายในด้านการทรงตัวขณะเคลื่อนไหวของโรงเรียนศึกษาพิเศษชัยนาท อำเภอเมือง จังหวัดชัยนาท จำนวน 20 คน คัดเลือกแบบเฉพาะเจาะจงตามเกณฑ์คุณสมบัติที่กำหนด เครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการวิจัย คือ 1) โปรแกรมการทรงตัวขณะเคลื่อนไหวโดยใช้ Magic Animal Way มีค่าดัชนีความตรงเชิงเนื้อหาอยู่ระหว่าง .94 - .98 และ 2) แบบประเมินการทรงตัว Pediatric balance scale (PBS) ซึ่งมีค่าสัมประสิทธิ์แอลฟาของครอนบาคเท่ากับ .72 วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลด้วยสถิติบรรยาย และเปรียบเทียบคะแนนเฉลี่ยการทรงตัวก่อนและหลังเข้าร่วมโปรแกรมด้วยสถิติ t-test แบบ Dependent
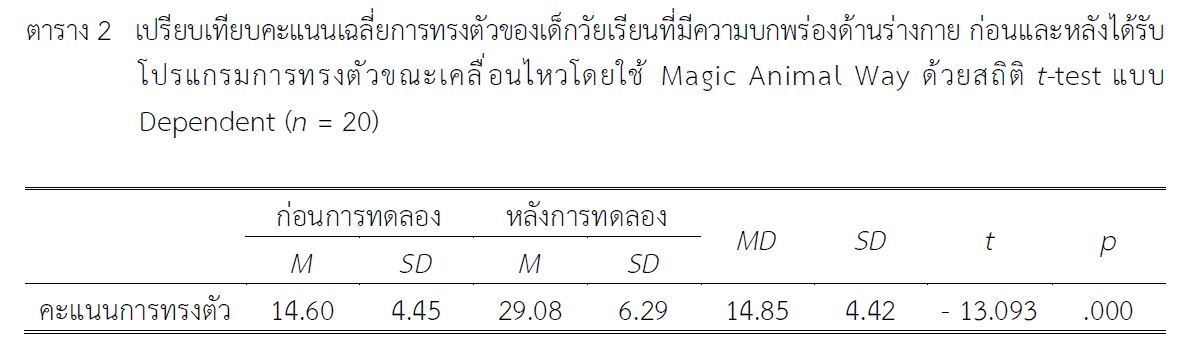
ผลการศึกษาพบว่า เด็กวัยเรียนที่มีความบกพร่องด้านร่างกายหลังได้รับโปรแกรมการทรงตัวขณะเคลื่อนไหวโดยใช้ Magic Animal Way มีคะแนนเฉลี่ยการทรงตัวสูงกว่าก่อนได้รับโปรแกรม อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ .05 (M = 29.08, SD = 6.29 และ M = 14.60, SD = 4.45 ตามลำดับ, t = - 13.093, p = .000) การวิจัยนี้จึงเสนอแนะว่า ควรนำโปรแกรมนี้ไปประยุกต์ใช้ในการฝึกการทรงตัวของเด็กวัยเรียนที่มีความบกพร่องด้านร่างกาย จะช่วยให้การทรงตัวขณะเคลื่อนไหวดีขึ้น และสามารถช่วยเหลือตนเองได้มากขึ้น
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Bhattacherjee, A. (2012). Social science research: Principles, methods, and practices. Textbooks Collection 3. Retrieved from https://digitalcommons.usf.edu/ oa_textbooks/3
Charoensuksiri, K., Danwong, W., Srijumpa, S., & Unchuen, R. (2022). Balance, the ability to stand up from a sitting position and the ability to walk, in children with cerebral palsy, at the Nonthaburi Special Education Center and Maha Chakri Sirindhorn Nakhonnayok Special Education Center. BJM, 9(2), 49-60.
Chayuthi, K. (2020). The development of large muscle skills by using a spin bike balance training in balance of children with physical disabilities or movement or health in preparatory classroom 6 of Special Education Center, Ranong Province.
Department of Empowerment of person with Dissabilities. (2023). Situation of people with disabilities in Thailand. Retrieved from https://dep.go.th/th/law-academic/knowledge-base/disabled-person-situation
Franjoine, M. R., Gunther, J. S., & Taylor, M. J. (2003). Pediatric balance scale: a modified version of the berg balance scale for the school-age child with mild to moderate motor impairment. Pediatric Physical Therapy, 15, 114-128.
Ingpoo, P. (2022). The Developmental patterns of parents of children with movement disabilities special education center Roi Kaen Sarasin Province (Doctor of Educational Management). Rajabhat Maha Sarakham University, Maha Sarakham.
Kittikanampol, T. (2017). The Study of physical development needs of Special Child at Special Education Center, (Northern, Southern and Northeastern) to develop the Therapeutic Sculpture for Special child. Art Pritas Journal, Faculty of Fine and Applied Arts, 11(2), 94-105.
Panme, P., Taechaboonsermsak, P., Nanthamongkochai, S., Pitikultang, S., & Munsawaengsub, C. (2016). Factors influencing quality of life among disabled people in Nakhon Pathom province. Journal of Public Health, 46(2), 141-152.
Phongniran, K. (2020). A study on gross motor ability of down syndrome children by using role playing activities. Lawarath Social E-Journal, 2(1), 55-64.
Sangkarit, N., Tapanya, W., Kumfu, S., Prangkeaw, P., & Arma, A. (2019). Correlation of segmental of trunk control and functional balance in children with inadequate trunk control. Thai Journal Physical Therapy, 41(1), 1-15.
Sanpet, A., Thustaro, C., & Boonrat, A. (2023). Effects of exercise program and 3R technique to increase Muscle power and Balance of Children with Intellectual Disabilities. Al-Hikmah Journal FTU, 13(25), 37-49.
Schmidt, R. A., & Lee, T. (2011). Motor control and learning: A behavioral emphasis. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
Thailand Development Research Institute (TDRI) & UNICEF Thailand. (2022). Services for children with disabilities in Thailand: Situation, challenges, and ways forward. Retrieved from https://www. unicef.org/thailand/media/12116/file/Services%20for%20Children%20with%20Disabilities%20in%20Thailand%20EN.pdf
Umphred, D. A., Lazaro, R. T., Roller, M., & Burton, G. (2013). Neurological rehabilitation. St. Louis, Missouri: Elsevier Mosby.
Youyen, M. (2022). Effect of nine squares training with music on balance and agility of children with special needs: Integration learning. Academic Journal of Thailand National Sports University, 14(3), 241-252.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 วารสารพยาบาลตำรวจและวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ผลงานที่ได้ตีพิมพ์แล้วจะเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารพยาบาลตำรวจ














