ความชุกของภาวะสมองเสื่อม ความพร้อมและแนวทางการเตรียมความพร้อมของญาติในการดูแลผู้ป่วยสมองเสื่อม จังหวัดนนทบุรี
คำสำคัญ:
ความชุกของโรค, ความพร้อมของญาติ, ผู้ป่วยสมองเสื่อมบทคัดย่อ
การวิจัยนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษา 1) ความชุกของภาวะสมองเสื่อม และ 2) ความพร้อมและแนวทางการเตรียมความพร้อมของญาติในการดูแลผู้ป่วยสมองเสื่อมจังหวัดนนทบุรี ตัวอย่างและผู้ให้ข้อมูล แบ่งออกเป็น 2 กลุ่ม ได้แก่ 1) ตัวอย่างในการศึกษาความชุกของภาวะสมองเสื่อม เป็นผู้ที่มีอายุ 60 ปีขึ้นไป ในจังหวัดนนทบุรี จำนวน 400 คน ได้มาโดยการสุ่มแบบแบ่งชั้น 2) ผู้ให้ข้อมูลแนวทางการเตรียมความพร้อมของญาติในการดูแลผู้ป่วยสมองเสื่อม ได้แก่ ญาติของผู้ที่มีความเสี่ยงต่อภาวะสมองเสื่อมที่พบในการศึกษาความชุกของภาวะสมองเสื่อม จำนวน 13 คน และบุคลากรทีมสุขภาพที่ดูแลรักษาผู้ป่วยภาวะสมองเสื่อม จำนวน 5 คน เครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการวิจัยได้แก่ 1) แบบทดสอบสภาพสมองเบื้องต้น (MMSE) 2) แบบประเมินโมคา (MoCA) 3) ประเด็นสนทนากลุ่ม และ 4) แบบสอบถามความพร้อมของญาติในการดูแลผู้ป่วยโรคสมองเสื่อมซึ่งมีค่าความเที่ยงเท่ากับ .83 การวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลใช้ความถี่ ร้อยละ ค่าเฉลี่ย ส่วนเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐาน และการวิเคราะห์เนื้อหา
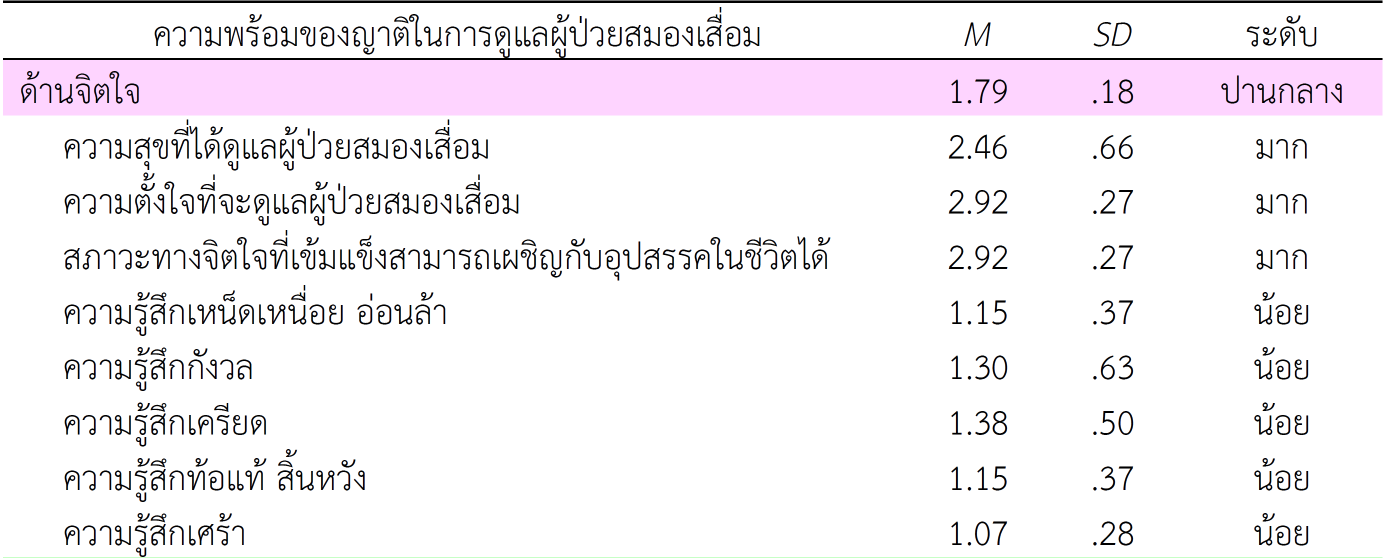
ผลการวิจัยพบว่า 1) ความชุกของภาวะสมองเสื่อมในจังหวัดนนทบุรีมีร้อยละ 3.25 ส่วนใหญ่พบในเพศหญิง โดยพื้นที่อำเภอเมืองนนทบุรีมีความชุกมากที่สุด ร้อยละ 1.50 และไม่พบผู้ป่วยภาวะสมองเสื่อมเลยในพื้นที่อำเภอบางใหญ่ 2) ความพร้อมของญาติในภาพรวมอยู่ในระดับปานกลาง โดยความพร้อมด้านร่างกายมีค่าเฉลี่ยสูงสุด และด้านข้อมูลข่าวสารและแหล่งช่วยเหลือมีค่าเฉลี่ยน้อยที่สุด 3) แนวทางการเตรียมความพร้อมของญาติในการดูแลผู้ป่วยสมองเสื่อมมีดังนี้ 1) ทีมสุขภาพที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการดูแลผู้ป่วยสมองเสื่อมควรให้ความรู้และสร้างความเข้าใจแก่ญาติ เกี่ยวกับอาการของผู้ป่วยภาวะสมองเสื่อมและวิธีการดูแลรักษาอย่างถูกต้อง 2) ญาติผู้ดูแลจำเป็นต้องมีสภาพร่างกายที่แข็งแรงและสมบูรณ์ มีสุขภาพจิตดี ยอมรับกับสภาพอาการของผู้ป่วยที่เปลี่ยนแปลงได้ตลอดเวลา และมีความพร้อมด้านการเงิน ส่วนข้อมูลการดูแลผู้สูงอายุสมองเสื่อมเพิ่มเติม ได้แก่ การบริหารจัดการเวลาในการดูแล ความพร้อมด้านสถานที่ วัสดุ และอุปกรณ์ บุคลากรทีมสุขภาพจะต้องมีความรู้และทักษะการใช้แบบคัดกรองภาวะสมองเสื่อม มีสายด่วนให้คำปรึกษาสำหรับการดูแลผู้ป่วยภาวะสมองเสื่อมโดยเฉพาะ มีการจัดตั้งคลินิกเฉพาะทาง หน่วยงานที่เกี่ยวข้องต้องร่วมกันบูรณาการนโยบายการดูแลผู้ป่วยสมองเสื่อม และเพิ่มช่องทางการเข้าถึงบริการดูแลรักษาที่ได้มาตรฐาน
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Anundilokrit, P. (2021). Dementia. Regional Health Promotion Center 9 Journal, 15(37), 392-398.
Kamsuan, B. (2011). Prevalence of dementia risk and factors affecting risk on occurrence to dementia of the elderly in Numrat sub-district, Nong Muang Khai district, Phrae province (Master public health program). Graduate School, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai.
Hiransaroj, B., Wirojratana, V., Vongsirimas, N., & Senanarong, V. (2020). Factors Influencing depressive symptoms in caregivers of older adults with dementia. Journal of Thailand Nursing and Midwifery Council, 35(2), 85-98.
Mangmee, S., Monkong, S., & Sutti, N. (2021). Relationships between mutuality, preparedness, and predictability to care, and caregiver role strain from caregiving activities for older people with dementia. The Journal of Thailand Nursing and Midwifery Council, 36(3), 151-164.
Panakorn, L., Nanthamongkolchai, S., Pitikultung, S., Munsawaengsub, C., & Teachaboonsermsak, P. (2015). Factors influencing dementia in elderly women in Lumphun province. Journal of Public Health, 45(2), 197-208.
Pibarnwong, P., Juntaparuk, C., Pangsuk, P., Pinyo, P., Talordpong, P., & Hamchanan, H. (2018). A study of dementia and factors associated with dementia among elderly in North East, Thailand. Journal of Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Surin, 8(2), 46-57.
Saipanya, A. (2022). Prevalence and factors associated with dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) among elderly in Na-Mafuang subdistrict, Amphur Muang, Nongbua Lamphu province. Udonthani Hospital Medical Journal, 30(3), 376-386.
Silpa-anan, D. (2014). Prevalence of dementia in the elderly in Bangkruay hospital. Journal of Medical and Public Health Aging, 4(4), 1-5.
Siritipakorn, P. (2015). Nursing manual for caring and preparing readiness of relatives and caregivers for dementia elderly. Bangkok: Department of Nursing Siriraj Hospital, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University.
Suwan, A., & Trakulsithichoke, S. (2016). Prevalence and factors associated with dementia among elderly in Lukhok subdistrict, Muang district, Pathumtani province. APHEIT Journals, 5(2), 21-32.
World Health Organization. (2023). Dementia. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/ detail/dementia
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 วารสารพยาบาลตำรวจและวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ผลงานที่ได้ตีพิมพ์แล้วจะเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารพยาบาลตำรวจ














