เด็กวัยเรียนกับความกลัวและโรคกลัว
คำสำคัญ:
เด็กวัยเรียน, ความกลัว, โรคกลัว, พยาบาลเด็ก, การควบคุมพฤติกรรมบทคัดย่อ
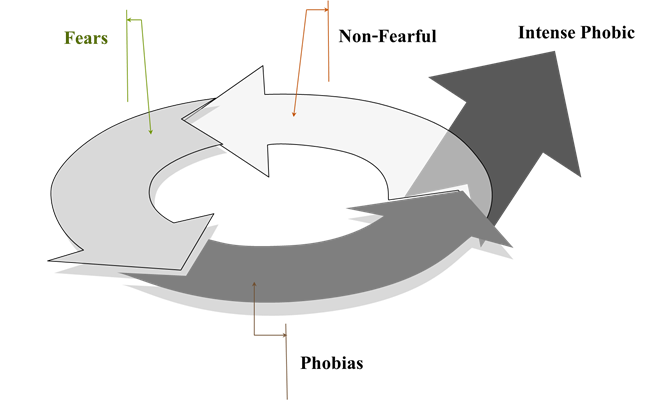
ความกลัวในเด็กวัยเรียนเกิดจากหลายสาเหตุที่ชัดเจนแตกต่างกันขึ้นอยู่กับประสบการณ์อันไม่พึงประสงค์ ในวัยเด็กของแต่ละคน แต่ก็มีบางคนกลัวโดยที่ไม่มีเหตุผล บางคนมีความกลัวเกิดขึ้นแล้วหากไม่ได้รับการดูแลหรือแก้ปัญหาให้ถูกต้องทั้งวิธีการและช่วงเวลาที่เหมาะสม ความกลัวอาจจะมีระดับความรุนแรงเพิ่มมากขึ้นเรื่อย ๆ จนกลายเป็นโรคกลัวที่ยากแก่การดูแลรักษา อย่างไรก็ตามอาการบ่งชี้ระดับความรุนแรงของโรคกลัว แต่ละประเภทที่เกิดขึ้นกับเด็กวัยเรียนน่าจะเป็นแนวทางช่วยให้ผู้เกี่ยวข้องสามารถวิเคราะห์หาทางป้องกัน และดูแลเด็กวัยเรียนกลุ่มดังกล่าวให้ลดกลัวได้เร็วขึ้น บทความนี้จึงมีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อนำเสนอสาเหตุและ
ระดับความรุนแรงของความกลัว สัญญาณบ่งชี้ความกลัวและโรคกลัว เพื่อให้บุคคลที่เกี่ยวข้องและพยาบาลเด็ก ได้เข้าใจถึงสาเหตุและวิธีการป้องกันความกลัวและโรคกลัวของเด็กกลุ่มนี้ได้ซึ่งการดูแลสุขภาพเด็กแบบ องค์รวมของพยาบาลจะช่วยให้เข้าใจถึงสาเหตุระดับความรุนแรงของความกลัวและแนวทางแก้ไขได้โดยการ บันทึกประวัติการเจ็บป่วย ใช้ข้อมูลสร้างเสริมจินตนาการทางบวก และสุดท้ายติดตามผลการดูแลอย่างมี ส่วนร่วมต่อเนื่อง เพื่อควบคุมพฤติกรรมไม่ให้เด็กวัยเรียนเป็นโรคกลัวที่รุนแรงขึ้น
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Susan O. Growth and development of the school-aged child. Pediatric Nursing Philadephia: W.B. Saunders; 2002.
Taylor S. Anxiety Sensitivity: Theory, Research, and treatment of the fear of anxiety.New York: University of British Columbia; 2014.
Carleton RN. McCreary RD, Norton PJ, Asmundson GJG. Brief Fear of negative evaluation scale-revised. The Official Journal of ADAA [Online] 2016 [cited 10 September 2020]; 23(5):297-303. Available from:https://doi.org /10.1002/da.20142
Khorsuk C, Anusornteerakul S. Nursing care to reduce fear of childbirth. Journal of Nursing Science & Health 2017; 40(3): 160-70. (in Thai)
Lang PJ, Davis M, Öhman A. Fear and anxiety: animal models and human cognitive psychophysiology [Online] 2000 [cited 10 September 2018];61(3):137–59. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0327(00)00343-8
Ohman A, Mineka S. Fears, phobias, and preparedness: Toward an evolved module of fear and fear learning. Psychological Review 2001; 108(3): 483-522. doi:10.1037//0033-295X. 108.3.483
John R, James D. Anxiety disorders a pocket guide for primary care. West Virginia University: Morgantown, WV; 2008.
Joseph EL, Daniel SP. Using neuroscience to help understand fear and anxiety: A two-system framework. [Online] 2016 [cited 10 September 2020];173(11): 1083-93. Available from:https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp. 2016.16030353
Teachman B, Woody SR. Automatic processing in spider phobia: Implicit fear associations over the course of treatment. Journal of Abnormal Psychology 2003;112(1):100–9. doi:10.1037/0021-843X.112.1.100
Askew C, Reynolds G, Field AP. The prevention and reversal of vicarious learning of fear in children aged 6 - 11 years in: BPS developmental section & social section psychology annual conference 2015; 2015-09-09-2015-09-11, Manchester, UK;2015.
Hockenberry MJ, Wilson D, Wong DL. Wong, s essentials of pediatric nursing 9th ed. St. Louis: Elsevier/Mosby, 2013.
Antonio D, Carvalho B. The nature of feelings: Evolutionary and neurobiological origins. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2013;14:143–52.
Custers K, Van den Bulck J. Fear effects by the media. European Journal of Pediatrics [Internet] 2012 Apr [cited 2020 Sep 28];171(4):613–6. Available from: http://search. ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=rzh& AN=104399639&site=ehost-live
Hockenberry M. Wilson D. Wong’s nursing care of infants and children, department of pediatrics baylor college of medicine; Nurse Scientist, Texas Children’s Hospital, Texas; 2014.
MuksingW, Tohyusoh N,Punriddum J.Factors related to health care behavior among school childrenin NakhonSi ThammaratMunicipality. The Southern College Network Journal of NursingandPublic Health 2016;3(3):65-75. (in Thai)
Wonginchan A. Fear of school-age children with onlinemediain Thailand 4.0.Journal of Nursing Science & Health 2018; 41(4):145-54. (in Thai)
Reynolds G, Field AP, Askew C. Preventing the development of observationally learnt fears in children by devaluing the model’s negative response. J Abnorm Child Psychol 2015; 43(7):1355–67. doi: 10.1007/ s10802-015-0004-0
Pillitteri A. Maternal & child health nursing: Care of the childbearing & childrearing family. Philadelphia:WoltersKluwerHealth/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2014.
Schaefer HS, Larson LC, Davidson RJ, Coan JA. Brain, body, and cognition: Neural, physiological and self-report correlates of phobic and normative fear. Biol Psychol 2014; 98(Apr): 59-69. doi:10.1016/j.bi opsycho.2013.12.011
Marks IM. Fears and phobias. New York: AcademicPress, Inc, 111 fifth Avenue; 1969.
Olick RS. Ethics in public health carcinogenic plumes and aerophobia: Ethical tensions in the public smoking debate. J Public Health ManagementPractice 2004; 10(6): 569-70.
Emmelkamp PMG, Krijn M, Hulsbosch AM, De VS, Schuemie MJ, Van der Mast CAPG, et al. Virtual reality treatment versus exposure in vivo: A comparative evaluation in acrophobia. Behaviour Research and Therapy 2002; 40: 509–16.
Eshed I, Althoff CE, Hamm B, Hermann KGA. Claustrophobia and premature termina tion of magnetic resonance imaging examinations. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2007;26:401–4.
Nevin MERT. Fear culture II. International Journal of Learning & Development 2012;2(2):31-9.
Ahmed MS. School phobia and Its consequences on school children: The Way Forward. Journal of Sociology, Psychology and Anthropology inPractice 2015;7(3):46-56.
Craske MG, Simos G. Panic disorder and agoraphobia. In, Simos G, Hofmann SG, editors. CBT forAnxietyDisorders:APractitionerBook. 1st ed. West Succex, Wiley-Blacwell.; 2013.
Laas A. Combating bullying in schools: A South African legal perspective. Pretoria: Faculty of Law, University of Pretoria; 2012.
Heitmann AJ. Reviews: ‘Republic of drivers: A cultural history of automobility in America and autophobia: Love and hate in the automo tive age, University of Dayton 2010;115(1): 254-6.
YildirimC, CorreiaA. Exploringthedimensions of nomophobia: Development and validation of a self-reported questionnaire. Computers in Human Behavior, journal homepage [Internet] 2015 Apr [cited 2020 Sep 28];49:130-7. Available from: http://www.elsevier.com/ locate/comphumbeh
Heimberg RG, Dodge CS, Hope DA, Kennery CR, Zollo LJ. Cognitive-behavioral group treatment for social phobia: Comparison with a credible placebo control. Cognitive Therapy and Research 1990; 14:1-13.
Heimberg RG, Juster HR. Treatment of social phobia in cognitive-behavioral groups. JournalofClinicalPsychiatry 1994;55:38-46.
Davidson JRT. International advances in the treatment of social phobia. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1994;55:123-9.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
วารสารพยาบาลศาสตร์และสุขภาพเป็นเจ้าของลิขสิทธิ์ในการเผยแพร่ผลงานที่ตีพิมพ์ห้ามผู้ใดนำบทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารพยาบาลศาสตร์และสุขภาพไปเผยแพร่ในลักษณะต่าง ๆ ดังนี้ การนำบทความไปเผยแพร่ออนไลน์ การถ่ายเอกสารบทความเพื่อกิจกรรมที่ไม่ใช่การเรียนการสอน การส่งบทความไปตีพิมพ์เผยแพร่ที่อื่น ยกเว้นเสียแต่ได้รับอนุญาตจากวารสารพยาบาลศาสตร์และสุขภาพ


