Gadolinium-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: A 10-Year Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: In studies conducted in Europe and the United States, gadolinium-associated acute kidney injury (GA-AKI) has been reported in high-risk patients after receiving gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs). Currently, there is no data available on Asian populations to confirm these findings.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study of chronic kidney disease patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≤ 60 ml/min/1.73m2 who received GBCAs from 2013 to 2023 at a tertiary care hospital. The outcomes were the incidence of GA-AKI and the associated risk factors.
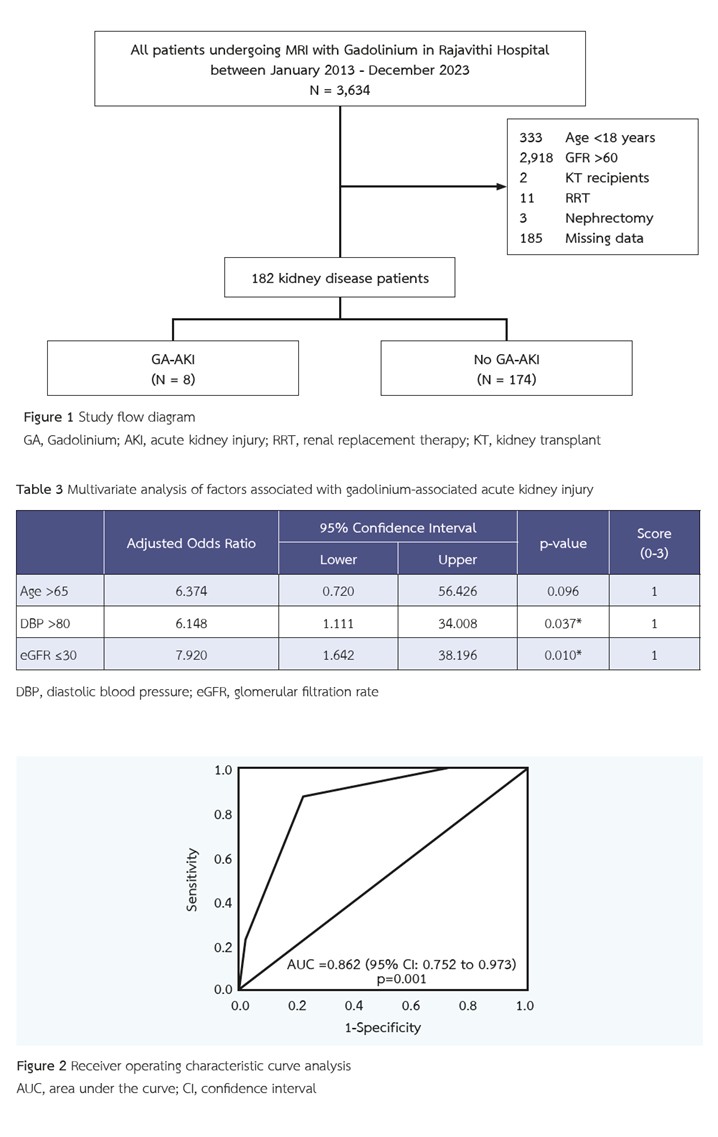
Results: Among the 182 patients, the incidence of GA-AKI was 4.4%. Although the GA-AKI group had significantly higher age (> 65 years) (OR 6.374; 95% CI 0.720-56.426, p=0.096), diastolic blood pressure > 80 (OR 6.148; 95% CI 1.111-34.008, p=0.037) and eGFR ≤30 ml/min/1.73m2 (OR 7.920; 95% CI 1.642-38.196, p=0.010). The ROC curve analysis for predicting GA-AKI scored 2 out of 3, with a sensitivity of 87.5% and a specificity of 78.2%.
Conclusions: The incidence of GA-AKI was low. The associated factors included older age, higher diastolic blood pressure, and eGFR ≤ 30 ml/min/1.73m2.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This article is published under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, which allows for non-commercial reuse of the published paper as long as the published paper is fully attributed. Anyone can share (copy and redistribute) the material in any medium or format without having to ask permission from the author or the Nephrology Society of Thailand.
References
Mathur M, Jones JR, Weinreb JC. Gadolinium Deposition and Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: A Radiologist’s Primer. Radiographics 2020;40(1):153–62. doi: 10.1148/rg.2020190110.
Thomsen HS, Stacul FS, Bellin MB, Bongartz G, Brismar T, Clement O, et al. ESUR Guidelines on Contrast Agents, European Society of Urogenital Radiology. European Journal of Radiology. 2018.
Carolyn W, Asch D, Bashir MSR, Callahan MJ, Dillman J, Ellis J, et al. ACR Manual On Contrast Media. American College of Radiology. 2024.
Niendorf HP, Haustein J, Cornelius I, Alhassan A, Clauss W. Safety of gadolinium-DTPA: extended clinical experience. Magn Reson Med 1991;22(2):222–8; discussion 9–32. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910220212.
Arsenault TM, King BF, Marsh JW, Jr., Goodman JA, Weaver AL, Wood CP, et al. Systemic gadolinium toxicity in patients with renal insufficiency and renal failure: retrospective analysis of an initial experience. Mayo Clin Proc 1996;71(12):1150–4. doi: 10.4065/71.12.1150.
Prince MR, Arnoldus C, Frisoli JK. Nephrotoxicity of high-dose gadolinium compared with iodinated contrast. J Magn Reson Imaging 1996;6(1):162–6. doi: 10.1002/jmri.1880060129.
Swan SK, Lambrecht LJ, Townsend R, Davies BE, McCloud S, Parker JR, et al. Safety and pharmacokinetic profile of gadobenate dimeglumine in subjects with renal impairment. Invest Radiol 1999;34(7):443–8. doi: 10.1097/00004424-199907000-00001.
Eckardt KU, Kasiske B, Wheeler D, Uhlig K, Miskulin D, et al. KDIGO 2012 Clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2012;3:1-150.
Enderlein G. Daniel, Wayne W.: Biostatistics — A Foundations for Analysis in the Health Sciences. Wiley & Sons, New York—Chichester—Brisbane—Toronto—Singapore, 6th ed. 1995, 780 S., £58.—, ISBN 0–471–58852-0 (cloth). Biometrical Journal 2007;37(6):744–. doi: 10.1002/bimj.4710370610.
Rieger J, Sitter T, Toepfer M, Linsenmaier U, Pfeifer KJ, Schiffl H. Gadolinium as an alternative contrast agent for diagnostic and interventional angiographic procedures in patients with impaired renal function. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2002;17(5):824–8. doi: 10.1093/ndt/17.5.824.
Briguori C, Colombo A, Airoldi F, Melzi G, Michev I, Carlino M, et al. Gadolinium-based contrast agents and nephrotoxicity in patients undergoing coronary artery procedures. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 2006;67(2):175–80. doi: 10.1002/ccd.20592.
Sam AD, 2nd, Morasch MD, Collins J, Song G, Chen R, Pereles FS. Safety of gadolinium contrast angiography in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. J Vasc Surg 2003;38(2):313–8. doi: 10.1016/s0741-5214(03)00315-x.
Ergun I, Keven K, Uruc I, Ekmekci Y, Canbakan B, Erden I, et al. The safety of gadolinium in patients with stage 3 and 4 renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006;21(3):697–700. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfi304.
Takahashi EA, Kallmes DF, Mara KC, Harmsen WS, Misra S. Nephrotoxicity of gadolinium-based contrast in the setting of renal artery intervention: retrospective analysis with 10-year follow-up. Diagn Interv Radiol 2018;24(6):378–84. doi: 10.5152/dir.2018.18172.
Do C, DeAguero J, Brearley A, Trejo X, Howard T, Escobar GP, et al. Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent Use, Their Safety, and Practice Evolution. Kidney360 2020;1(6):561–8. doi: 10.34067/kid.0000272019.