Predictors and Outcomes of Erythrocytosis After Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Current evidence suggests that treatment with sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) may increase hemoglobin levels. An increase in hemoglobin may be beneficial in improving cardiovascular and renal outcomes. This study examined changes in hemoglobin, the prevalence, and predictors of erythrocytosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who received SGLT2i. The associations between erythrocytosis with cardiovascular events and renal outcomes were also investigated.
Methods: This retrospective study was conducted in patients with T2DM who received SGLT2i for at least 3 consecutive months between January 2020 and December 2022. Hemoglobin and hematocrit were collected at baseline and after 3-12 months of SGLT2i treatment until the end of the study. Erythrocytosis was defined as an increase in hemoglobin level ≥2 gm/dL from baseline during the study period.
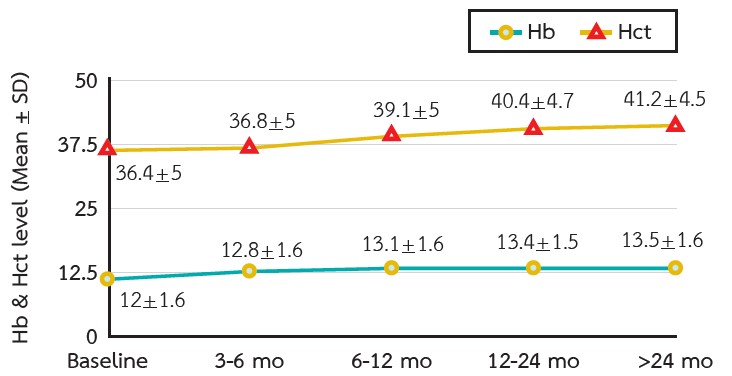
Results: Three hundred thirty-six patients were included in the study. The prevalence of erythrocytosis was 125 patients (37.2 %). The hemoglobin levels increased over time with median differences from baseline of 0.7, 1, 1.3, and 1.5 gm/dL at 3, 6, 12, and >24 months, respectively. The predictors of erythrocytosis were age >60 years, chronic kidney disease, using thiazide and beta-blockers, lower hemoglobin, and estimated glomerular filtration rate at baseline. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes were not different between the erythrocytosis and non-erythrocytosis groups.
Conclusion: A gradual increase in hemoglobin levels was observed in patients with T2DM after SGLT2i treatment. Erythrocytosis was common but was not associated with adverse cardiovascular events or renal outcomes.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This article is published under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, which allows for non-commercial reuse of the published paper as long as the published paper is fully attributed. Anyone can share (copy and redistribute) the material in any medium or format without having to ask permission from the author or the Nephrology Society of Thailand.
References
Vejakama P, Ingsathit A, Attia J, Thakkinstian A. Epidemiological Study of Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: A Large-Scale Population-Based Cohort Study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(4):e475.
Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, et al. Effects of Losartan on Renal and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(12):861–9.
Rodby RA, Rohde RD, Clarke WR, Hunsicker LG, Anzalone DA, Atkins RC, et al. The Irbesartan Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Trial: study design and baseline patient characteristics. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000;15(4):487–97.
Cheungpasitporn W, Thongprayoon C, Chiasakul T, Korpaisarn S, Erickson SB. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors linked to anemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. QJM. 2015;108(11):879–84.
Kendrick J, Chonchol MB. Nontraditional risk factors for cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2008;4(12):672–81.
Washburn WN, Poucher SM. Differentiating sodiumglucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors in development for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013;22(4):463-86.
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(22):2117–28.
The EMPA-KIDNEY Collaborative Group, Herrington WG, Staplin N, Wanner C, Green JB, Hauske SJ, et al. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(2):117–27.
Heerspink HJL, Stefánsson BV, Correa-Rotter R, Chertow GM, Greene T, Hou FF, et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(15):1436–46.
Rossing P, Caramori ML, Chan JCN, Heerspink HJL, Hurst C, Khunti K, et al. KDIGO 2022 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2022;102(5S):S1-S127.
American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022 Abridged for Primary Care Providers. Clin Diabetes. 2022;40(1):10–38.
Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):347–57.
Wang X, Fu R, Liu H, Ma Y, Qiu X, Dong Z. The effects of sodium glucose co-transporter (SGLT) 2 inhibitors on hematocrit levels: a systematic review and metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Palliat Med. 2021;10(6):6467-81.
Levin A, Thompson CR, Ethier J, Carlisle EJ, Tobe S, Mendelssohn D, et al. Left ventricular mass index increase in early renal disease: impact of decline in hemoglobin. Am J Kidney Dis. 1999;34(1):125–34.
Marathias KP, Lambadiari VA, Markakis KP, Vlahakos VD, Bacharaki D, Raptis AE, et al. Competing Effects of Renin Angiotensin System Blockade and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors on Erythropoietin Secretion in Diabetes. Am J Nephrol. 2020;51(5):349–56.
Souma T, Suzuki N, Yamamoto M. Renal erythropoietinproducing cells in health and disease. Front Physiol. 2015;6:167.
Souma T, Nezu M, Nakano D, Yamazaki S, Hirano I, Sekine H, et al. Erythropoietin Synthesis in Renal Myofibroblasts Is Restored by Activation of Hypoxia Signaling. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(2):428–38.
Ghanim H, Abuaysheh S, Hejna J, Green K, Batra M, Makdissi A, et al. Dapagliflozin Suppresses Hepcidin And Increases Erythropoiesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105(4):dgaa057.
Tilg H, Moschen AR. Inflammatory Mechanisms in the Regulation of Insulin Resistance. Mol Med. 2008;14(3–4):222–31.
Fleming RE. Iron and inflammation: cross-talk between pathways regulating hepcidin. J Mol Med (Berl). 2008;86(5):491–4.
Mithoowani S, Laureano M, Crowther MA, Hillis CM. Investigation and management of erythrocytosis. CMAJ. 2020;192(32):E913–8.
Gašperšič J, Kristan A, Kunej T, Zupan IP, Debeljak N. Erythrocytosis: genes and pathways involved in disease development. Blood Transfus. 2021;19(6):518–32.
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A. G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods. 2007;39(2):175–91.
Sano M, Goto S. Possible Mechanism of Hematocrit Elevation by Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and Associated Beneficial Renal and Cardiovascular Effects. Circulation. 2019;139(17):1985–7.