The Outcome of Hemoperfusion as an Adjuvant Therapy in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia can result in cytokine release syndrome and a high mortality rate. In addition to anti-viral medications, immunomodulators, and systemic corticosteroids, cytokine removal therapy, also known as hemoperfusion, might have a role in improving patient outcomes.
Methods: This is a retrospective observational study of patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia who received hemoperfusion using HA 330® in addition to conventional treatment compared to conventional treatment alone during May 2021 – June 2022. The primary outcome was the 28-day survival rate.
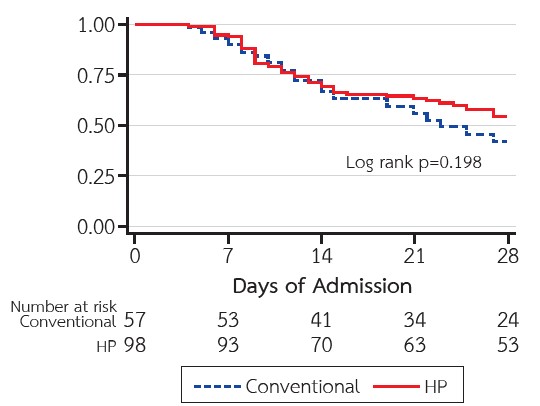
Results: 155 patients were included; 98 patients in the hemoperfusion group; and 57 patients in the conventional treatment group. Patients who received hemoperfusion had a higher Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score (10±3.3 vs. 7±2.9; p<0.001). There was no significant difference in the 28-day survival rate between the two groups (54.1% vs. 42.1%; p=0.198). Hemoperfusion for 24-48 hours significantly improved PaO2/FiO2 ratio (P=0.001) and reduced high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (p<0.001) and ferritin levels (P=0.003). Acute kidney injury was associated with an increased risk of 28-day mortality (Hazard ratio (95% confidence interval): 4.72 (2.87 to 7.77); p<0.001). The most common cause of death was bacterial pneumonia.
Conclusions: Hemoperfusion using HA330® was not associated with an improvement in 28-day survival in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia during the delta variant outbreak.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This article is published under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, which allows for non-commercial reuse of the published paper as long as the published paper is fully attributed. Anyone can share (copy and redistribute) the material in any medium or format without having to ask permission from the author or the Nephrology Society of Thailand.
References
Abbasi S, Naderi Z, Amra B, Atapour A, Dadkhahi SA, Eslami MJ, et al. Hemoperfusion in patients with severe COVID-19 respiratory failure, lifesaving or not? J Res Med Sci. 2021;26:34.
Chang K, Li Y, Qin Z, Zhang Z, Wang L, Yang Q, et al. Effect of extracorporeal hemoadsorption in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A narrative review. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1074465.
Schmidt JJ, Borchina DN, van T Klooster M, Bulhan-Soki K, Okioma R, Herbst L, et al. Interim-analysis of the COSA (COVID-19 patients treated with the Seraph® 100 Microbind® Affinity filter) registry. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021:347.
Chen G, Zhou Y, Ma J, Xia P, Qin Y, Li X. Is there a role for blood purification therapies targeting cytokine storm syndrome in critically severe COVID-19 patients? Ren Fail. 2020;42(1):483-88.
Safari S, Salimi A, Zali A, Jahangirifard A, Bastanhagh E, Aminnejad R, et al. Extracorporeal Hemoperfusion as a Potential Therapeutic Option for Severe COVID-19 patients; a Narrative Review. Arch Acad Emerg Med. 2020;8(1):e67.
Melegari G, Bertellini E, Melegari A, Trenti T, Malaguti S, Barbieri A. Hemoadsorption cartridge and coronavirus disease 2019 infections: A case report and brief literature review. Artif Organs. 2021;45(5):E130-E135.
Ricci Z, Romagnoli S, Reis T, Bellomo R, Ronco C. Hemoperfusion in the intensive care unit. Intensive Care Med. 2022;48(10):1397-1408.
Ronco C, Bagshaw SM, Bellomo R, Clark WR, Husain-Syed F, Kellum JA, et al. Extracorporeal Blood Purification and Organ Support in the Critically Ill Patient during COVID-19 Pandemic: Expert Review and Recommendation. Blood Purif. 2021;50(1):17-27.
Ankawi G, Fan W, Pomarè Montin D, Lorenzin A, Neri M, Caprara C, et al. A New Series of Sorbent Devices for Multiple Clinical Purposes: Current Evidence and Future Directions. Blood Purif. 2019;47(1-3):94-100.
Mikaeili H, Taghizadieh A, Nazemiyeh M, Rezaeifar P, Zununi Vahed S, Safiri S, et al. The early start of hemoperfusion decreases the mortality rate among severe COVID-19 patients: A preliminary study. Hemodial Int. 2022;26(2):176-82.
Peerapornratana S, Sirivongrangson P, Tungsanga S, Tiankanon K, Kulvichit W, Putcharoen O, et al. Endotoxin Adsorbent Therapy in Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia. Blood Purif. 2021;1-8.
Rampino T, Gregorini M, Perotti L, Ferrari F, Pattonieri EF, Grignano MA, et al. Hemoperfusion with CytoSorb as Adjuvant Therapy in Critically Ill Patients with SARS-CoV2 Pneumonia. Blood Purif. 2021;50(4-5):566-71.
De Rosa S, Cutuli SL, Ferrer R, Antonelli M, Ronco C; COVID-19 EUPHAS2 Collaborative Group. Polymyxin B hemoperfusion in coronavirus disease 2019 patients with endotoxic shock: Case series from EUPHAS2 registry. Artif Organs. 2021;45(6):E187-E194.
Soleimani A, Taba SMM, Hasibi Taheri S, Loghman AH, Shayestehpour M. The effect of hemoperfusion on the outcome, clinical and laboratory findings of patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective study. New Microbes New Infect. 2021;44:100937.
Katagiri D, Ishikane M, Asai Y, Izumi S, Takasaki J, Katsuoka H, et al. Direct hemoperfusion using a polymyxin B-immobilized polystyrene column for COVID-19. J Clin Apher. 2021;36(3):313-21.
Hwang EJ, Kim H, Yoon SH, Goo JM, Park CM. Implementation of a Deep Learning- Based Computer-Aided Detection System for the Interpretation of Chest Radiographs in Patients Suspected for COVID-19. Korean J Radiol. 2020;21(10):1150-60.
NIAID-RML. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guideline. NIH gov Published 2020.
Shadvar K, Tagizadiyeh A, Gamari AA, Soleimanpour H, Mahmoodpoor A. Hemoperfusion as a Potential Treatment for Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients with Cytokine Storm. Blood Purif. 2021;50(3):405-07.
Tang Y, Liu J, Zhang D, Xu Z, Ji J, Wen C. Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: The Current Evidence and Treatment Strategies. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1708.
Shokouhi S, Barati S, Kazeminia N, Jamali F, Roshan B, Sahraei Z. Evaluating the elimination status of medications used for COVID-19 during hemoperfusion and therapeutic plasma exchange: A review. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;97:107707.
Abdullayev R, Gul F, Bilgili B, Seven S, Cinel I. Cytokine Adsorption in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients, a Case-Control Study. J Intensive Care Med. 2022;37(9):1223-28.
Supady A, Weber E, Rieder M, Lother A, Niklaus T, Zahn T, et al. Cytokine adsorption in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (CYCOV): a single centre, open-label, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021;9(7):755-62.
Surasit K, Srisawat N. The Efficacy of Early Additional Hemoperfusion Therapy for Severe COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study. Blood Purif. 2022;51(11):879-88.
Sandnes M, Ulvik RJ, Vorland M, Reikvam H. Hyperferritinemia-A Clinical Overview. J Clin Med. 2021;10(9):2008.
Poudel A, Poudel Y, Adhikari A, Aryal BB, Dangol D, Bajracharya T, et al. D-dimer as a biomarker for assessment of COVID-19 prognosis: D-dimer levels on admission and its role in predicting disease outcome in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. PLoS One. 2021;16(8):e0256744.
Sabaghian T, Kharazmi AB, Ansari A, Omidi F, Kazemi SN, Hajikhani B, et al. COVID-19 and Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:705908.