Factors Associated with Hemofilter Clotting in Patients with Acute Kidney Injury Requiring Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Hemofilter clotting compromises efficacy of continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). However, risk factors associated with filter clotting are not well characterized. Recently, a new calculation of filtration fraction (FF) which incorporates systemic and post-filter hematocrit into the formula (FFHct) has been purposed. This study aimed to evaluate the associations between FFHct, conventional FF, and other related factors with filter survival in patients receiving CRRT.
Method: This prospective cohort study was conducted in patients with acute kidney injury undergoing CRRT without anticoagulation. Factors related to filter clotting were documented at baseline and every 8 hours for 72 hours or until filter loss.
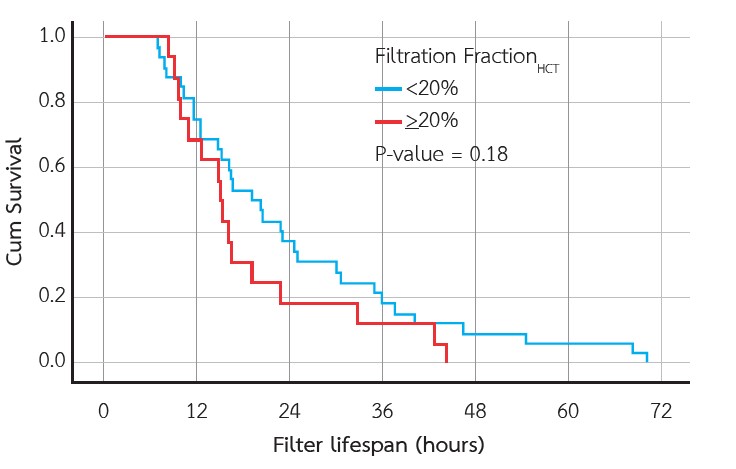
Results: Twenty-one patients using 48 filters were included. The median filter survival was 20.5 hours, and all filters clotted within 72 hours. In the multivariate analysis, the independent predictors for filter clotting were FFHct > 20% (HR: 2.18, 95% CI: 1.10 - 4.31, p=0.03), sites of dialysis catheter other than the right internal jugular vein (HR: 2.23, 95% CI: 1.16 - 4.29, p=0.02), and platelet count >100,000 /μl (HR: 2.22, 95% CI: 1.08 - 4.60, p=0.03). Arterial pressure circuit (<-150 mmHg), sieving coefficient (<0.9), conventional FF cut-off of (≥20%), and post-filter hematocrit (≥35%) were not associated with filter survival.
Conclusion: FFHct > 20% was an independent predictor of decreased filter lifespan in patients with acute kidney injury undergoing CRRT without anticoagulation. Future trials are needed to validate these preliminary findings.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This article is published under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, which allows for non-commercial reuse of the published paper as long as the published paper is fully attributed. Anyone can share (copy and redistribute) the material in any medium or format without having to ask permission from the author or the Nephrology Society of Thailand.
References
Brain M, Winson E, Roodenburg O, McNeil J. Non-anti-coagulant factors associated with filter life in continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT): a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2017;18(1):69.
Khwaja A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract. 2012;120(4):c179-84.
Ferreruela M, Raurich JM, Ayestarán I, Llompart-Pou JA. Hyperlactatemia in ICU patients: Incidence, causes and associated mortality. J Crit Care. 2017;42:200–5.
Helms J, Severac F, Merdji H, Clere-Jehl R, François B, Mercier E, et al. Performances of disseminated intravascular coagulation scoring systems in septic shock patients. Ann Intensive Care. 2020;10(1):92.
Joannidis M, Oudemans-van Straaten HM. Clinical review: Patency of the circuit in continuous renal replacement therapy. Crit Care Lond Engl. 2007;11(4):218.
Kramer P, Kaufhold G, Gröne HJ, Wigger W, Rieger J, Matthaei D, et al. Management of anuric intensive-care patients with arteriovenous hemofiltration. Int J Artif Organs. 1980;3(4):225–30.
Lauer A, Saccaggi A, Ronco C, Belledonne M, Glabman S, Bosch JP. Continuous Arteriovenous Hemofiltration in the Critically Ill Patient. Ann Intern Med. 1983;99(4):455–60.
Jenkins RD, Funk JE, Chen B, Golper TA. Operational Instability in Extracorporeal Filtration of Blood. Blood Purif. 1992;10(5–6):292–308.
MacEwen C, Watkinson P, Winearls C. Circuit life versus bleeding risk: the impact of achieved activated partial thromboplastin time versus achieved filtration fraction. Ther Apher Dial. 2015;19(3):259-66
Ricci Z, Ronco C, Bachetoni A, D’amico G, Rossi S, Alessandri E, et al. Solute removal during continuous renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients: convection versus diffusion. Crit Care. 2006;10(2):R67.
Davies HT, Leslie G, Pereira SM, Webb S a. R. A randomized comparative crossover study to assess the affect on circuit life of varying pre-dilution volume associated with CVVH and CVVHDF. Int J Artif Organs. 2008;31(3):221–7.
Califano AM, Bitker L, Baldwin I, Fealy N, Bellomo R. Circuit Survival during Continuous Venovenous Hemodialysis versus Continuous Venovenous Hemofiltration. Blood Purif. 2020;49(3):281–8.
Kakajiwala A, Jemielita T, Hughes JZ, Windt K, Denburg M, Goldstein SL, et al. Membrane pressures predict clotting of pediatric continuous renal replacement therapy circuits. Pediatr Nephrol. 2017;32(7):1251–61.
Dunn WJ, Sriram S. Filter lifespan in critically ill adults receiving continuous renal replacement therapy: the effect of patient and treatment-related variables. Crit Care Resusc. 2014;16(3):225–31.
Hatamizadeh P, Tolwani A, Palevsky P. Revisiting filtration fraction as an index of hemofilter clotting in continuous venovenous hemofiltration. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;15:1660-2.