FACTORS INFLUENCING BURDEN OF CAREGIVERS OF CHILDREN WITH ADHD DURING COVID-19 PANDEMIC
Keywords:
burden of care, caregivers of children with ADHD, COVID-19 pandemicAbstract
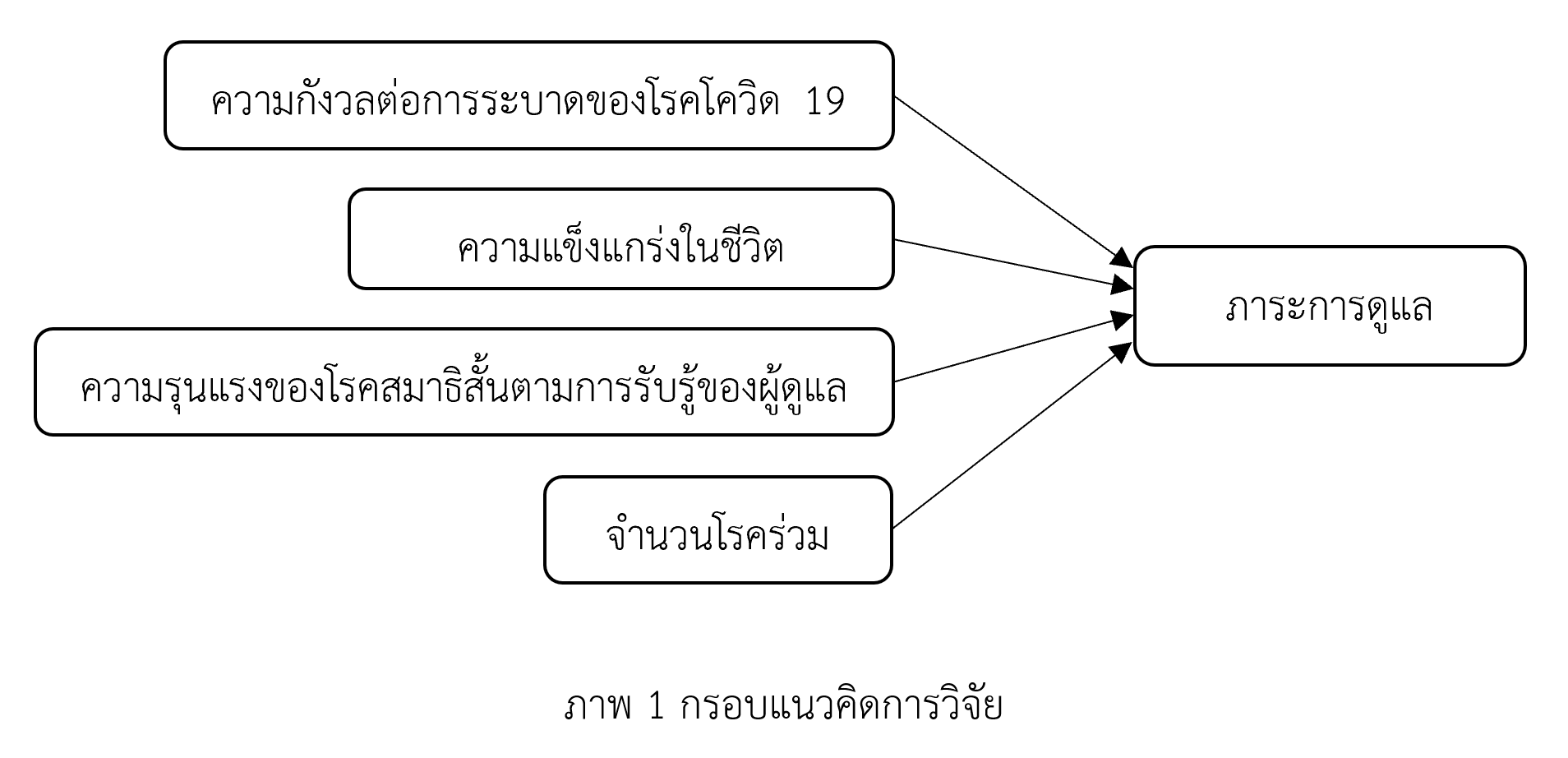
This predictive correlational research aimed to investigate: 1) the relationships between the worry about the COVID-19 pandemic, resilience, caregiver-perceived severity of ADHD, and number of comorbidities, and the burden of caregivers of children with ADHD; and 2) the predictive ability of these factors on caregiver burden during the COVID-19 pandemic. The participants were 204 caregivers of children with ADHD who sought services at the outpatient clinic of a tertiary hospital in Bangkok. The research tools consisted of the caregiver burden scale, the worry about COVID-19 scale, the resilience inventory, and the SNAP-IV. The Cronbach’s alpha coefficients of the research instrument were .93, .93, .93 and .94, respectively. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficients, Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients, and hierarchical multiple regression analysis.
The findings revealed that 34.8 percent of caregivers of children with ADHD had moderate to high levels of caregiver burden. The worry about the COVID-19 pandemic and the perceived severity of ADHD were positively and significantly associated with caregiver burden, while resilience was negatively and significantly related to caregiver burden. The worry the COVID-19 pandemic, caregiver-perceived severity of ADHD, resilience, and the number of comorbidities collectively explained 27.6% of the variance in caregiver burden, with statistical significance. The worry about the COVID-19 pandemic had the greatest impact on caregiver burden (Beta = .310, p = .000), followed by caregiver-perceived severity of ADHD (Beta = .300, p = .000) and resilience (Beta = -.192, p = .002). However, the number of comorbidities was not significantly correlated with caregiver burden (r = .133, p > .05) and did not significantly affect caregiver burden (Beta = .108, p > .05).
The results of this study could serve as foundational data for developing guidelines to prevent or reduce caregiver burden among those caring for children with ADHD.
Downloads
References
Able, S. L., Johnston, J. A., Adler, L. A., & Swindle, R. W. (2007). Functional and psychosocial impairment in adults with undiagnosed ADHD. Psychological Medicine, 37(1), 97-107.
Al-Balushi, N., Al-Alawi, M., Al Shekaili, M., Al-Balushi, M., Mirza, H., Al-Huseini, S., & Al-Adawi, S. (2019). Predictors of burden of care among caregivers of drug-naive children and adolescents with ADHD: A cross-sectional correlative study Muscat, Oman. Journal of Attention Disorders, 23(5), 517-526.
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-V) (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing.
Baweja, R., Waschbusch, D. A., & Mayes, S. D. (2023). Physical aggression toward others and self: Correlates in autism, attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder, and population-based child samples. JAACAP Open, 1(4), 274-283.
Boon-yasidhi, V. (2012). Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Diagnosis and management. Journal of the Psychiatric Association of Thailand, 57(4), 373-386.
Cadman, T., Eklund, H., Howley, D., Hayward, H., Clarke, H., Findon, J., & Glaser, K. (2012). Caregiver burden as people with autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder transition into adolescence and adulthood in the United Kingdom. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent, 51(9), 879-888.
Carey, P. J., Oberst, M. T., McCubbin, M. A., & Hughes, S. H. (1991). Appraisal and caregiving burden in family members caring for patients receiving chemotherapy. Oncology Nursing Forum, 18, 1341–1348.
Department of Disease Control. (2020). Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Retrieved from https://www.ddc.moph.go.th/viralpneumonia/file/g_km/handout001_12032020.pdf
Eakes, G. G. (1995). Chronic sorrow: The lived experience of parents of chronically mentally III individuals. Archives of Psychiatric Nursing, 9(2), 77-84.
Fianco, A., Sartori, R. D., Negri, L., Lorini, S., Valle, G., & Delle Fave, A. (2015). The relationship between burden and well-being among caregivers of Italian people diagnosed with severe neuromotor and cognitive disorders. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 39, 43–54.
Fridman, M., Banaschewski, T., Sikirica, V., Quintero, J., Erder, M. H., & Chen, K. S. (2017). Factors associated with caregiver burden among pharmacotherapy-treated children/adolescents with ADHD in the caregiver perspective on pediatric ADHD survey in Europe. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 13, 373–386.
Grotberg, E. H. (1995). The internacional resilience project: Promoting resilience in children. Retrieved from https://files.eric.ed.gov/ fulltext/ED383424.pdf
Grotberg, E. H. (1997). The international resilience project: Findings the research and the effectiveness of Interventions. Retrieved from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED419584.pdf
Health Systems Research Institute. (2017). Get to know attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Retrieved from https://www.hsri.or.th/ people/media/infographic/detail/9128
Iamyingpanich, R. (1996). Burden of care and well-being in families of mothers with mentally retarded children (Master’s thesis). Mahidol University.
Juntratip, P., Pongjaturawit, Y., & Chaimongkol, N., (2020). Factors influencing burden of child caregivers of children with delayed development. The Journal of Faculty of Nursing Burapha University, 28(2), 52-63.
Mohler-Kuo, M., Dzemaili, S., Foster, S., Werlen, L., & Walitza, S. (2021). Stress and mental health among children/adolescents, their parents, and young adults during the first COVID-19 lockdown in Switzerland. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(9), 4668.
Montirosso, R., Mascheroni, E., Guida, E., Piazza, C., Sali, M. E., Molteni, M., & Reni, G. (2021). Stress symptoms and resilience factors in children with neurodevelopmental disabilities and their parents during the COVID-19 pandemic. Health Psychology: Official Journal of the Division of Health Psychology, American Psychological Association, 40(7), 428–438.
Mutluer, T., Doenyas, C., & Aslan Genc, H. (2020). Behavioral implications of the COVID-19 process for autism spectrum disorder, and individuals' comprehension of and reactions to the pandemic conditions. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 11, 561882.
Nintachan, P., Sangon, S., Sumdaengrit, B., Deesamer, S., Kulvirogesopon, V., Boonchuay, N., . . . Gumphun, S. (2023). The mediating effect of resilience in the relationships between psychosocial factors and mental health problems of village health volunteers in Thailand during the third year of COVID-19 pandemic. Research report, Ramathibodi School of Nursing, Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University.
Nintachan, P., Sangon, S., & Thaweekoon, T. (2010). Development of a resilience assessment: Research report Thai population potential development project. Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University.
Oberst, M. T. (1991). Appraisal of caregiving scale. Madison, WI: University of Wisconsin.
Oberst, M. T., Thomas, S. E., Gass, K. A., & Ward, S. E. (1989). Caregiving demands and appraisal of stress among family caregivers. Cancer Nursing, 12(4), 209-215.
Ohlmeier, M. D., Peters, K., Te Wildt, B. T., Zedler, M., Ziegenbein, M., Wiese, B., Emrich, H. M., & Schneider, U. (2008). Comorbidity of alcohol and substance dependence with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Alcohol and Alcoholism (Oxford, Oxfordshire), 43(3), 300–304.
Orapiriyakul, R., Benjakul, W., & Kwunkaew, S. (2014). Predictors of burden of care in primary family caregivers of children with autism in the West-Coast Southern Thailand. Songklanagarind Journal of Nursing, 34(3), 39-58.
Panda, P. K., Gupta, J., Chowdhury, S. R., Kumar, R., Meena, A. K., Madaan, P., Sharawat, I. K., & Gulati, S. (2021). Psychological and behavioral impact of lockdown and quarantine measures for COVID-19 pandemic on children, adolescents and caregivers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics, 67(1), 1-13. , 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1093/tropej/fmaa122
Peasgood, T., Bhardwaj, A., Brazier, J. E., Biggs, K., Coghill, D., Daley, D., & Sonuga-Barke, E. J. S. (2021). What is the health and well-being burden for parents living with a child with ADHD in the United Kingdom? Journal of Attention Disorders, 25(14), 1962-1976.
Pitakbud, N. (2007). The influences of family relationship and burden on child care behaviors of mothers having autistic children (Master’s thesis). Prince of Songkla University, Songkla.
Pityaratstian, N., Booranasuksakul, T., Juengsiragulwit, D., & Benyakorn, S. (2014). ADHD screening properties of the Thai version of Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham IV scale (SNAP-IV) and strengths and difficulties questionnaire (SDQ). Journal of the Psychiatrist Association of Thailand, 59(2), 97–110.
Pornnoppadol, C. (Ed.). (2018). ADHD: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Ideol Digital Print.
Ronis, S. D., Baldwin, C. D., Blumkin, A., Kuhlthau, K., & Szilagyi, P. G. (2015). Patient-centered medical home and family burden in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics: JDBP, 36(6), 417–425.
Russell, B. S., Hutchison, M., Tambling, R., Tomkunas, A. J., & Horton, A. L. (2020). Initial challenges of caregiving during COVID-19: Caregiver burden, mental health, and the parent-child relationship. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 51(5), 671–682.
Russell, B. S., Tomkunas, A. J., Hutchison, M., Tambling, R. R., & Horton, A. L. (2021). The protective role of parent resilience on mental health and the parent-child relationship during COVID-19. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 53(1), 183-196.
Sideropoulos, V., Dukes, D., Hanley, M., Palikara, O., Rhodes, S., Riby, D. M., . . . Van Herwegen, J. (2021). The impact of COVID-19 on anxiety and worries for families of individuals with special education needs and disabilities in the UK. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 52(6), 2656-2669.
Thongphet, O. (2002). Caregiving burden among mothers of autistic children (Master’s thesis). Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai.
Wacharasin, C. (2017). Nursing interventions for families experiencing chronic illness (2nd ed.). Chonburi Printing.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 JOURNAL OF THE POLICE NURSES AND HEALTH SCIENCE

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ผลงานที่ได้ตีพิมพ์แล้วจะเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารพยาบาลตำรวจ














