ASSOCIATION BETWEEN INTRINSIC MOTIVATION AND DISEASE CONTROL BEHAVIORS AMONG OLDER ADULTS WITH HYPERTENSION IN CHIANG RAI PROVINCE
Keywords:
intrinsic motivation, disease control behavior, hypertension disease, older adultsAbstract
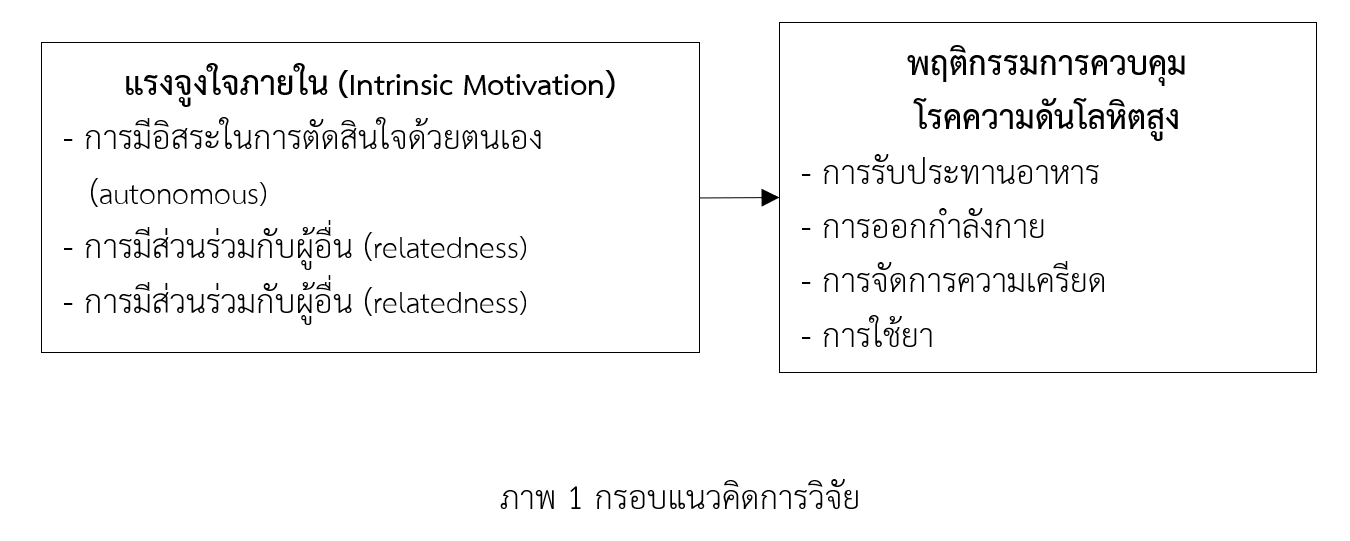
This descriptive correlational research aimed to study 1) intrinsic motivation and disease control behaviors among older adults with hypertension and 2) the association between intrinsic motivation and disease control behaviors among older adults with hypertension in Chiang Rai Province. The study framework utilized the concept of self-determination theory by Deci and Ryan (1985). The sample consisted of individuals aged 60 years and over with hypertension receiving services at Subdistrict Health Promoting Hospitals in Chiang Khong District, Chiang Rai Province, from April to May 2023. 312 participants were selected. The research instruments included a demographic data form, intrinsic motivation questionnaires, and questionnaires on disease control behaviors among older adults with hypertension. The content validity indices of both questionnaires were 1.0, and reliability, as measured by Cronbach’s alpha coefficients, showed values of .81 and .85, respectively. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
The research results found that: 1) Participants exhibited a high level of intrinsic motivation for disease control among older adults with hypertension (M = 81.38, SD = 5.18), and they demonstrated a high level of behaviors for disease control among older adults with hypertension (M = 56.61, SD = 4.62); and 2) Older adults with hypertension who had a high level of intrinsic motivation showed statistically significant correlation with a high level of behaviors for disease control (r = .411, p = .000).
This study demonstrated that intrinsic motivation is an important factor related to disease control behaviors among older adults with hypertension in Chiang Rai Province. These results provide health providers with insights to promote intrinsic motivation among older adults with hypertension to encourage appropriate disease control behaviors.
Downloads
References
Boonkaew, N., Jitramontree, N., & Wirojratana, V. (2015). The relationship between intrinsic motivation and glycemic control behaviors among older persons with type 2 diabetes. Nursing Journal, 45(1), 212-225.
Chiang Rai Provincial Health Office. (2022). Morbidity rate with hypertension per population 2022. Retrieved from http://61.19.32.29/hdc/reports/report.php?
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (1985). Intrinsic motivation and self-determination in human behavior. Boston, MA: Springer.
Hedman, M. (2018). Autonomy and participation in care for older people (Doctor of Philosophy). Faculty of Medicine, Uppsala University, Sweden, Uppsala.
Hudsadin, L. (2020). Factors predicting with self-care behaviors in hypertensive aging in out-patient department Ranode hospital. Journal of MCU Nakhondhat, 7(7), 373-386.
Jaiyungyuen, U., & Voraroon, S. (2016). Relationships among perceived self-efficacy, family support and health-promoting behaviors of older people with hypertension. Journal of Nursing, Siam University, 17(33), 20-30.
Kaewbanjak, N., Shumwangwapee, P., & Suwanaphant, K. (2020). Health literacy factors associated with health behavior among elderly with hypertension disease in Khoksi sub-district, Muang district, Khon Kaen province. Thai Journal of Public Health and Health Sciences, 3(3), 1-15.
Meesub, P. (2021). Prevalence and factors affecting uncontrolled blood pressure in elderly hypertensive patients in Chiang Khong hospital, Chiang Rai province. Journal of Primary Care and Family Medicine, 4(2), 61-69.
Oliveros, E., Patel, H., Kyung, S., Fugar, S., Goldberg, A., Madan, N., & Williams, K. A. (2020). Hypertension in older adults: Assessment, management, and challenges. Clinical cardiology, 43(2), 99-107.
Ostchega, Y., Fryar, C. D., Nwankwo, T., & Nguyen, D. T. (2020). Hypertension prevalence among adults aged 18 and over: United States, 2017–2018. National Center for Health Statistics Data Brief, 364(1), 1-8.
Peng, S., Shen, T., Liu, J., Tomlinson, B., Sun, H., Chen, X., . . . Zhang, Y. (2017). Uncontrolled hypertension increases with age in an older community-dwelling Chinese population in Shanghai. Aging and disease, 8(5), 558-569.
Saensunon, C., & Suwannaphant, K. (2021). Factors associated with quality of life among hypertension patients in Banphai district, Khon Kaen province. Academic Journal of Comminuty Public Health, 7(2), 42-61.
Serametakul, D., Wonghongkul, T., Klunklin, P., & Mesukko, J. (2019). A causal model of self-management for adolescents with asthma. Pacific Rim International Journal of Nursing Research, 23(4), 320-333.
Sheeran, P., Wright, C. E., Avishai, A., Villegas, M. E., Lindemans, J. W., Klein, W. M., . . . Ntoumanis, N. (2020). Self-determination theory interventions for health behavior change: Meta-analysis and meta-analytic structural equation modeling of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 88(8), 726-737.
Sithikan, W. (2017). Factors associated with health promotion behaviors of the elderly in Ban Hong subdistrict municipality, Ban Hong district, Lamphun province (Master of Public Health). Faculty of science and technology Chiang Mai Rajabhat University, Chiang Mai.
Srisathitnarakoon, B. (2020). Effect size power analysis sample size calculation using G*Power program. Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Printing House.
Strategy and Planning Division Permanent Secretary Ministry of Public Health. (2019). Summary incidence of illness report 2019. Bangkok: Digital health group strategy and planning division.
Suwan, N. (2015). Drug use behaviors and related factors of hypertensive patients in Kong Khaek health promotion hospital, Mae Chaem district, Chiang Mai province (Master of Public Health). Faculty of Public Health, University of Chiang Mai, Chiang Mai.
Tantiekkarat, S., Makmee, P., Suksanguam, N., & Sattaphan, N. (2020). Factors associated with self-care behavior of the elder with hypertension in Buriram Province by using the precede framework theory. Valaya Alongkorn Rajabhat University under the Royal Patronage Research and Development Journal Science and Technology, 15(1), 59-73.
Thai Hypertension Society. (2019). 2019 Thai guidelines on the treatment of hypertension. Bangkok: Trickthink publication.
Weinstein, N., Legate, N., Kumashiro, M., & Ryan, R. M. (2016). Autonomy support and diastolic blood pressure: Long term effects and conflict navigation in romantic relationships. Motivation and Emotion, 40(2), 212-225.
Yosaphol, D. (2017). Factors related to self- care behaviors of elderly with hypertension in Aranyik sub-district, Nakhon Luang district, Pranakhon Si Ayutthaya province (Master of Public Health). Faculty of Liberal Arts, Krirk University, Bangkok, Bang Khen.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 JOURNAL OF THE POLICE NURSES

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ผลงานที่ได้ตีพิมพ์แล้วจะเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารพยาบาลตำรวจ














