ผลของการเรียนโดยใช้สถานการณ์จำลองเสมือนจริงต่อความสามารถในการตัดสินทางคลินิกของนักศึกษาพยาบาล ในรายวิชาปฏิบัติการพยาบาลเด็กและวัยรุ่น
คำสำคัญ:
การเรียนโดยใช้สถานการณ์จำลองเสมือนจริง, ความสามารถในการตัดสินทางคลินิก, นักศึกษาพยาบาลบทคัดย่อ
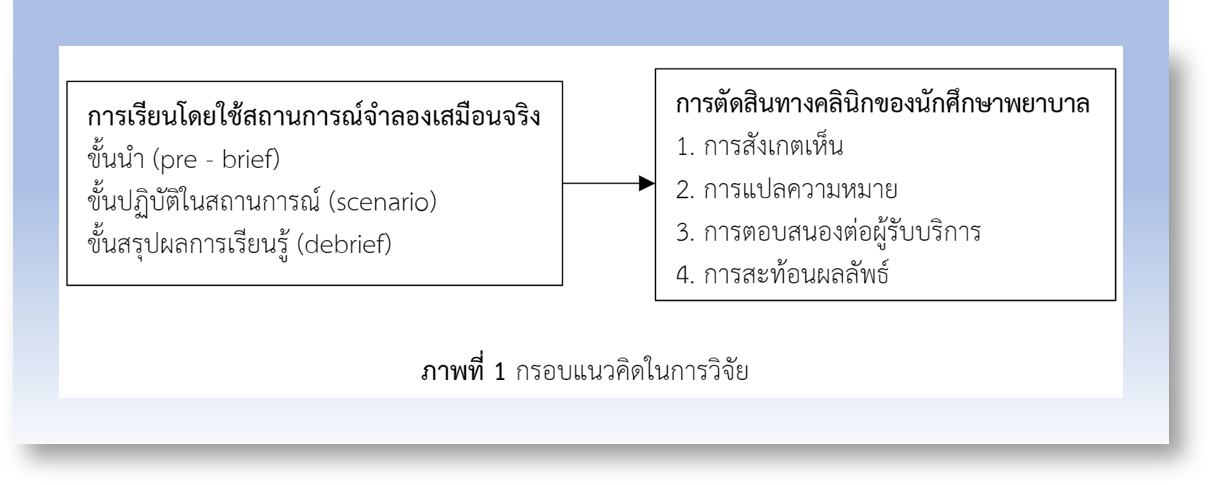
การวิจัยเชิงทดลองชนิดหนึ่งกลุ่มวัดผลก่อนและหลังทดลอง มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อเปรียบเทียบความสามารถในการตัดสินทางคลินิกของนักศึกษาพยาบาล โดยใช้สถานการณ์จำลองเสมือนจริงในรายวิชาปฏิบัติการพยาบาลเด็กและวัยรุ่น กลุ่มตัวอย่าง คือ นักศึกษาหลักสูตรพยาบาลศาสตรบัณฑิต ชั้นปีที่ 3 ที่ฝึกปฏิบัติรายวิชาปฏิบัติการพยาบาลเด็กและวัยรุ่น เลือกกลุ่มตัวอย่างแบบเฉพาะเจาะจง จำนวน 64 ราย โดยกลุ่มตัวอย่างได้รับการสอนโดยใช้สถานการณ์จำลองเสมือนจริง จำนวน 3 สถานการณ์ เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูลด้วยแบบสอบถามการตัดสินทางคลินิกของลาซาเตอร์ฉบับภาษาไทย ได้ค่าความเชื่อมั่น เท่ากับ .92 วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลด้วยสถิติเชิงพรรณนา และสถิติทดสอบค่าที (paired t-test)
ผลการวิจัย พบว่า นักศึกษาหลังได้รับการสอนโดยใช้สถานการณ์จำลองเสมือนจริง มีระดับขั้นของความสามารถในการตัดสินทางคลินิกส่วนใหญ่อยู่ในขั้นชำนาญ ซึ่งสูงกว่าก่อนได้รับการสอนที่อยู่ในขั้นกำลังพัฒนา ความสามารถในการตัดสินทางคลินิกสูงกว่าก่อนได้รับการสอนอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ (Mean difference: 8.19, 95%CI: -6.62, p-value < .01) คะแนนเฉลี่ยความสามารถของนักศึกษาในการตัดสินทางคลินิก เกณฑ์ผ่านร้อยละ 70.00 มีจำนวนร้อยละ 71.88 จากผลการศึกษานี้บ่งชี้ได้ว่า การจัดการเรียนการสอนโดยใช้สถานการณ์จำลองเสมือนจริง สามารถเพิ่มความสามารถของนักศึกษาพยาบาลในการตัดสินทางคลินิกในการปฏิบัติการพยาบาล ดังนั้น ควรนำไปประยุกต์กับเนื้อหา และรายวิชาอื่น ๆ เพื่อนำไปสู่การปฏิบัติทางการพยาบาลที่มีประสิทธิภาพต่อไป
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Sinthuchai S, Ubolwan K. Fidelity simulation based learning: implementation to learning and teaching management. Journal of The Royal Thai Army Nurses 2017;18(1):29-38. (in Thai)
Doo HJ, Lee YJ. Perception of nursing students’ experience of simulation-based learning: an application of Q-methodology. Journal of Bio-Science and Bio-Technology 2016;8(1):313-28. doi: 10.14257/ijbsbt.2016.8.1.28.
Lertlum L, Tanasansutee C, Panawatthanapisuit S, Bumrungsri C. Development of a simulation-based learning model. The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health 2019;6 Suppl 1:S43-58. (in Thai)
Punsumreung T, Kanhadilok S, Inchaithep S. The Thai version of Lasater clinical judgement rubric (T-LCJR): psychometric properties. Journal of Nursing and Education 2020;13(1):14-26. (in Thai)
Suksawatdiporn P, Pasiphol S, Na-songkhla J. Development of the clinical judgement test in obstetric nursing for nursing students. Journal of The Police Nurses and Health Science 2019;11(2):464-73. (in Thai)
Lasater K. Clinical judgment development: using simulation to create an assessment rubric. The Journal of Nursing Education 2007;46(11):496-503. doi: 10.3928/01484834-20071101-04.
Shin H, Park CG, Shim K. The Korean version of the Lasater clinical judgment rubric: a validation study. Nurse Education Today 2015;35(1):68-72. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2014.06.009.
Sinthuchai S, Ubolwan K, Bunsonti N, Yod-A-Sa P, Doungsuriya P. Effect of high fidelity simulation based learning on clinical decision making ability of nursing students. Journal of The Police Nurses and Health Science 2019;11(1):172-83. (in Thai)
Phormpayak D, Sattayawong W, Rattana-Umpa J, Hamtanon P, Rungkavat V. The effects of using simulation based learning and reflective thinking skill promoting on nursing students’ reflective thinking behavior and clinical decision-making abilities. Journal of Health and Nursing Education 2019;25(2):57-71. (in Thai)
Norkaeo D. Simulation based learning for nursing education. Journal of Boromarajonani College of Nursing 2015;31(3):112-22. (in Thai)
Jeffries PR. Simulation in nursing education: from conceptualization to evaluation. 2nd ed. Philadelphia PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012.
Kanhadilok S, Punsumreung T. Simulation based learning: design for nursing education. Journal of Nursing and Education 2016;9(1):1-14. (in Thai)
Punsomreung T, Kanhadilok S. Clinical judgement: an essential skill for nursing intervention. Journal of Nursing, Siam University 2017;18(35):81-94. (in Thai)
Srisatidnarakul B. Effect size, power analysis, optimal sample size calculations, using G* power software. Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University; 2020. (in Thai)
Deeprasert A, Nantasanee S, Saiboonsri U. Effects of scenario-based learning management on confidence and therapeutic communication skills in nursing students, Faculty of Nursing Suan Dusit University. Kuakarun Journal of Nursing 2022;29(2):244-60. (in Thai)
Seesanea S, Kunoy C, Karunchareonphanit S, Rupngam S. Effects of simulation-based learning on knowledge, clinical judgment, and nursing skills in caring for critical patients with acute myocardial infarction: a case study. Journal of Nursing and Health Research 2022;23(1):123-33. (in Thai)
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 วารสารเกื้อการุณย์

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
















