Exploring machine learning approaches for early diabetes risk prediction: A comprehensive examination of health indicators and models
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: The increased prevalence of morbidity and mortality associated with Type 2 diabetes is due to changing lifestyles, demanding improved disease management measures. To tackle this, scientists are increasingly looking to technological advances, notably machine learning, for illness prevention and management, particularly in non-communicable diseases. The emphasis is on establishing an early detection system to identify Type 2 diabetes risk factors, enabling prompt treatments and preventative steps to reduce the disease’s rising prevalence.
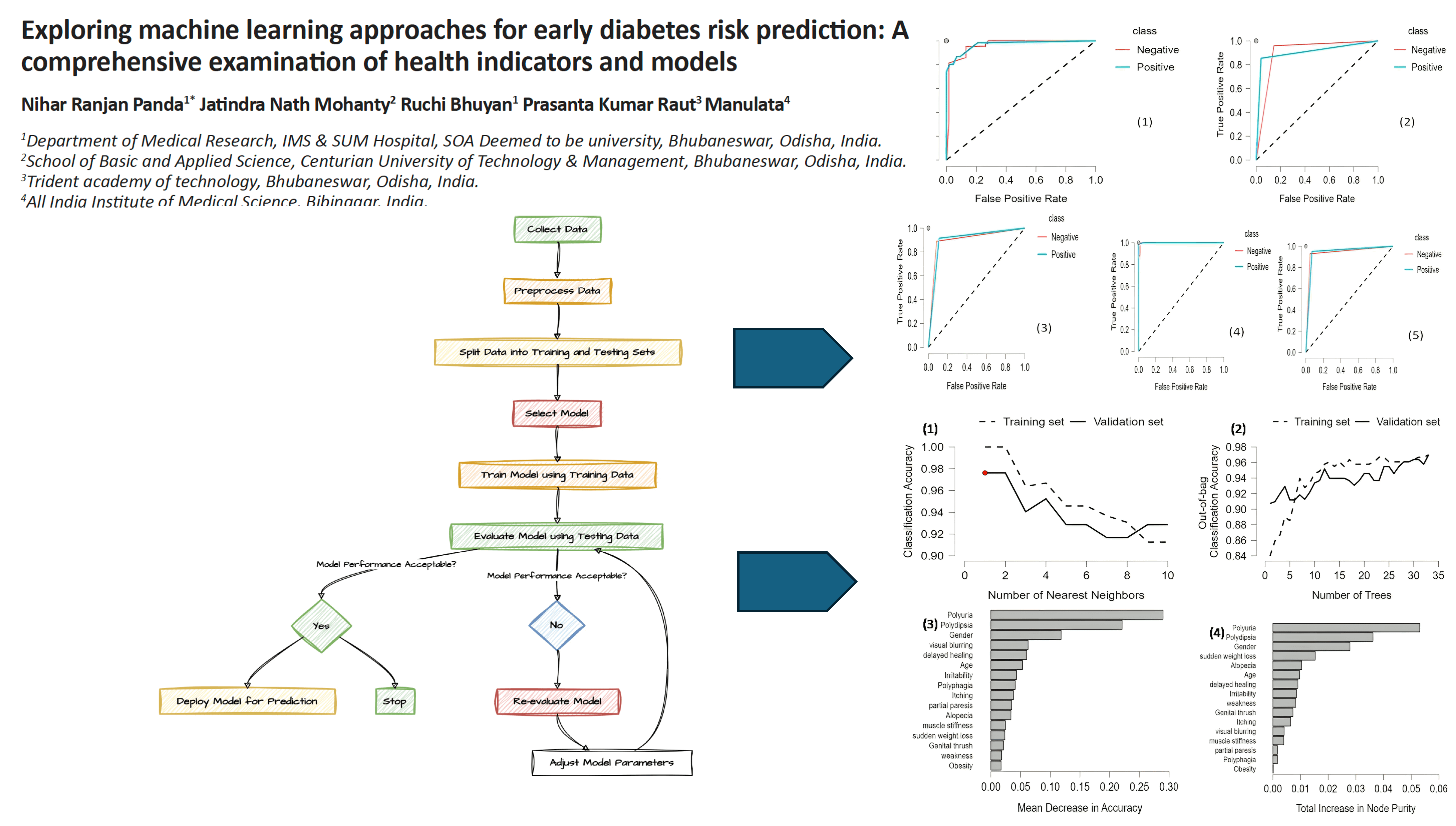
Materials and methods: The research aimed to assess the association of diabetes class with health indicators. Five machine learning models were employed with cross-validation techniques to predict early diabetes risk. The performance matrices of the models were evaluated and compared with the existing work.
Results: In multivariate analysis, we found polyuria (β=3.492; Aor=32.872; 95% CI=11.09,97.35; p<0.001), polydipsia (β=-4.100; Aor=60.378; 95%CI=18.28,199.37; p<0.001), polyphagia (β=1.181; Aor=3.25; 95%CI=1.23,8.57; p=0.017), genital thrush (β=1.08; Aor=2.96; 95%CI=1.26,7.53; p=0.023), irritability (β=2.28; Aor=9.82; 95%CI=3.41,28.26; p<0.001), and partial paresis (β=1.2406; Aor=3.45; 95% CI=1.35,8.79; p=0.009) are the potential health risk indicators for positive diabetes class.
Conclusion: Using an interpretable feature learning approach for early diabetes prediction improves the use of global health data. This method forecasts hazards correctly and gives insights into influential aspects. As a result, a more proactive healthcare strategy is implemented, allowing for more prompt treatments and encouraging a more hopeful future by improving patient outcomes and lowering the total burden of diabetes on individuals and healthcare systems.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Personal views expressed by the contributors in their articles are not necessarily those of the Journal of Associated Medical Sciences, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University.
References
Caughey GE, Roughead EE, Vitry AI, McDermott RA, Shakib S, Gilbert AL. Comorbidity in the elderly with diabetes: Identification of areas of potential treatment conflicts. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010; 87(3): 385- 93. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2009.10.019.
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37(Supp1): S81-90. doi: 10.2337/dc14-S081.
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Groop L, Henry RR, Herman WH, Holst JJ, Hu FB, Kahn CR, Raz I, Shulman GI, Simonson DC. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015; 1(1): 1-22. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2015.19.
Olokoba AB, Obateru OA, Olokoba LB. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review of current trends. Oman Med J. 2012; 27(4): 269. doi: 10.5001/omj.2012.68.
Ginter E, Simko V. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, pandemic in 21st century. Diabetes: an old disease, a new insight. 2013: 42-50. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5441-0_6.
Buchanan TA, Xiang AH. Gestational diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115(3): 485-91. doi: 10.1172/ JCI24531.
Plows JF, Stanley JL, Baker PN, Reynolds CM, Vickers MH. The pathophysiology of gestational diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(11): 3342. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113342.
Tasin I, Nabil TU, Islam S, Khan R. Diabetes prediction using machine learning and explainable AI techniques. Healthc Technol Lett. 2023; 10(1-2): 1-10. doi: 10.1049/htl2.12039.
Ahamed BS, Arya MS, Nancy V AO. Prediction of type-2 diabetes mellitus disease using machine learning classifiers and techniques. Front Comput Sci. 2022; 4: 835242. doi.org/10.3389/fcomp.2022.835242.
Modak, S.K.S., Jha, V.K. Diabetes prediction model using machine learning techniques. Multimed Tools Appl. 2023; 83: 38523-49. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-16745-4.
Zou Q, Qu K, Luo Y, Yin D, Ju Y, Tang H. Predicting diabetes mellitus with machine learning techniques. Front Genet. 2018; 9: 515. doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00515.
Sutton CD. Classification and regression trees, bagging, and boosting. Handbook of statistics. 2005; 24: 303- 29. doi: 10.1016/S0169-7161(04)24011-1.
Song YY, Ying LU. Decision tree methods: applications for classification and prediction. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2015; 27(2): 130. doi: 10.11919/j.issn.1002-0829.215044.
Panda NR, Pati JK, Pati T, Satpathy S, Bhuyan R. Comparison of artificial neural network and decision tree methods for predicting the maternal outcome in a tertiary care hospital in Odisha, India. Nat J Community Med. 2022; 13(11): 821-7. doi.org/10.55489/njcm.131120222262.
Speiser JL, Miller ME, Tooze J, Ip E. A comparison of random forest variable selection methods for classification prediction modeling. Expert Syst Appl. 2019; 134: 93-101. doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.05.028.
Panda NR, Mahanta KL, Pati JK, Varanasi PR, Bhuyan R. Comparison of Some Prediction Models and their Relevance in the Clinical Research. Int J Stats Med Res. 2023; 12: 12-9. doi.org/10.6000/1929-6029.2023.12.02.
Mucherino A, Papajorgji PJ, Pardalos PM, Mucherino A, Papajorgji PJ, Pardalos PM. K-nearest neighbor
classification. Data Mining in Agr. 2009: 83-106. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-88615-2_4.
Yu H, Kim S. SVM Tutorial-Classification, Regression and Ranking. Handbook of Nat comp. 2012; 1: 479-506. doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-92910-9_15.
Patle A, Chouhan DS. SVM kernel functions for classification. In: 2013 International conference on advances in technology and engineering (ICATE). 2013 Jan 23 (pp.1-9), IEEE. doi. 10.1109/ICAdTE. 2013.6524743.
Charoensakulchai S, Usawachoke S, Kongbangpor W, Thanavirun P, Mitsiriswat A, Pinijnai O, Kaensingh S, Chaiyakham N, Chamnanmont C, Ninnakala N, Hirio-Tappa P. Prevalence and associated factors influencing depression in older adults living in rural Thailand: A cross-sectional study. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2019; 19(12): 1248-53. doi: 10.1111/ggi.13804.
Gao M, Jebb SA, Aveyard P, Ambrosini GL, PerezCornago A, Papier K, Carter J, Piernas C. Associations between dietary patterns and incident type 2 diabetes: prospective cohort study of 120,343 UK biobank participants. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45(6): 1315-25. doi: 10.2337/dc21-2258.
Permana BA, Ahmad R, Bahtiar H, Sudianto A, Gunawan I. Classification of diabetes disease using decision tree algorithm (C4. 5). In: Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2021; 1869 (1): 012082, IOP Publishing. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1869/1/012082.
Olufemi I, Obunadike C, Adefabi A, Abimbola D. Application of Logistic Regression Model in Prediction of Early Diabetes Across United States. Int J Sci Manag Res. 2023; 6(05): 34-48. doi: 10.0130/2023230563.
Dritsas E, Trigka M. Data-driven machine-learning methods for diabetes risk prediction. Sensors. 2022; 22(14): 5304. doi.org/10.3390/s22145304.
Wicaksana AL, Apriliyasari RW, Tsai PS. Effect of self-help interventions on psychological, glycemic, and behavioral outcomes in patients with diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Nurs Stud. 2024; 149: 104626. doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2023.104626.
AtınçYılmaz. PREDICTION OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS USING FEATURE SELECTION-BASED MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS. Health Prob Civil. 2022; 16(2): 128-39. doi.org/10.5114/hpc.2022.114541.
Sabejon JA, Rejas JB, Lumacad GS, Zarate RL, Mendez EA, Tinoy FM. XGBoost–Based Analysis of the EarlyStage Diabetes Risk Dataset. In: 2023 International Conference in Advances in Power, Signal, and Information Technology (APSIT) 2023 Jun 9 (pp. 19- 24). IEEE. doi: 10.1109/APSIT58554.2023.10201658.
Ghosh P, Azam S, Karim A, Hassan M, Roy K, Jonkman M. A comparative study of different machine learning tools in detecting diabetes. Procedia Comput Sci. 2021; 192: 467-77. doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2021.08.048.
Early-stage diabetes risk prediction dataset, 2020, doi.org/10.24432/C5VG8H, UCI Machine Learning Repository.
Panda NR, Mahanta KL, Pati JK, Pati T. Development and Validation of Prediction Model for Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) Admission Using Machine Learning and Multivariate Statistical Approach. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2024; 74(3): 1-9. doi: 10.1007/s13224-024-02009-0.
Panda NR. A review on logistic regression in medical research. Nat J Community Med. 2022; 13(04): 265- 70. doi.org/10.55489/njcm.134202222.