ยากับการเกิดโรคไตอักเสบ
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
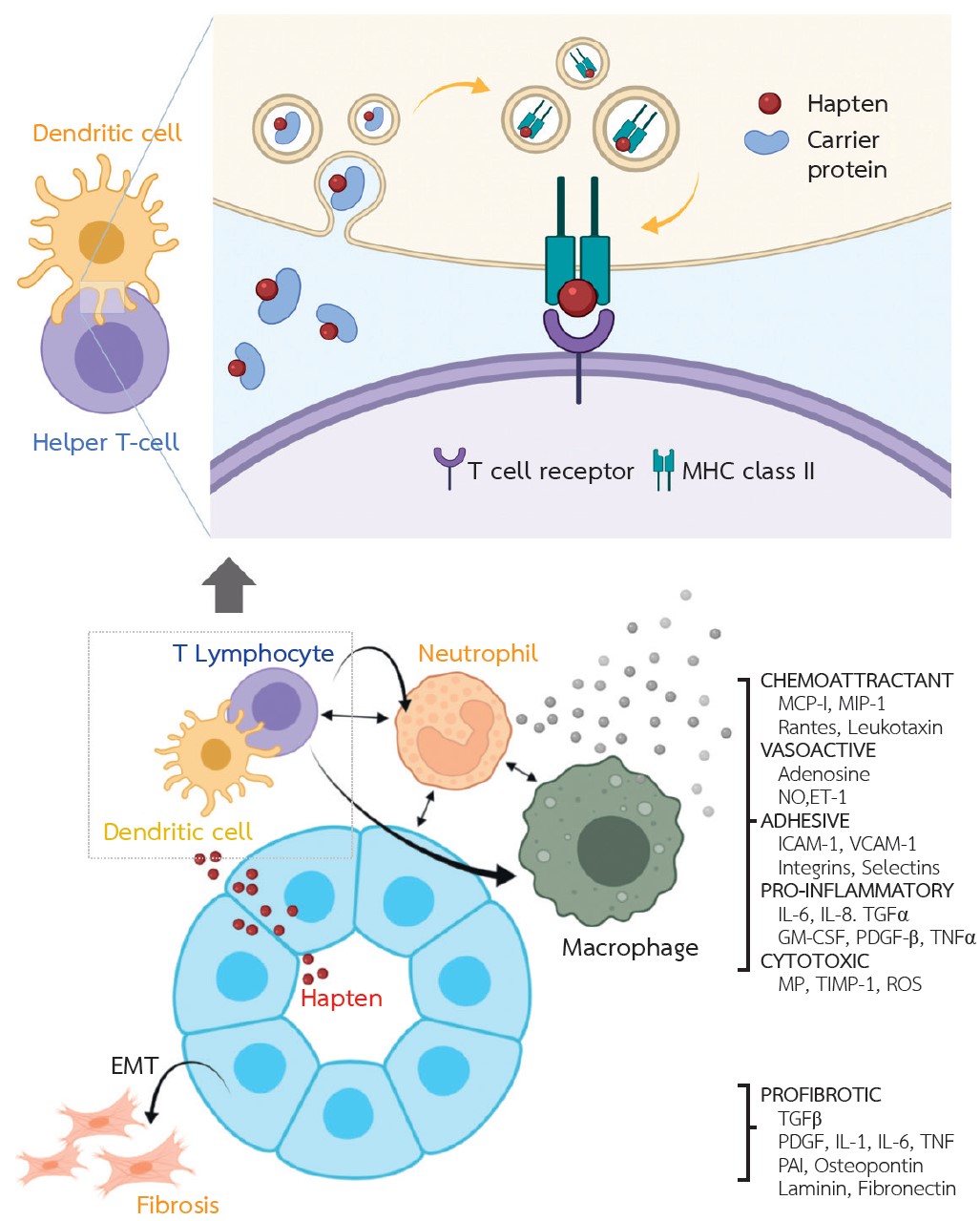
ภาวะ acute interstitial nephritis (AIN) เป็นสาเหตุสำคัญของภาวะไตวายเฉียบพลัน ยาปฎิชีวนะ ยาลดกรดในกระเพาะอาหารและยาแก้ปวดชนิด non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) เป็นสาเหตุหลักของยาที่ทำให้เกิด AIN กลไกการเกิดโรคเกิดจากภาวะภูมิคุ้มกันไวเกินต่อยา อาการแสดงของโรคหลัก 3 ข้อ คือ ผื่น ไข้ และเม็ดเลือดขาว eosinophil เพิ่มขึ้นพบเพียงร้อยละ 10 ของยาที่ทำให้เกิด AIN การเกิด AIN ใช้ระยะเวลาเป็นสัปดาห์ หรือเดือนหลังได้รับยา จำเป็นต้องคิดถึงโรคนี้ในผู้ป่วยไตวายเฉียบพลันไม่ทราบสาเหตุ และจำเป็นต้องทำการตรวจชิ้นเนื้อไตเพื่อการวินิจฉัยโรค หลักการรักษาโรคคือ การหยุดยาที่เป็นสาเหตุของโรคให้เร็วที่สุด ร่วมกับพิจารณาใช้ยากดภูมิในรายที่เหมาะสมเพื่อชะลอการเกิดโรคไตเรื้อรัง จากข้อมูลการรักษาในปัจจุบันส่วนใหญ่มาจากการศึกษาแบบสังเกต เพื่อดูประสิทธิภาพของการใช้สเตียรอยด์ขนาดสูง พบว่าการหยุดยาที่เป็นสาเหตุได้เร็ว ร่วมกับการใช้ยาสเตียรอยด์ในรายที่เพิ่งเกิดอาการและมีลักษณะพยาธิสภาพจากชิ้นเนื้อไตเป็นพังผืดไม่รุนแรงจะมีการตอบสนองต่อการรักษาที่ดี ควรหยุดยาสเตียรอยด์หากไม่มีการตอบสนองหลังการรักษามากกว่า 8 สัปดาห์ เพราะว่ายาจะเพิ่มความเสี่ยงจากผลข้างเคียงของการรักษา
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความนี้ตีพิมพ์ภายไต้การอนุญาต CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 ซึ่งอนุญาตให้สามารถใช้บทความนี้พื่อวัตถุประสงค์ใดๆ ก็ตามที่ไม่ใช่เชิงพาณิชย์ โดยต้องมีการอ้างถึงที่มาของบทความอย่างครบถ้วน ใครก็ตามสามารถคัดลอกและแจกจ่ายทุกส่วนของบทความนี้โดยไม่ต้องขออนุญาตจากผู้ประพันธ์หรือสมาคมโรคไตแห่งประเทศไทย
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Perazella MA, Rosner MH. Tubulointerstitial diseases. In: YU ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, editors. Brenner & Rector’s the kidney. 11 ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2019. p. 1196-222.
Muriithi AK, Leung N, Valeri AM, Cornell LD, Sethi S, Fidler ME, et al. Biopsy-proven acute interstitial nephritis, 1993-2011: a case series. Am J Kidney Dis 2014;64(4):558-66.
Moledina DG, Perazella MA. Treatment of drug-induced acute tubulointerstitial nephritis: the search for better evidence. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2018;13(12):1785-7.
Thong BYH, Tan T-C. Epidemiology and risk factors for drug allergy. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2011;71(5):684-700.
Raghavan R, Shawar S. Mechanisms of drug-induced interstitial nephritis. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 2017;24(2):64-71.
Border WA, Lehman DH, Egan JD, Sass HJ, Glode JE, Wilson CB. Antitubular basement-membrane antibodies in methicillin-associated interstitial nephritis. N Engl J Med 1974;291(8):381-4.
Wuillemin N, Adam J, Fontana S, Krähenbühl S, Pichler WJ, Yerly D. HLA haplotype determines hapten or p-i T cell reactivity to flucloxacillin. J Immunol 2013;190(10): 4956-64.
Ko TM, Chung WH, Wei CY, Shih HY, Chen JK, Lin CH, et al. Shared and restricted T-cell receptor use is crucial for carbamazepine-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011;128(6):1266-76.e11.
González E, Gutiérrez E, Galeano C, Chevia C, de Sequera P, Bernis C, et al. Early steroid treatment improves the recovery of renal function in patients with drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int 2008;73(8):940-6.
Perazella MA, Markowitz GS. Drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Nat Rev Nephrol 2010;6(8):461-70.
Clarkson MR, Giblin L, O’Connell FP, O’Kelly P, Walshe JJ, Conlon P, et al. Acute interstitial nephritis: clinical features and response to corticosteroid therapy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2004;19(11):2778-83.
Rossert J. Drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int 2001;60(2):804-17.
Mills RM. Severe hypersensitivity reactions associated with allopurinol. JAMA 1971;216(5):799-802.
Corwin HL, Korbet SM, Schwartz MM. Clinical correlates of eosinophiluria. Arch Intern Med 1985;145(6):1097-9.
Nolan CR, Anger MS, Kelleher SP. Eosinophiluria--a new method of detection and definition of the clinical spectrum. N Engl J Med 1986;315(24):1516-9.
Corwin HL, Bray RA, Haber MH. The detection and interpretation of urinary eosinophils. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1989;113(11):1256-8.
Ruffing KA, Hoppes P, Blend D, Cugino A, Jarjoura D, Whittier FC. Eosinophils in urine revisited. Clin Nephrol 1994; 41(3):163-6.
D’Agati VD, Theise ND, Pirani CL, Knowles DM, Appel GB. Interstitial nephritis related to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents and beta-lactam antibiotics: a comparative study of the interstitial infiltrates using monoclonal antibodies. Mod Pathol 1989;2(4):390-6.
Baker RJ, Pusey CD. The changing profile of acute tubulointerstitial nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2004;19(1):8-11.
Raza MN, Hadid M, Keen CE, Bingham C, Salmon AH. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis, treatment with steroid and impact on renal outcomes. Nephrology (Carlton) 2012;17(8): 748-53.
Valluri A, Hetherington L, McQuarrie E, Fleming S, Kipgen D, Geddes CC, et al. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis in Scotland. QJM 2015;108(7):527-32.
Prendecki M, Tanna A, Salama AD, Tam FW, Cairns T, Taube D, et al. Long-term outcome in biopsy-proven acute interstitial nephritis treated with steroids. Clin Kidney J. 2017; 10(2):233-9.
Fernandez-Juarez G, Perez JV, Caravaca-Fontán F, Quintana L, Shabaka A, Rodriguez E, et al. Duration of treatment with corticosteroids and recovery of kidney function in acute interstitial nephritis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2018;13(12):1851-8.
Preddie DC, Markowitz GS, Radhakrishnan J, Nickolas TL, D’Agati VD, Schwimmer JA, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil for the treatment of interstitial nephritis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2006;1(4):718-22.