Factors Associated with Non-Recovery of Renal Function in Patients with Septic Acute Kidney Injury
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication in patients with infection and septicemia, contributing to increased mortality and longer hospital stays. However, factors predicting renal recovery in patients with septic AKI remain unclear. This study investigated biochemical factors associated with renal recovery in septic AKI patients.
Methods: This was a retrospective, single-center study of patients admitted with infection-associated AKI between January 1st, 2015, and December 31st, 2020. Patients were categorized into full recovery and non-recovery groups, and factors associated with non-recovery of renal function within 90 days were analyzed.
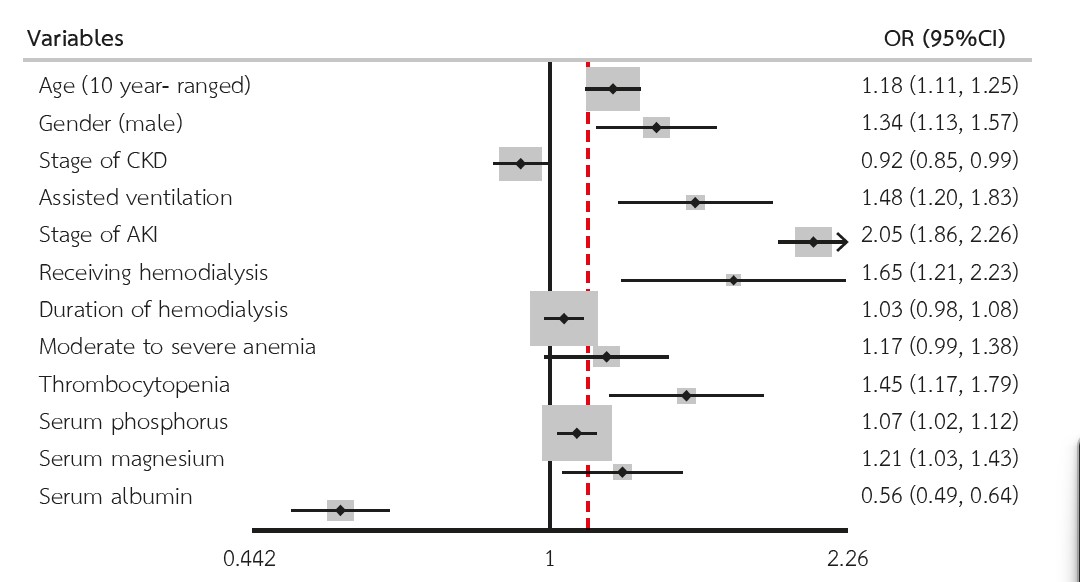
Results: A total of 4,431 patients with septic AKI were included in the final analysis. Of these, 2,429 patients (54.82%) were in the full recovery group, and 2,002 patients (45.18%) were in the non-recovery group. Independent predictors of non-recovery included older age, male gender, AKI severity, the need for dialysis and assisted ventilation, thrombocytopenia, elevated serum phosphorus and magnesium levels, and lower serum albumin. There was no association between underlying conditions or the degree of chronic kidney disease and renal outcomes.
Conclusions: Older age, male gender, infection and AKI severity, the need for dialysis, thrombocytopenia, and lower serum albumin were associated with non-recovery of renal function in patients with septic AKI.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This article is published under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, which allows for non-commercial reuse of the published paper as long as the published paper is fully attributed. Anyone can share (copy and redistribute) the material in any medium or format without having to ask permission from the author or the Nephrology Society of Thailand.
References
Hoste EAJ, Bagshaw SM, Bellomo R, Cely CM, Colman R, Cruz DN, et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: the multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med. 2015;41(8):1411–23.
Motzkus CA, Chrysanthopoulou SA, Luckmann R, Rincon TA, Lapane KL, Lilly CM. ICU Admission Source as a Predictor of Mortality for Patients With Sepsis. J Intensive Care Med. 2018;33(9):510–6.
Bagshaw SM, Uchino S, Bellomo R, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, et al. Septic Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients: Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;2(3):431–9.
Palevsky PM, Molitoris BA, Okusa MD, Levin A, Waikar SS, Wald R, et al. Design of Clinical Trials in Acute Kidney Injury: Report from an NIDDK Workshop on Trial Methodology. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;7(5):844–50.
Khwaja A. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron. 2012;120(4):c179–84.
Goldstein SL, Chawla L, Ronco C, Kellum JA. Renal recovery. Crit Care. 2014;18(1):301. doi: 10.1186/cc13180.
Chawla LS, Eggers PW, Star RA, Kimmel PL. Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease as Interconnected Syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(1):58–66.
Kellum JA. How Can We Define Recovery after Acute Kidney Injury? Considerations from Epidemiology and Clinical Trial Design. Nephron Clin Pract. 2014;127(1–4):81–8.
Hsu C, Hsu RK, Yang J, Ordonez JD, Zheng S, Go AS. Elevated BP after AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(3):914–23.
Go AS, Hsu C, Yang J, Tan TC, Zheng S, Ordonez JD, et al. Acute Kidney Injury and Risk of Heart Failure and Atherosclerotic Events. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;13(6):833–41.
Legrand M, Rossignol P. Cardiovascular Consequences of Acute Kidney Injury. Ingelfinger JR, editor. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(23):2238–47.
Fiorentino M, Tohme FA, Wang S, Murugan R, Angus DC, Kellum JA. Long-term survival in patients with septic acute kidney injury is strongly influenced by renal recovery. Ricci Z, editor. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(6):e0198269. doi: 10.1371/journal. pone.0198269.
Kellum JA, Chawla LS, Keener C, Singbartl K, Palevsky PM, Pike FL, et al. The Effects of Alternative Resuscitation Strategies on Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Septic Shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193(3):281–7.
Sood MM, Shafer LA, Ho J, Reslerova M, Martinka G, Keenan S, et al. Early reversible acute kidney injury is associated with improved survival in septic shock. J Crit Care. 2014;29(5):711–7.
Chen JCY, Hu B, Frank RD, Kashani KB. Inpatient Kidney Function Recovery among Septic Shock Patients Who Initiated Kidney Replacement Therapy in the Hospital. Nephron. 2020;144(8):363–71.
Sukmark T, Lumlertgul N, Praditpornsilpa K, Tungsanga K, Eiam-Ong S, Srisawat N. SEA-MAKE score as a tool for predicting major adverse kidney events in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: results from the SEA-AKI study. Ann Intensive Care. 2020;10(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13613-020-00657-9.
Alobaidi R, Basu RK, Goldstein SL, Bagshaw SM. Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury. Semin Nephrol. 2015;35(1):2–11.
Pannu N, James M, Hemmelgarn B, Klarenbach S, for the Alberta Kidney Disease Network. Association between AKI, Recovery of Renal Function, and Long-Term Outcomes after Hospital Discharge. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;8(2):194–202.
de Boer IH, Caramori ML, Chan JCN, Heerspink HJL, Hurst C, Khunti K, et al. KDIGO 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2020;98(4):S1–115.
Kellum JA, Sileanu FE, Bihorac A, Hoste EAJ, Chawla LS. Recovery after Acute Kidney Injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195(6):784–91.
Forni LG, Darmon M, Ostermann M, Oudemans-van Straaten HM, Pettilä V, Prowle JR, et al. Renal recovery after acute kidney injury. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43(6):855–66.
Herrmann FR. Serum Albumin Level on Admission as a Predictor of Death, Length of Stay, and Readmission. Arch Intern Med. 1992;152(1):125-30.
Lee C-W, Kou H, Chou H-S, Chou H, Huang S-F, Chang C-H, et al. A combination of SOFA score and biomarkers gives a better prediction of septic AKI and in-hospital mortality in critically ill surgical patients: a pilot study. World J Emerg Surg. 2018;13(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13017-018-0202-5.