The Effect of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist as Add-on Therapy to SGLT-2 Inhibitor on Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes with Chronic Kidney Disease
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: The effectiveness GLP-1 receptor agonist as an add-on therapy to SGLT-2 inhibitor in reducing albuminuria in diabetic kidney disease remains largely underexplored. This trial aims to evaluate the impact of this dual therapy compared to SGLT-2 inhibitor alone on albuminuria reduction over 6 months in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included patients with type 2 diabetes and albuminuria between January 2018 and December 2023. A total of 122 patients who received either SGLT-2 inhibitors alone or in combination with GLP-1 receptor agonists were included. The primary outcome was the difference in the mean percent change in the urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) at 6 months. Secondary outcomes included changes in HbA1c, blood pressure, body weight, serum creatinine, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and adverse events.
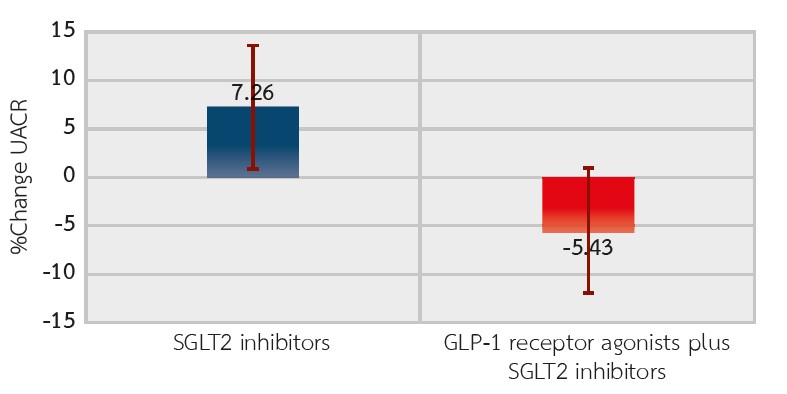
Results: The mean percent change in UACR from baseline was 7.26% (-21.84, 36.36) in the SGLT-2 inhibitor group and -5.43% (-28.1, 17.25) in the combination therapy group. The between-group difference was -12.7% (-48.8, 23.4) (P=0.491). While the combination group showed a trend toward HbA1c and blood pressure reductions, these differences did not reach statistical significance. Neither group had significant changes in body weight, serum creatinine, or eGFR. Adverse events were similar between the two groups.
Conclusion: Adding GLP-1 receptor agonist to SGLT-2 inhibitor did not significantly reduce albuminuria, blood pressure, or HbA1C after 6 months of follow-up in patients with diabetic kidney disease.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This article is published under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, which allows for non-commercial reuse of the published paper as long as the published paper is fully attributed. Anyone can share (copy and redistribute) the material in any medium or format without having to ask permission from the author or the Nephrology Society of Thailand.
References
Brown E, Heerspink HJL, Cuthbertson DJ, Wilding JPH. SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists: established and emerging indications. Lancet. 2021;398(10296):262-76.
Palmer BF. Change in albuminuria as a surrogate endpoint for cardiovascular and renal outcomes: A meta-analysis of 34 clinical trials involving 66,273 participants. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2022;16(2):116-24.
de Boer IH, Khunti K, Sadusky T, Tuttle KR, Neumiller JJ, Rhee CM, et al. Diabetes management in chronic kidney disease: a consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Diabetes Care. 2020;45(12):3075-90.
Cowie MR, Fisher M. SGLT2 inhibitors: mechanisms of cardiovascular benefit beyond glycemic control. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17(12):761-72.
Drucker DJ. Mechanisms of action and therapeutic application of glucagon-like peptide-1. Cell Metab. 2018;27(4):740-56.
Muskiet MHA, Tonneijck L, Smits MM, van Baar MJB, Kramer MHH, Hoorn EJ, et al. GLP-1 and the kidney: from physiology to pharmacology and outcomes in diabetes. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13(10):605-28.
Thomas MC. The potential and pitfalls of GLP-1 receptor agonists for renal protection in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2017;43Suppl1:2S20-7.
Muskiet MHA, Tonneijck L, Smits MM, van Baar MJB, Kramer MHH, Hoorn EJ, et al. GLP-1 and the kidney: from physiology to pharmacology and outcomes in diabetes. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13(10):605-28.
Mann JFE, Ørsted DD, Brown-Frandsen K , Marso SP, Poulter NR, Rasmussen S, et al. Liraglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(9):839-48.
Davies MJ, Aroda VR, Collins BS, Gabbay RA, Green J, Maruthur NM, et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia. 2022;65(12):1925-66.
Heerspink HJL, Greene T, Tighiouart H, Gansevoort RT, Coresh J, Simon AL, et al. Change in albuminuria as a surrogate endpoint for progression of kidney disease: a meta-analysis of treatment effects in randomised clinical trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(2):128-39.
Andersen TB, JØdal L, Nielsen NS, Petersen LJ. Comparison of simultaneous plasma clearance of (99m)Tc-DTPA and (51) Cr-EDTA: can one tracer replace the other? Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2019;79(7):463-7.
van der Aart-van der Beek AB, Apperloo E, Jongs N, Rouw DB, Sjöström CD, Friedli I, et al. Albuminuria-lowering effect of dapagliflozin, exenatide, and their combination in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized cross-over clinical study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023;25(6):1758-68.
Wheeler DC, Stefánsson BV, Jongs N, Chertow GM, Greene T, Hou FF, et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on major adverse kidney and cardiovascular events in patients with diabetic and non-diabetic chronic kidney disease: a prespecified analysis from the DAPA-CKD trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9(1):22-31.
Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(24):2295-2306.
Herrington WG, Staplin N, Wanner C, Green JB, Hauske SJ, Emberson JR, et al. Empagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(2):117-27.
van der Aart-van der Beek AB, Apperloo E, Jongs N, Rouw DB, Sjöström CD, Friedli I, et al. Albuminuria-lowering effect of dapagliflozin, exenatide, and their combination in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized cross-over clinical study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023;25(6):1758-68.
van Ruiten CC, van der Aart-van der Beek AB, IJzerman RG, Nieuwdorp M, Hoogenberg K, van Raalte DH, et al. Effect of exenatide twice daily and dapagliflozin, alone and in combination, on markers of kidney function in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: A prespecified secondary analysis of a randomized controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021;23(8):1851-8.
Sivalingam S, Wasehuus VS, Curovic VR, Blond MB, Hansen TW, Persson F, et al. Albuminuria-lowering effect of adding semaglutide on top of empagliflozin in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A randomized and placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024;26(1):54-64.
van der Aart-van der Beek AB, van Raalte DH, Guja C, Hoogenberg K, Suchower LJ, Hardy E, et al. Exenatide once weekly decreases urinary albumin excretion in patients with type 2 diabetes and elevated albuminuria: pooled analysis of randomized active controlled clinical trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020;22(9):1556-66.
Pfeffer MA, Claggett B, Diaz R, Dickstein K, Gerstein HC, Køber LV, et al. Lixisenatide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Acute Coronary Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(23):2247-57.
Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JFE, Nauck MA, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(4):311-22.
Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jódar E, Leiter LA, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(19):1834-44.
Gullaksen S, Vernstrøm L, Sørensen SS, Ringgaard S, Laustsen C, Funck KL, et al. Separate and combined effects of semaglutide and empagliflozin on kidney oxygenation and perfusion in people with type 2 diabetes: a randomised trial. Diabetologia. 2023;66(5):813-25.
Frías JP, Guja C, Hardy E, Ahmed A, Dong F, Öhman P, et al. Exenatide once weekly plus dapagliflozin once daily versus exenatide or dapagliflozin alone in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy (DURATION-8): a 28-week, multicentre, double-blind, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016;4(12):1004-16.
Zinman B, Bhosekar V, Busch R, Holst I, Ludvik B, Thielke D, et al. Semaglutide once weekly as add-on to SGLT-2 inhibitor therapy in type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 9): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(5):356-67.