Chronic Active Antibody-Mediated Rejection and Kidney Allograft Survival: A 14-Year Single-Center Retrospective Analysis
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Chronic active antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR) is a significant cause of graft loss in kidney transplants. The current treatment strategies have not been very effective. The present study examined kidney allograft survival after diagnosis and treatment of chronic active ABMR and explored factors associated with allograft survival.
Methods: 144 kidney transplants were identified from 2007 to 2021. Thirty patients had ABMR, and 15 cases in 12 patients were classified as having chronic active ABMR according to the 2017 Banff classification.
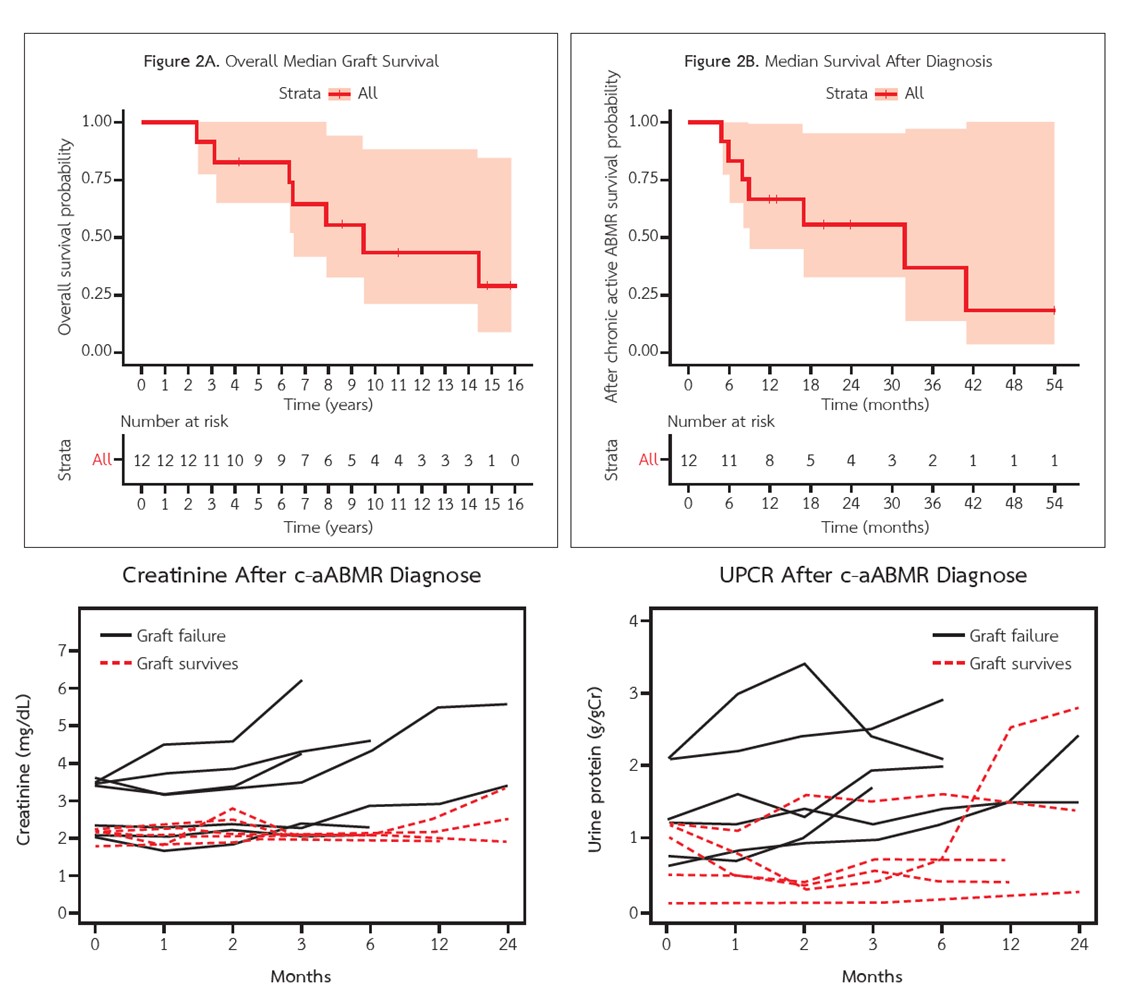
Results: The average time from transplantation to the diagnosis of chronic active ABMR was six years. The median graft survival after the diagnosis was 2.6 years. Fifty-eight percent of the patients lost their grafts. The average serum creatinine and urine protein/creatinine ratio at the time of diagnosis of chronic active ABMR were 2.6 mg/dL and 1.5 g/g, respectively. Higher serum creatinine was the only factor significantly associated with graft failure. The association between heavier proteinuria and graft loss was also noted, but the difference did not reach statistical significance.
Conclusion: Chronic active ABMR was associated with poor graft survival. Decreased allograft function at diagnosis was significantly associated with graft failure.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This article is published under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, which allows for non-commercial reuse of the published paper as long as the published paper is fully attributed. Anyone can share (copy and redistribute) the material in any medium or format without having to ask permission from the author or the Nephrology Society of Thailand.
References
Gruessner AC, Gruessner RWG. Comment on the Article “OPTN/SRTR 2015 Annual Data Report: Pancreas.” Am J Transplant. 2017;17(7):1952–3.
Wiebe C, Gibson IW, Blydt-Hansen TD, Karpinski M, Ho J, Storsley LJ, et al. Evolution and Clinical Pathologic Correlations of De Novo Donor-Specific HLA Antibody Post Kidney Transplant. Am J Transplant. 2012;12(5):1157–67.
Sellarés J, de Freitas DG, Mengel M, Reeve J, Einecke G, Sis B, et al. Understanding the Causes of Kidney Transplant Failure: The Dominant Role of Antibody-Mediated Rejection and Nonadherence. Am J Transplant. 2012;12(2):388–99.
Schinstock CA, Mannon RB, Budde K, Chong AS, Haas M, Knechtle S, et al. Recommended Treatment for Antibodymediated Rejection After Kidney Transplantation: The 2019 Expert Consensus From the Transplantion Society Working Group. Transplantation. 2020;104(5):911–22.
Chiu HF, Wen MC, Wu MJ, Chen CH, Yu TM, Chuang YW, et al. Treatment of chronic active antibody-mediated rejection in renal transplant recipients – a single center retrospective study. BMC Nephrol. 2020;21(1):6.
Redfield RR, Ellis TM, Zhong W, Scalea JR, Zens TJ, Mandelbrot D, et al. Current outcomes of chronic active antibody mediated rejection – A large single center retrospective review using the updated BANFF 2013 criteria. Hum Immunol. 2016;77(4):346–52.
Yilmaz VT, Dandin O, Kisaoglu A, Avanaz A, Kamaci D, Toru HS, et al. Prognosis and Treatment for Active and Chronic Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Renal Transplant Recipients; Single Center Experience. Transplant Proc. 2022;54(7):1809–15.
Sazpinar O, Gaspert A, Sidler D, Rechsteiner M, Mueller TF. Histologic and Molecular Patterns in Responders and Non-responders With Chronic-Active Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Kidney Transplants. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:820085.