Factors Associated with Low Trabecular Bone Score in Patients Receiving Maintenance Hemodialysis
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Low bone mineral density (BMD) is common among maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) patients and associated with increased fracture risk and mortality. However, BMD does not provide information on bone quality. The dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA)-derived lumbar spine trabecular bone score (TBS) facilitates the assessment of bone quality. The present study examined BMD, TBS, and factors associated with low TBS in MHD patients.
Methods: This is a single-center, cross-sectional study of 132 MHD patients. Areal BMD and lumbar spine TBS were determined by DXA. The degree of abdominal aortic calcification (AAC) was evaluated in a lateral lumbar spine radiograph using Kauppila score.
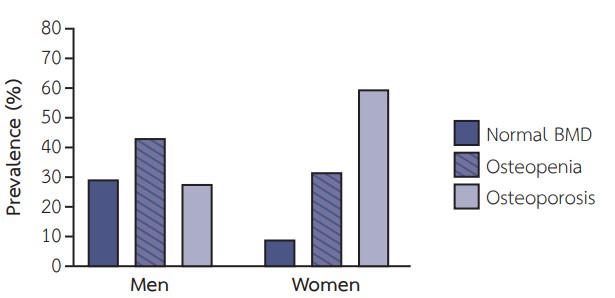
Results: The median age was 67 years and 35.3% were women. The average dialysis vintage was 4.9+5.9 years. The prevalence of osteoporosis was 39.2%. Higher prevalence of osteoporosis was observed in women (women 59.6% vs. men 27.9%). The prevalence of low TBS (<1.31) was 33.8%. TBS was also significantly lower in women (women 1.29+0.12 vs. men 1.40+0.12; P<0.001). The group of patients with low TBS showed higher percentage of female and higher serum cholesterol, alkaline phosphatase, and homocysteine compared with the group with normal TBS. Serum calcium, phosphate, magnesium, parathyroid hormone, 25-hydroxyvitamin D, and beta-2-microglobulin were comparable between the two groups. The prevalence of severe AAC (Kauppila scores ≥6) was 52.6%. There were no correlations between AAC score with BMD or TBS. In multivariate analysis, female sex was the only independent predictor of low TBS.
Conclusions: Low TBS was observed in approximately one-third of MHD patients. Female sex was the only independent predictor of low TBS. There were no correlations between mineral parameters and AAC with TBS. Whether low TBS could predict fracture risk will require further study.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This article is published under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license, which allows for non-commercial reuse of the published paper as long as the published paper is fully attributed. Anyone can share (copy and redistribute) the material in any medium or format without having to ask permission from the author or the Nephrology Society of Thailand.
References
Ketteler M, Block GA, Evenepoel P, Fukagawa M, Herzog CA, McCann L, et al. Executive Summary of the 2017 KDIGO Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Guideline Update: What’s Changed and Why It Matters. Kidney Int. 2017;92(1):26-36.
Jamal SA, Hayden JA, Beyene J. Low Bone Mineral Density and Fractures in Long-Term Hemodialysis Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49(5):674-81.
Ramalho J, Marques IDB, Hans D, Dempster D, Zhou H, Patel P, et al. The Trabecular Bone Score: Relationships with Trabecular and Cortical Microarchitecture Measured by Hr-Pqct and Histomorphometry in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Bone. 2018;116:215-20.
Brunerova L, Ronova P, Veresova J, Beranova P, Potoekova J, Kasalicky P, et al. Osteoporosis and Impaired Trabecular Bone Score in Hemodialysis Patients. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2016;41(3):345-54.
Yavropoulou MP, Vaios V, Pikilidou M, Chryssogonidis I, Sachinidou M, Tournis S, et al. Bone Quality Assessment as Measured by Trabecular Bone Score in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease on Dialysis. J Clin Densitom. 2017;20(4):490-7.
Aleksova J, Kurniawan S, Elder GJ. The Trabecular Bone Score Is Associated with Bone Mineral Density, Markers of Bone Turnover and Prevalent Fracture in Patients with End Stage Kidney Disease. Osteoporos Int. 2018;29(6):1447-55.
Yoon HE, Kim Y, Shin SJ, Hong YS, Kang KY. Factors Associated with Low Trabecular Bone Scores in Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019;37(3):475-83.
Naylor KL, Prior J, Garg AX, Berger C, Langsetmo L, Adachi JD, et al. Trabecular Bone Score and Incident Fragility Fracture Risk in Adults with Reduced Kidney Function. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11(11):2032-40.
Kauppila LI, Polak JF, Cupples LA, Hannan MT, Kiel DP, Wilson PW. New Indices to Classify Location, Severity and Progression of Calcific Lesions in the Abdominal Aorta: A 25-Year Follow-up Study. Atherosclerosis. 1997;132(2):245-50.
Kanis JA. Assessment of Fracture Risk and Its Application to Screening for Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: Synopsis of a WHO Report. WHO Study Group. Osteoporos Int. 1994;4(6):368-81.
McCloskey EV, Oden A, Harvey NC, Leslie WD, Hans D, Johansson H, et al. A Meta-Analysis of Trabecular Bone Score in Fracture Risk Prediction and Its Relationship to FRAX. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(5):940-8.
Abdalbary M, Sobh M, Elnagar S, Elhadedy MA, Elshabrawy N, Abdelsalam M, et al. Management of Osteoporosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Osteoporos Int. 2022;33(11):2259-74.
Iseri K, Qureshi AR, Dai L, Ripsweden J, Heimburger O, Barany P, et al. Bone Mineral Density at Different Sites and 5 Years Mortality in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients: A Cohort Study. Bone. 2020;130:115075.
Lorentzon M, Cummings SR. Osteoporosis: The Evolution of a Diagnosis. J Intern Med. 2015;277(6):650-61.
Malluche HH, Porter DS, Pienkowski D. Evaluating Bone Quality in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013;9(11):671-80.
Perez-Saez MJ, Herrera S, Prieto-Alhambra D, Vilaplana L, Nogues X, Vera M, et al. Bone Density, Microarchitecture, and Material Strength in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients at the Time of Kidney Transplantation. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(9):2723-7.
Aleksova J, Ebeling PR, Milat F, Elder GJ. Dxa-Derived Advanced Hip Analysis and the Trabecular Bone Score in End-Stage Kidney Disease Secondary to Type 1 Diabetes. Eur J Endocrinol. 2022;187(6):883-92.
Yun HJ, Ryoo SR, Kim JE, Choi YJ, Park I, Shin GT, et al. Trabecular Bone Score May Indicate Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (Ckd-Mbd) Phenotypes in Hemodialysis Patients: A Prospective Observational Study. BMC Nephrol. 2020;21(1):299.
Behera J, Bala J, Nuru M, Tyagi SC, Tyagi N. Homocysteine as a Pathological Biomarker for Bone Disease. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(10):2704-9.
Bai J, Zhang A, Zhang Y, Ren K, Ren Z, Zhao C, et al. Abdominal Aortic Calcification Score Can Predict All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients. Ren Fail. 2023;45(1):2158869.
Atta MG. A Molecular Target of Vascular Calcification in Chronic Kidney Disease. J Clin Invest. 2022;132(1):e156257.
Cannata-Andia JB, Roman-Garcia P, Hruska K. The Connections between Vascular Calcification and Bone Health. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(11):3429-36.
Cejka D, Weber M, Diarra D, Reiter T, Kainberger F, Haas M. Inverse Association between Bone Microarchitecture Assessed by HR-pQCT and Coronary Artery Calcification in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease. Bone. 2014;64:33-8.
Barreto DV, Barreto Fde C, Carvalho AB, Cuppari L, Draibe SA, Dalboni MA, et al. Association of Changes in Bone Remodeling and Coronary Calcification in Hemodialysis Patients: A Prospective Study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;52(6):1139-50.
Aleksova J, Kurniawan S, Vucak-Dzumhur M, Kerr P, Ebeling PR, Milat F, et al. Aortic Vascular Calcification Is Inversely Associated with the Trabecular Bone Score in Patients Receiving Dialysis. Bone. 2018;113:118-23.