A study of correlation between Cholelithiasis and Fatty liver from ultrasonography of patients in Vajira Hospital
Main Article Content
Abstract
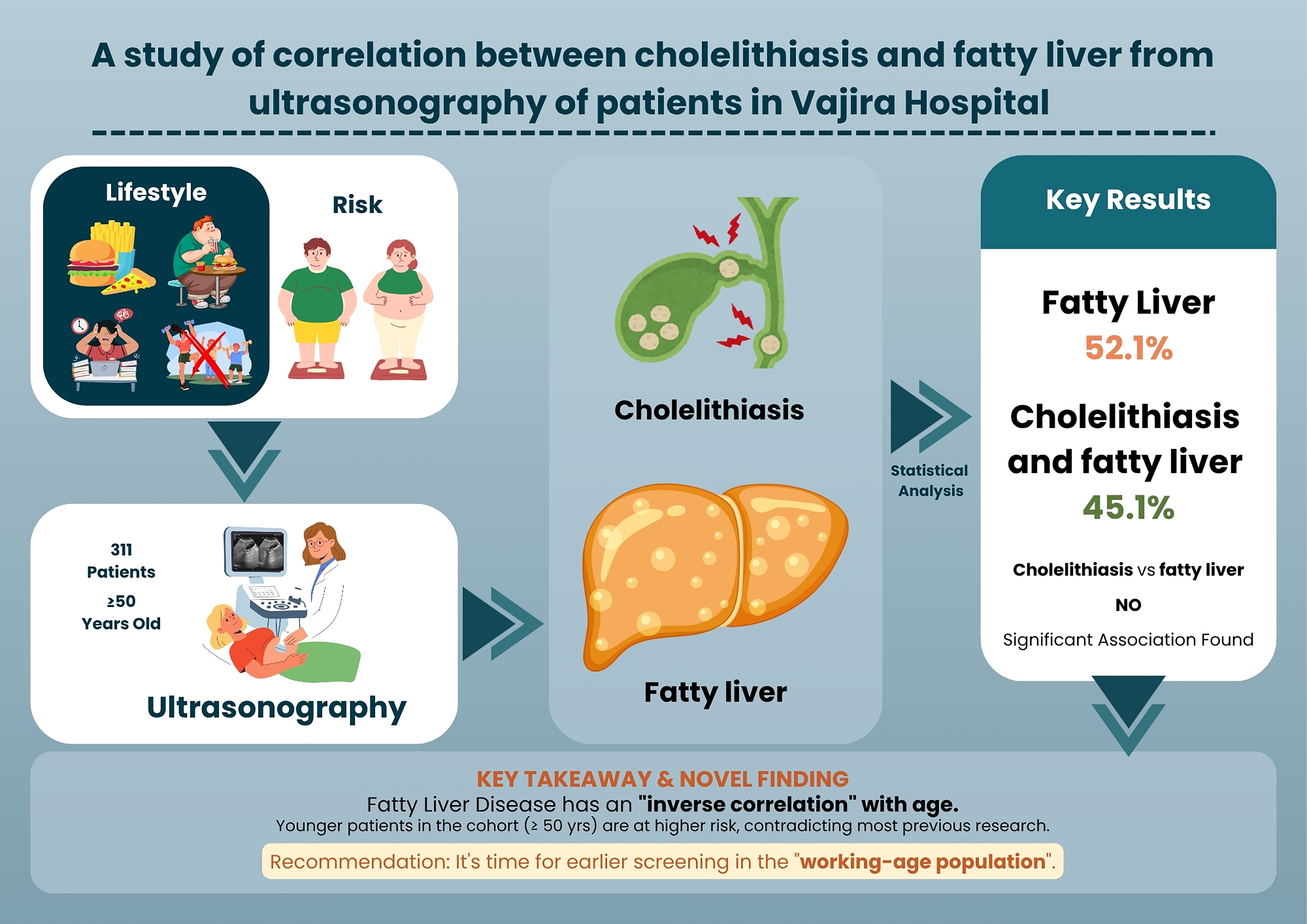
Background: The rising consumption of Western-style fast food—high in carbohydrates, sugar, and fat—together with a fast-paced lifestyle, occupational stress, and physical inactivity, represents a major risk factor for fatty liver disease, which can progress to hepatitis, cirrhosis, or hepatocellular carcinoma. Evidence linking fatty liver and cholelithiasis is growing globally, yet data from Thailand and Southeast Asia remain scarce, despite both conditions being increasingly prevalent. Cholelithiasis, a common gastrointestinal disorder affecting 5–10% of the Thai population, particularly females and older adults, may also be associated with fatty liver disease.
Objectives: This study investigated the correlation between cholelithiasis and fatty liver disease using ultrasonographic data from patients at Vajira Hospital, aiming to address this regional knowledge gap and inform preventive strategies.
Materials and methods: A retrospective analysis was performed on 311 patients aged ≥50 years who underwent upper abdominal ultrasonography at Vajira Hospital between 2023 and 2024. Collected data included gender, age, gallstone size, and diagnostic findings. Patients were classified into two groups: 132 with cholelithiasis and 179 without. Statistical analyses included descriptive statistics (mean, SD, frequency, percentage) and inferential tests (t-test, chi-square test, and logistic regression).
Results: Of the 311 patients, 162 (52.1%) had fatty liver, with a mean age of 62±8.46 years; 62.3% were female and 37.7% were male. Among these, 73 patients (45.1%) had concurrent cholelithiasis (66% female, 34% male), with a mean gallstone size of 1.09±0.53 cm. The remaining 89 patients (54.9%) had fatty liver disease without cholelithiasis (60% female, 40% male). A significant inverse association was observed between age and fatty liver disease (p=0.003), indicating that younger patients within this ≥50-year cohort were more likely to be affected.
Conclusion: Cholelithiasis was not significantly associated with fatty liver disease. However, fatty liver showed a novel inverse correlation with age, with higher prevalence among younger adults within the ≥50-year cohort. This finding, which contrasts with previous reports of increasing prevalence with age, may reflect methodological factors and lifestyle influences in Thailand’s urban population. These results emphasize the need for early screening and targeted public health interventions for working-age adults, while acknowledging limitations related to study design, absence of key confounders, and restricted age range.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Personal views expressed by the contributors in their articles are not necessarily those of the Journal of Associated Medical Sciences, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University.
References
Sono S, Kaewdech A, Wongsawanon C, Varanuntakul T, Jarupanich T, Sritanabutr N, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) in the adult population attending a health check-up program in Thailand: prevalence and fibrosis status. Sci Rep. 2025; 15(1): 21429. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06874-1.
Huh Y, Cho YJ, Nam GE. Recent Epidemiology and Risk Factors of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2022; 31(1): 17-27. doi: 10.7570/jomes22021.
Wong VW-S, Ekstedt M, Wong GL-H, Hagström H. Changing epidemiology, global trends and implications for outcomes of NAFLD. J Hepatol. 2023; 79(3): 842-52. doi: 10.1016/ j.jhep.2023.04.036.
Sepehrimanesh M, Niknam R, Ejtehadi F, Fattahi MR, Safarpour A. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome with gallstone disease, South Iran: A populationbased study. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020; 13: 1449-58. doi: 10.2147/dmso.S246949.
Srisubat A, Thaiyakul A, Kwanjaroensub S, Sa-nga N, Paiprarert S, Pinyoteppratarn R, et al. Economic evaluation of laparoscopic cholecystectomy versus open cholecystectomy. J Dept Med Serv. 2023; 48(1): 93-103. doi: 10.14456/jdms.2023.12.
Kichloo A, Solanki S, Haq KF, Dahiya D, Bailey B, Solanki D, et al. Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with gallstone disease in the United States hospitalized patient population. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2021; 12(2): 14-24. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v12.i2.14.
Slouha E, Biput SJ, Kuteyi A, Kalloo AE, Gorantla VR. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and gallstones: A systematic review. Cureus. 2023; 15(9): e45027. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45027.
Hernaez R, Lazo M, Bonekamp S, Kamel I, Brancati FL, Guallar E, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and reliability of ultrasonography for the detection of fatty liver: A meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2011; 54(3): 1082-90. doi: 10.1002/hep.24452.
Pitug B. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and correlation between revalence of NAFLD and obesity in people living in borabue district, Mahasarakham province. Mahasarakham Hosp J. 2019; 14(2): 22-8. Available from: https://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/MKHJ/article/view/204616 [cited 2025 Sep 11].
Chairattanasakun J, Porruan R. The prevalence and associated factors of fatty liver among participants in Cholangiocarcinoma Screening and Care Program (CASCAP) of Mueang Chiang Rai District. Chiangrai Med J. 2024; 16(2): 1-9. Available from: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/crm journal/article/view/261988 [cited 2025 Sep 11].
Ashraf A, Yousaf F, Omer M, Bacha DR, Waseem M, Ullah K, et al. Sonographic association between fatty liver and gall bladder stones among all adult patients visiting private clinics of Lahore City. Health Med Sci. 2019; 2: 21-6. doi: 10.31014/aior.1994.02.01.15.
Wang HH, Liu M, Clegg DJ, Portincasa P, Wang DQ. New insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying effects of estrogen on cholesterol gallstone formation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009; 1791(11): 1037-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.06.006.
Sun H, Warren J, Yip J, Ji Y, Hao S, Han W, et al. Factors influencing gallstone formation: A review of the literature. Biomolecules. 2022;12(4): 550. doi: 10.3390/biom12040550.
Dong J, Dennis KMJH, Venkatakrishnan R, Hodson L, Tomlinson JW. The impact of estrogen deficiency on liver metabolism: Implications for hormone replacement therapy. Endocr Rev. 2025; Epub ahead of print. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnaf018.
Kim SE, Min JS, Lee S, Lee DY, Choi D. Different effects of menopausal hormone therapy on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on the route of estrogen administration. Sci Rep. 2023; 13(1): 15461. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42788-6.
Kasarinaite A, Sinton M, Saunders PTK, Hay DC. The influence of sex hormones in liver function and disease. Cells. 2023; 12(12): 1604. doi: 10.3390/cells12121604.
Charatcharoenwitthaya P, Kuljiratitikal K, Aksornchanya O, Chaiyasoot K, Bandidniyamanon W, Charatcharoenwitthaya N. Moderate-intensity aerobic vs resistance exercise and dietary modification in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized clinical trial. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2021; 12(3): e00316. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000316.
Katsagoni CN, Georgoulis M, Papatheodoridis GV, Panagiotakos DB, Kontogianni MD. Effects of lifestyle interventions on clinical characteristics of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Metabolism. 2017; 68: 119-32. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2016.12.006.
Rattanangamkul M. Relation of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and metabolic syndrome in Thais.: College of Integrative Medicine, Dhurakij Pundit University; 2017.
Kim YK, Kwon OS, Her KH. The grade of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is an independent risk factor for gallstone disease: An observational Study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98(27): e16018. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000016018.
Li X, Gao P. Fatty liver increases gallstone disease risk in younger Chinese patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98(22): e15940. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000015940.
Hallsworth K, Adams LA. Lifestyle modification in NAFLD/NASH: Facts and figures. JHEP Rep. 2019; 1(6): 468-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2019.10.008.
Jindarattanaporn N, Phulkerd S, Chamratrithirong A, Soottipong Gray R, Pattaravanich U, Loyfah N, et al. How an agreement with restriction of unhealthy food marketing and sodium taxation influenced high fat, salt or sugar (HFSS) food consumption. BMC Public Health. 2024; 24(1): 586. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18069-w.
Lim GY, Chang Y, Kim I, Ryu S, Kwon R, Song J. Long working hours and increased risks of lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease among Korean men and women. Sci Rep. 2023; 13(1): 12230. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39154-x.
Ling Z, Zhang C, He J, Ouyang F, Qiu D, Li L, et al. Association of healthy lifestyles with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective cohort study in Chinese government employees. Nutrients. 2023; 15(3): 604. doi: 10.3390/nu15030604.
Rehman T, Shafi S, Amwar M, Nazeer M, Hanjra H, Hassan S, et al. Sonographic evaluation of cholelithiasis and its correlation with normal/fatty liver. Int J Health Med Nurs Pract. 2021; 91: 51-60. doi: 10.7176/JHMN/91-07.
Lu Y, Hu L, Song J, Wan J, Chen H, Yin J. Gallstone disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr Disord. 2021; 21(1): 231. doi: 10.1186/s12902-021-00899-z.