Enhanced detection of Trypanosoma evansi in Cattle: Superior performance of LAMP compared to PCR and CATT/T. evansi test
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Trypanosoma evansi, the causative agent of surra, poses a major veterinary concern in tropical regions, particularly affecting cattle and buffalo. The disease leads to reproductive failures, including abortion, and significant economic losses. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective control, especially in endemic, resource-limited areas.
Objectives: This study aimed to develop a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for rapid detection of T. evansi and evaluate its diagnostic performance in comparison with conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and the CATT/T. evansi card agglutination test.
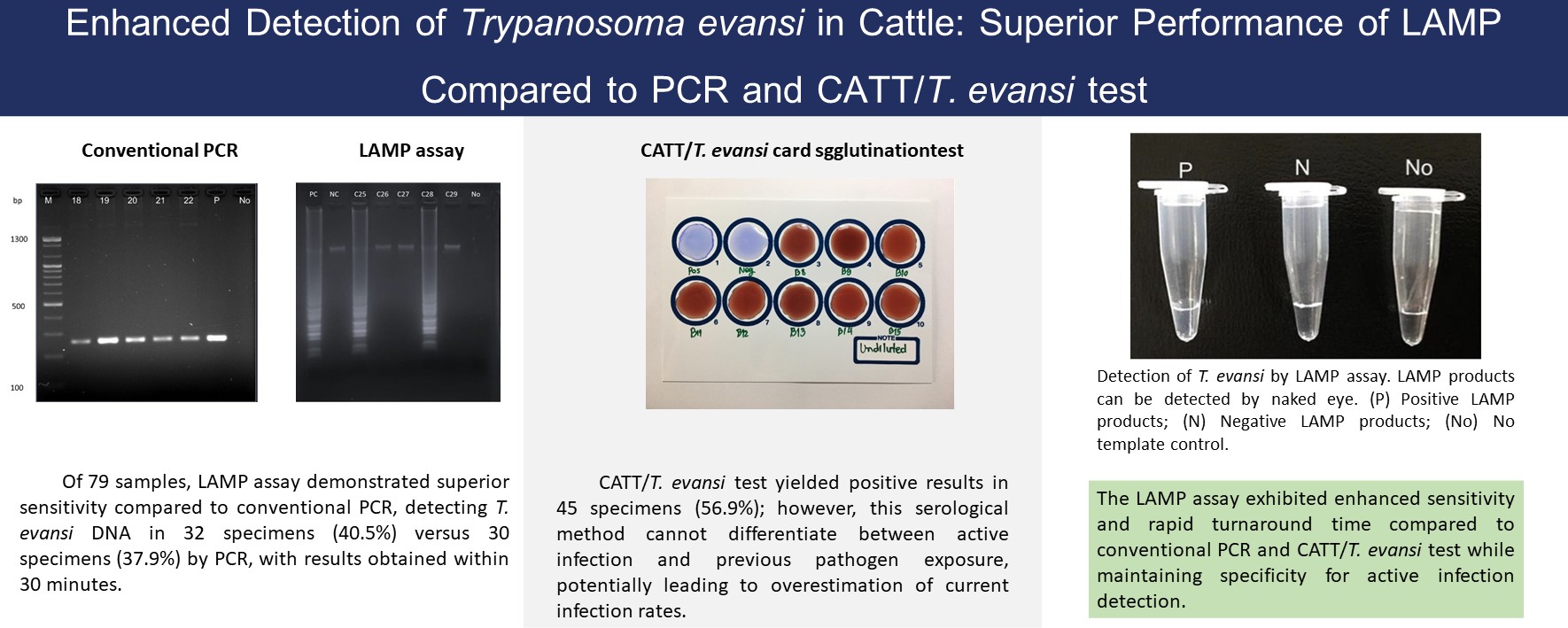
Materials and methods: Four LAMP primers were designed to target the RoTat 1.2 variant surface glycoprotein (VSG) gene of T. evansi. Optimal reaction parameters, including temperature and incubation time, were established. The LAMP assay, conventional PCR, and the CATT/T. evansi card agglutination test were performed on 79 blood samples collected from cattle with suspected trypanosomiasis in northern Thailand (Lamphun and Chiang Mai). Diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, and agreement between tests were statistically analyzed.
Results: The LAMP assay detected T. evansi in 32 (40.5%, 95% CI: 29.8-51.9%) samples, slightly outperforming PCR, which detected 30 (37.9%, 95% CI: 27.6-49.0%). However, this difference was not statistically significant (McNemar’s test, p=0.724). The CATT/T. evansi test yielded 45 (56.9%) positives but lacked the ability to differentiate active infection from prior exposure.
Conclusion: The LAMP assay demonstrated high sensitivity, specificity, and rapid detection capabilities under simplified conditions, making it highly suitable for field applications. When paired with colorimetric or lateral flow readouts, LAMP offers a promising point-of-care diagnostic tool for improving trypanosomiasis control in endemic regions.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Personal views expressed by the contributors in their articles are not necessarily those of the Journal of Associated Medical Sciences, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University.
References
Lun ZR, Fang Y, Wang CJ, Brun R. Trypanosomiasis of domestic animals in China. Parasitol Today. 1993; 9(2): 41-5.
Aregawi WG, Agga GE, Abdi RD, Büscher P. Systematic review and meta-analysis on the global distribution, host range, and prevalence of Trypanosoma evansi. Parasit Vectors. 2019; 12(1): 67.
Davison HC, Thrusfield MV, Husein A, Muharsini S, Partoutomo S, Rae P, et al. The occurrence of Trypanosoma evansi in buffaloes in Indonesia, estimated using various diagnostic tests. Epidemiol Infect. 2000; 124(1): 163-72.
Desquesnes M, Holzmuller P, Lai DH, Dargantes A, Lun ZR, Jittaplapong S. Trypanosoma evansi and surra: a review and perspectives on origin, history, distribution, taxonomy, morphology, hosts, and pathogenic effects. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013: 194176.
Joshi PP, Shegokar VR, Powar RM, Herder S, Katti R, Salkar HR, et al. Human trypanosomiasis caused by Trypanosoma evansi in India: the first case report. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005; 73(3): 491-5.
Ngaira JM, Olembo NK, Njagi EN, Ngeranwa JJ. The detection of non-RoTat 1.2 Trypanosoma evansi. Exp Parasitol. 2005; 110(1): 30-8.
Monzón CM, Mancebo OA, Roux JP. Comparison between six parasitological methods for diagnosis of Trypanosoma evansi in the subtropical area of Argentina. Vet Parasitol. 1990; 36(1-2): 141-6.
Omanwar S, Rao JR, Basagoudanavar SH, Singh RK, Butchaiah G. Direct and sensitive detection of Trypanosoma evansi by polymerase chain reaction. Acta Vet Hung. 1999; 47(3): 351-9.
Verloo D, Magnus E, Büscher P. General expression of RoTat 1.2 variable antigen type in Trypanosoma evansi isolates from different origin. Vet Parasitol. 2001; 97(3): 183-9.
Reid SA, Husein A, Copeman DB. Evaluation and improvement of parasitological tests for Trypanosoma evansi infection. Vet Parasitol. 2001; 102(4): 291-7.
Zayed AA, Habeeb SM, Allam NAT, Ashry HM, Mohamed AH, Ashour AA, et al. A critical comparative study of parasitological and serological differential diagnostic methods of Trypanosoma evansi infections in some farm animals in Egypt. Am-Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci. 2010; 8(6): 633-42.
Holland WG, My LN, Dung TV, Thanh NG, Tam PT, Vercruysse J, et al. The influence of ambient temperature on the performance of the polymerase chain reaction for the diagnosis of Trypanosoma evansi infections in experimentally infected water buffalo. Vet Parasitol. 2001; 102(4): 331-40.
Pirolo M, Menezes M, Poulsen M, Søndergaard V, Damborg P, Poirier AC, et al. A LAMP point-of-care test to guide antimicrobial choice for treatment of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius pyoderma in dogs. Vet J. 2024; 304: 106105.
Ji C, Zhou L, Chen Y, Fang X, Liu Y, Du M, et al. Microfluidic-LAMP chip for the point-of-care detection of gene-deleted and wild-type African swine fever viruses and other four swine pathogens. Front Vet Sci. 2023; 10: 1116352.
Silva-Pereira TC, Martín-Hernández R, Higes M, Camacho-Nuez M, Brandariz S, Graça A, et al. SMART-LAMP: a smartphone-operated handheld device for real-time colorimetric point-of-care diagnosis of infectious diseases via loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022; 214: 114051.
Hartle-Mougiou K, Gubili C, Xanthopoulou P, Kasapidis P, Valiadi M, Gizeli E. Development of a quantitative colorimetric LAMP assay for fast and targeted molecular detection of the invasive lionfish Pterois miles from environmental DNA. Front Mar Sci. 2024; 11: 1358793.
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, Yonekawa T, Watanabe K, Amino N, et al. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000; 28(12): E63.
Mori Y, Nagamine K, Tomita N, Notomi T. Detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by turbidity derived from magnesium pyrophosphate formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001; 289(1): 150-4.
Kiatpathomchai W, Jaroenram W, Arunrut N, Jitrapakdee S, Flegel TW. Shrimp Taura syndrome virus detection by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick. J Virol Methods. 2008; 153(2): 214-7.
Park JY, Park S, Park YR, Kang DY, Kim EM, Jeon HS, et al. Reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) assay for the visual detection of European and North American porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses. J Virol Methods. 2016; 237: 10-13.
Kumar B, Maharana BR, Brahmbhatt NN, Thakre BJ, Parmar VL. Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay based on RoTat1.2 gene for detection ofTrypanosoma evansi in domesticated animals. Parasitol Res. 2021; 120(5): 1873-82.
Njiru ZK, Mikosza AS, Matovu E, Enyaru JC, Ouma JO, Kibona SN, et al. African trypanosomiasis: sensitive and rapid detection of the sub-genus Trypanozoon by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) of parasite DNA. Int J Parasitol. 2008; 38(5): 589-99.
Kim J, Álvarez-Rodríguez A, Li Z, Radwanska M, Magez S. Recent progress in the detection of surra, a neglected disease caused by Trypanosoma evansi with a one health impact in large parts of the tropic and sub-tropic world. Microorganisms. 2023; 12(1): 44.
Matthew MA, Christie J, Yang N, Yao C. A loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay specific to Trichomonas tenax is suitable for use at point-of-care. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(3): 594.
Salim B, Bakheit MA, Kamau J, Nakamura I, Sugimoto C. Molecular epidemiology of camel trypanosomiasis based on ITS1 rDNA and RoTat 1.2 VSG gene in the Sudan. Parasit Vectors. 2011; 4: 31.
Tong Q, Chen R, Kong Q, Goossens J, Radwanska M, Lou D, et al. DNA detection of Trypanosoma evansi: diagnostic validity of a new assay based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Vet Parasitol. 2018; 250: 1-6.
Ordóñez N, Salacinas M, Mendes O, Seidl MF, Meijer HJG, Schoen CD, et al. A loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay based on unique markers derived from genotyping by sequencing data for rapid in planta diagnosis of Panama disease caused by Tropical Race 4 in banana. Plant Pathol. 2019; 68(9): 1682-93.
Kuboki N, Inoue N, Sakurai T, Di Cello F, Grab DJ, Suzuki H, et al. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detection of African trypanosomes. J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 41(12): 5517-24.
Hayashida K, Kajino K, Hachaambwa L, Namangala B, Sugimoto C. Direct blood dry LAMP: a rapid, stable, and easy diagnostic tool for Human African Trypanosomiasis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015; 9(3): e0003578.
Kumagai T, Furushima-Shimogawara R, Ohmae H, Wang TP, Lu S, Chen R, et al. Detection of early and single infections of Schistosoma japonicum in the intermediate host snail, Oncomelania hupensis, by PCR and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010; 83(3): 542-8.
Plutzer J, Karanis P. Rapid identification of Giardia duodenalis by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) from faecal and environmental samples and comparative findings by PCR and real-time PCR methods. Parasitol Res. 2009; 104(6): 1527-33.
Kong QM, Lu SH, Tong QB, Lou D, Chen R, Zheng B, et al. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): early detection of Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice. Parasit Vectors. 2012; 5: 2.
Hilali M, Abdel-Gawad A, Nassar A, Abdel-Wahab A, Magnus E, Büscher P. Evaluation of the card agglutination test (CATT/T. evansi) for detection of Trypanosoma evansi infection in water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) in Egypt. Vet Parasitol. 2004; 121(1-2): 45-51.
Aquino LP, Machado RZ, Lemos KR, Marques LC, Garcia MV, Borges GP. Antigenic characterization of Trypanosoma evansi using sera from experimentally and naturally infected bovines, equines, dogs, and coatis. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet. 2010; 19(2): 112-8.
Verma R, Das G, Singh AP, Kumar S, Nath S, Sengupta PP, et al. Molecular and genetic diversity in isolates of Trypanosoma evansi from naturally infected horse and dogs by using RoTat 1.2 VSG gene in Madhya Pradesh, India. Mol Biol Rep. 2023; 50(9): 7347-56.
Thekisoe OM, Inoue N, Kuboki N, Tuntasuvan D, Bunnoy W, Borisutsuwan S, et al. Evaluation of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), PCR and parasitological tests for detection of Trypanosoma evansi in experimentally infected pigs. Vet Parasitol. 2005; 130(3-4): 327-30.