Single time-point kidney dosimetry in 177Lu-PSMA therapy: A comparison between AI-based and manual segmentation approaches
Main Article Content
Abstract
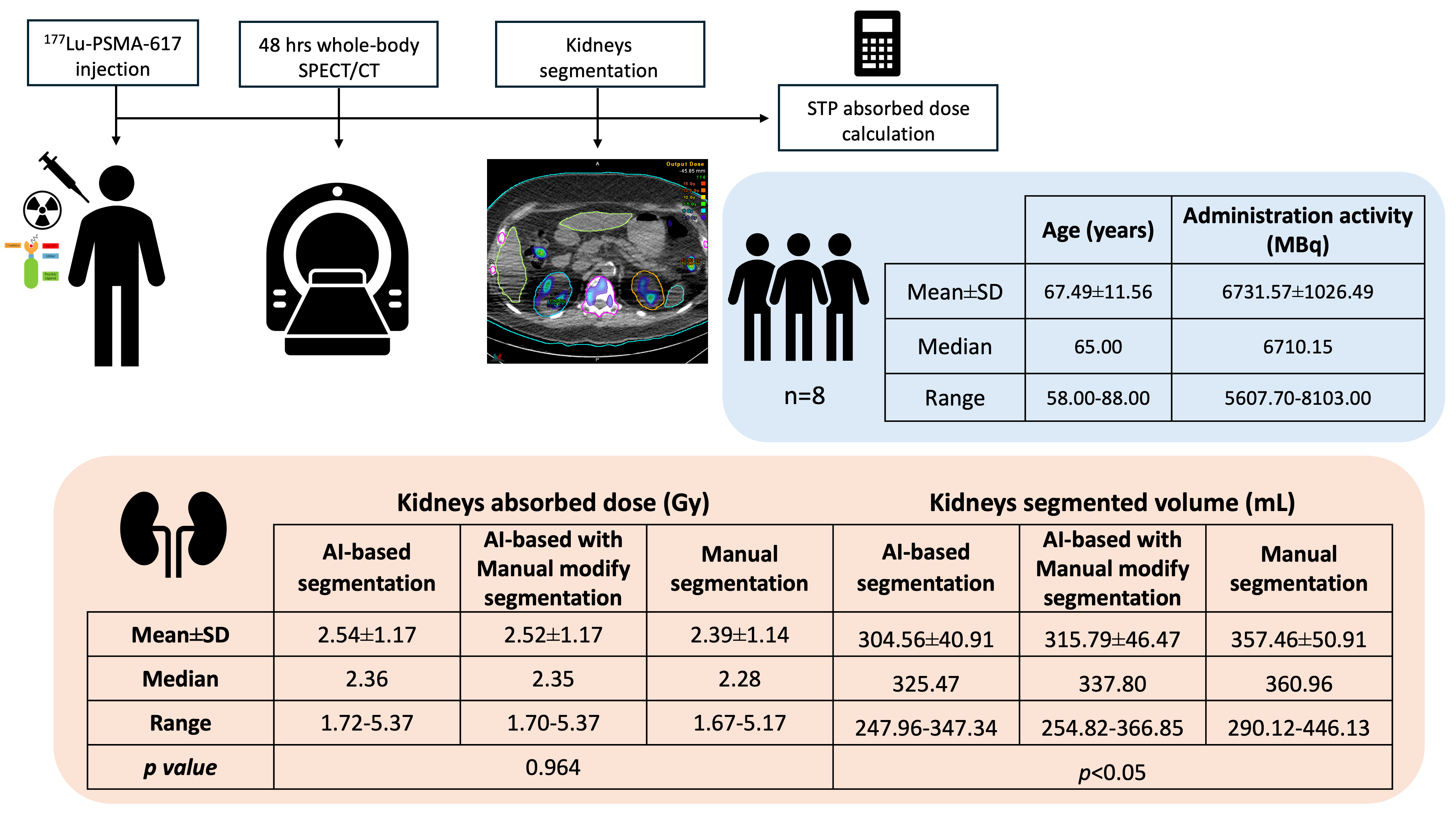
Background: Single time-point (STP) dosimetry has become a practical and efficient approach for personalised radioligand therapy (RLT), with 48-hours post-injection identified as optimal for kidney dose estimation in ¹⁷⁷Lu-PSMA therapy for prostate cancer. However, segmentation accuracy remains a critical factor affecting dosimetry reliability. AI-based segmentation has recently been integrated into commercial software to improve efficiency and reduce variability. Objectives: This study aims to quantify kidney absorbed doses in patients receiving ¹⁷⁷Lu-PSMA therapy using STP dosimetry and to compare the accuracy and consistency of AI-based segmentation versus manual segmentation techniques.
Materials and methods: Eight treatment cycles from 5 patients of ¹⁷⁷Lu-PSMA were retrospectively analysed. In this work, whole-body SPECT/CT imaging was performed approximately 48 hours post-injection. Then, kidney dosimetry was calculated using voxel-based STP (Hänscheid method) within MIM SurePlan™ MRT software. Kidney volumes of interest (VOIs) were segmented using three approaches: 1) AI-based automatic segmentation, 2) AI-based with manual refinement, and 3) fully manual segmentation. Mean absorbed doses and VOI volumes were compared across methods. Statistical analyses included ANOVA, Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC), and Jaccard Similarity Coefficient (JSC).
Results: No significant differences in mean kidney absorbed doses were found across segmentation methods (p=0.964), while kidney VOI volumes showed significant variation (p<0.05). AI-based segmentation achieved high concordance with manual delineation (DSC: 0.898±0.019; JSC: 0.816±0.031).
Conclusion: AI-based segmentation provides comparable absorbed dose results to manual segmentation, with reduced time and inter-observer variability.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Personal views expressed by the contributors in their articles are not necessarily those of the Journal of Associated Medical Sciences, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University.
References
Meyer C, Szidonya L, Winters C, Mench A, Mallak N, Mittra E. Quantitative imaging for 177Lu-PSMA treatment response monitoring and dosimetry. Front Nucl Med. 2023; 3: 1291253. doi: 10.3389/fnume.2023.1291253.
Violet J, Jackson P, Ferdinandus J, Sandhu S, Akhurst T, Iravani A, et al. Dosimetry of 177Lu-PSMA-617 in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Correlations between pretherapeutic imaging and whole-body tumor dosimetry with treatment outcomes. J Nucl Med. 2019; 60(4): 517-23. doi:10.2967/jnumed.118.219352.
Juzeniene A, Stenberg VY, Bruland ØS, Larsen RH. Preclinical and clinical status of PSMA-targeted alpha therapy for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021; 13(4): 779. doi:10.3390/cancers13040779.
Alsadi R, Djekidel M, Bouhali O, Doherty JO. Towards routine clinical use of dosimetry in [177Lu] Lu-PSMA prostate cancer radionuclide therapy: Current efforts and future perspectives. Front Phys. 2022; 10: 1-13 doi:10.3389/fphy.2022.940677.
Ramonaheng K, Qebetu M, Ndlovu H, Swanepoel C, Smith L, Mdanda S, et al. Activity quantification and dosimetry in radiopharmaceutical therapy with reference to 177Lutetium. Front Nucl Med. 2024; 4: 1355912. doi:10.3389/fnume.2024.1355912.
Brosch-Lenz J, Uribe C, Gosewisch A, Kaiser L, Todica A, Ilhan H, et al. Influence of dosimetry method on bone lesion absorbed dose estimates in PSMA therapy: application to mCRPC patients receiving Lu-177-PSMA-I&T. EJNMMI Phys. 2021; 8(1): 26. doi:10.1186/s40658-021-00369-4.
Gustafsson J, Sundlöv A, Sjögreen Gleisner K. SPECT image segmentation for estimation of tumour volume and activity concentration in 177Lu-DOTATATE radionuclide therapy. EJNMMI Res. 2017; 7(1): 18. doi: 10.1186/s13550-017-0262-7.
Siegel JA, Thomas SR, Stubbs JB, Stabin MG, Hays MT, Koral KF, et al. MIRD pamphlet no. 16: Techniques for quantitative radiopharmaceutical biodistribution data acquisition and analysis for use in human radiation dose estimates. J Nucl Med. 1999;40(2):
S-61S.
Hänscheid H, Lapa C, Buck AK, Lassmann M, Werner RA. Dose mapping after endoradiotherapy with 177Lu-DOTATATE/DTATOC by a single measurement after 4 days. J Nucl Med. 2018; 59(1): 75-81. doi:10.2967/jnumed.117.193706.
Brosch-Lenz J, Delker A, Völter F, Unterrainer LM, Kaiser L, Bartenstein P, et al. Toward single-timepoint image-based dosimetry of 177Lu-PSMA-617 therapy. J Nucl Med. 2023; 64(5): 767-74. doi:10.2967/jnumed.122.264594.
Kurth J, Heuschkel M, Tonn A, Schildt A, Hakenberg OW, Krause BJ, et al. Streamlined schemes for dosimetry of 177Lu-labeled PSMA targeting radioligands in therapy of prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021; 13(15): 3884. doi:10.3390/cancers13153884.
Jackson PA, Hofman MS, Hicks RJ, Scalzo M, Violet J. Radiation dosimetry in 177Lu-PSMA-617 therapy using a single treatment SPECT/CT scan: A novel methodology to generate time- and tissue-specific dose factors. J Nucl Med. 2020; 61(7): 1030-6.doi:10.2967/jnumed.119.233411.
Peters SMB, Mink MCT, Privé BM, de Bakker M, de Lange F, Muselaers CHJ, et al. Optimization of the radiation dosimetry protocol in Lutetium-177-PSMA therapy: toward clinical implementation. EJNMMI Res. 2023; 13(1): 6. doi:10.1186/s13550-023-00952-z.
Gawel J, Rogulski Z. The challenge of single-photon emission computed tomography image segmentation in the internal dosimetry of 177Lu molecular therapies. J Imaging. 2024; 10(1): 27-40. doi: 10.3390/jimaging10010027.
Makris NE, van Velden FH, Huisman MC,Menke CW, Lammertsma AA, Boellaard R. Validation of simplified dosimetry approaches in 89 Zr-PET/CT: The use of manual versus semi-automatic delineation methods to estimate organ absorbed doses. Medical Physics. 2014; 41(10): 102503. Doi: 10.1118/1.4895973.
Vomacka L, Gosewisch A, Delker A, Fendler W, Bartenstein P, Boening G. Automatic image segmentation for 3D dosimetry in Lu-177 DKFZ-PSMA 617 therapy of castrate-resistant metastatic prostate cancer using a robust cluster algorithm on 4D SPECT data. J Nucl Med. 2016; 57(suppl2): 497.
Hesamian MH, Jia W, He X, Kennedy P. Deep learning techniques for medical image segmentation: achievements and challenges. J Digit Imaging. 2019; 32(4): 582-96. doi: 10.1007/s10278-019-00227-x.
Danieli R, Milano A, Gallo S, Veronese I, Lascialfari A, Indovina L, et al. Personalized dosimetry in targeted radiation therapy: A look to methods, tools and critical aspects. J Pers Med. 2022; 12(2): 205. doi: 10.3390/jpm12020205.
Wendler T, Kreissl MC, Schemmer B, Rogasch JMM, De Benetti F. Artificial Intelligence-powered automatic volume calculation in medical imagesavailable tools, performance and challenges for nuclear medicine. Nuklearmedizin. 2023; 62(6): 343-53. doi: 10.1055/a-2200-2145.
MIM software Inc. MIM SurePlan™ MRT for Molecular Radiotherapy Dosimetry User Guide.
Dewaraja YK, Mirando DM, Peterson AB, Niedbala J, Millet JD, Mikell JK, et al. A pipeline for automated voxel dosimetry: Application in patients with multi-SPECT/CT imaging after 177Lu-peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. J Nucl Med. 2022; 63(11): 1665-72. doi:
2967/jnumed.121.263738.
Resch S, Ziegler SI, Sheikh G, Unterrainer LM, Zacherl MJ, Bartenstein P, et al. Impact of the reference multiple-time-point dosimetry protocol on the validity of single-time-point dosimetry for [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T therapy. J Nucl Med. 2024; 65(8): 1272-8. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.123.266871.
Nazari M, Jiménez-Franco LD, Schroeder M, Kluge A, Bronzel M, Kimiaei S. Automated and robust organ segmentation for 3D-based internal dose calculation. EJNMMI Res. 2021; 11(1): 53. doi: 10.1186/s13550-021-00796-5.