ImplicatIions of bilirubin testing and the prevalence of abnormal liver function tests among rural adults in Mae Ka Subdistrict, Chiang Mai, Thailand
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Liver function tests (LFTs) measure the levels of specific enzymes and proteins in the blood that can change when the liver is damaged. Bilirubin, a byproduct of heme degradation, primarily from red blood cell breakdown (approximately 80%), is commonly included in these assessments. Although bilirubin and liver enzymes are well-established markers of liver function, they do not always indicate the presence of liver lesions. Therefore, for accurate diagnosis, changes in liver enzyme and bilirubin concentrations should be interpreted in the context of baseline characteristics such as pesticide exposure, alcohol consumption,
and medication use.
Objectives: To investigate the prevalence of abnormal LFTs and alterations in bilirubin concentrations among adults in Mae Ka Subdistrict, Chiang Mai, Thailand.
Materials and methods: A descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted at the Department of Medical Technology, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University, from January to March 2024. Adults from Mae Ka Subdistrict participated
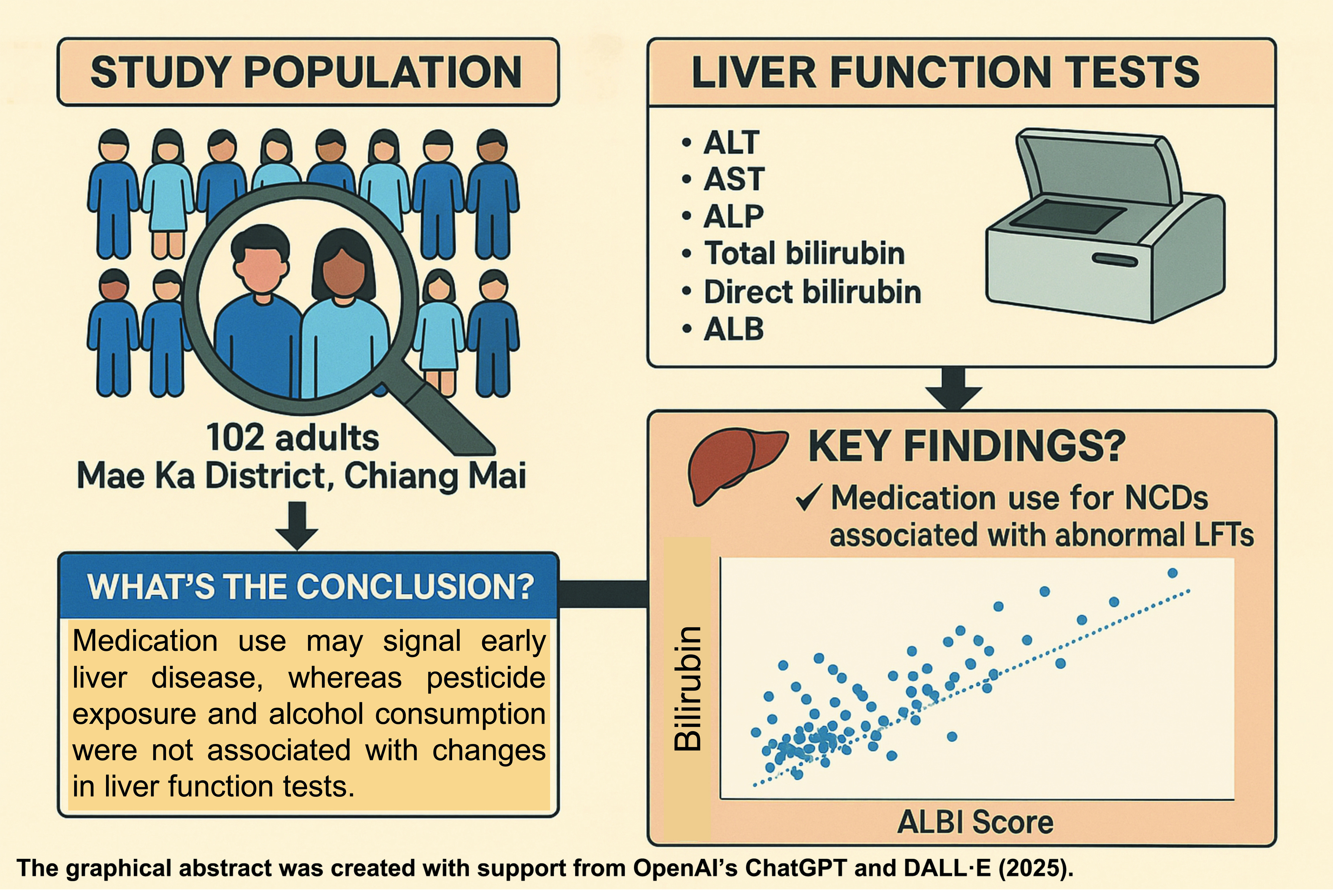
in the study. A total of 102 subjects, aged 23 to 75 years (mean age 56.88±11.26 years), were included. Liver function tests, including ALT, AST, ALP, ALB, total bilirubin, and direct bilirubin, were performed using an automated analyzer (BA 400). The ALBI score and Pearson correlation were used to evaluate the relationships between liver enzymes, bilirubin levels, and baseline characteristics. A p≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Data analysis was performed using SPSS version 17 and Microsoft Excel.
Results: A strong correlation was observed between the use of medications for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia and abnormal LFTs. Medication use was associated with elevations in total bilirubin (TB), ALBI score, ALT, and ALP. However, not all individuals with elevated bilirubin levels had abnormal liver enzymes, and not all individuals with abnormal liver enzymes had elevated bilirubin levels. The ALBI score identified two individuals with normal liver enzyme and albumin (ALB) levels who may require closer monitoring and further investigation for potential liver disease.
Conclusion: Medication use was associated with abnormal LFTs, potentially serving as an early warning sign. The underlying non-communicable diseases (NCDs) that necessitate medication use may be the primary contributors. Early diagnosis and treatment of liver disease, along with prevention of NCDs and metabolic syndrome, may improve health outcomes in this community.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Personal views expressed by the contributors in their articles are not necessarily those of the Journal of Associated Medical Sciences, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University.
References
Poovorawan K, Treeprasertsuk S, Thepsuthammarat K, Wilairatana P, Kitsahawong B, Phaosawasdi K. The burden of cirrhosis and impact of universal coverage public health care system in Thailand: Nationwide study. Ann Hepatol. 2015; 14(6): 862-8. doi: 10.5604/16652681.1171773.
Ramakrishnan A, Velmurugan G, Somasundaram A, Mohanraj S, Vasudevan D, Vijayaragavan P, et al. Prevalence of abnormal liver tests and liver fibrosis among rural adults in low and middle-income country: A cross-sectional study. EClinical Medicine. 2022; 51: 101553. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101553.
Lu F, Meng Y, Song X, Li X, Liu Z, Gu C, et al. Artificial intelligence in liver diseases: Recent Advances. Adv Ther. 2024; 41(3): 967-90. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-02781-5.
Ngoc Dinh M, Nygate J, Hoang Minh Tu V, Thwaites CL, Group GGCEV. New technologies to improve healthcare in low- and middle-income countries: Global Grand Challenges satellite event, Oxford University Clinical Research Unit, Ho Chi Minh City, 17th-18th September 2019. Wellcome Open Res. 2020; 5: 142. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.16008.2.
Zhang GM, Hu ZD. Conjugated bilirubin as a reflex test for increased total bilirubin in apparently healthy population. J Clin Lab Anal. 2018; 32(2): e22233. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22233.
Yamashita Y, Umemura T, Kimura T, Joshita S, Hirohara J, Nakano T, et al. Prognostic utility of albumin-bilirubin grade in Japanese patients with primary biliary cholangitis. JHEP Rep. 2023; 5(4): 100662. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100662.
Murillo Perez CF, Harms MH, Lindor KD, van Buuren HR, Hirschfield GM, Corpechot C, et al. Goals of treatment for improved survival in primary biliary cholangitis: Treatment target should be bilirubin within the normal range and normalization of alkaline phosphatase. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020; 115(7): 1066-74. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000557.
He C, Zhang G, Fu J, Zhang R, Li A, Liu D, et al. Clinical significance of albumin- and bilirubin-based biomarkers in glaucoma: A retrospective case-control study. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022; 2022: 8063651. doi: 10.1155/2022/8063651.
Cohen SD, Devant C, Delaval L, Charlier C, Canouï E, Chouchana L. Isolated conjugated hyperbilirubinemia with rifampicin and cross-reaction with rifabutin: A drug-endogenous substance interaction case report. Therapie. 2024; 79(4): 479-82. doi: 10.1016/j.therap.2023.09.006.
Macpherson I, Abeysekera KWM, Harris R, Mansour D, McPherson S, Rowe I, et al. Identification of liver disease: why and how. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2022; 13(5): 367-73. doi: 10.1136/flgastro-2021-101833.
Johnson PJ, Berhane S, Kagebayashi C, Satomura S, Teng M, Reeves HL, et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33(6): 550-8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.9151.
Radcke S, Dillon JF, Murray AL. A systematic review of the prevalence of mildly abnormal liver function tests and associated health outcomes. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 27(1): 1-7. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000233.
Lala V, Zubair M, Minter DA. Liver Function Tests. StatPearls Publishing, Tampa.2022.
Pinter M, Trauner M, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Sieghart W. Cancer and liver cirrhosis: implications on prognosis and management. ESMO Open. 2016;1(2) :e000042. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2016-000042.
Sun T, Du H, Li Z, Xiong J, Liu Y, Li Y, et al. Decoding the contributions of gut microbiota and cerebral metabolism in acute liver injury mice with and without cognitive dysfunction. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023; 29(Suppl 1): 31-42. doi: 10.1111/cns.14069.
Sun T, Feng M, Manyande A, Xiang H, Xiong J, He Z. Regulation of mild cognitive impairment associated with liver disease by humoral factors derived from the gastrointestinal tract and MRI research progress: a literature review. Front Neurosci. 2023; 17: 1206417. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1206417.
Kalas MA, Chavez L, Leon M, Taweesedt PT, Surani S. Abnormal liver enzymes: A review for clinicians. World J Hepatol. 2021; 13(11): 1688-98. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1688.
Varghese G, Madi L, Ghannam M, Saad R. A possible increase in liver enzymes due to amlodipine: A case report. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2020; 8: 2050313X20917822. doi: 10.1177/2050313X20917822.
Diogo J, Monteiro R, Coelho C, Ghiletchi A, Leão R, Loureiro C. Drug-induced liver injury due to Losartan. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2021; 8(11): 002856. doi: 10.12890/2021_002856.
Choi WJ, Kim GA, Park J, Jang S, Jung WJ, Shim JJ, et al. Incidence and pattern of aminotransferase elevation during anti-hypertensive therapy with angiotensin-II receptor blockers. J Korean Med Sci. 2022; 37(33): e255. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e255.
Bhardwaj SS, Chalasani N. Lipid-lowering agents that cause drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Clin Liver Dis. 2007;11(3):597-613, vii. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2007.06.010.
Ashraf J, Ali Khan M, Minhaj S, Khatti S, Aarij KM, Shehzad M, et al. Statins and abnormal liver function tests: Is there a correlation? Cureus. 2020; 12(8): e10145. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10145.
Siddiqui MT, Amin H, Garg R, Chadalavada P, Al-Yaman W, Lopez R, et al. Medications in type-2 diabetics and their association with liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2020; 26(23): 3249-59. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i23.3249.
Baeradeh N, Seif M, Rezaianzadeh A, Hosseini SV. Investigating the relationship between liver enzymes and incidence of hypertension: A population-based cohort study in Kharameh, a city in the South of Iran.Health Sci Rep. 2023; 6(10): e1601. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1601.
Yilmaz NS, Sen B, Gulbahar O. Contribution of the laboratory to a diagnosis process by sequential reflective testing: Paraprotein interference on a direct bilirubin assay. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2021; 31(2): 020801. doi: 10.11613/BM.2021.020801.
Lee HA, Jung JY, Lee YS, Jung YK, Kim JH, An H, et al. Direct bilirubin is more valuable than total bilirubin for predicting prognosis in patients with liver cirrhosis. Gut Liver. 2021; 15(4): 599-605. doi: 10.5009/gnl20171.
Toyoda H, Johnson PJ. The ALBI score: From liver function in patients with HCC to a general measure of liver function. JHEP Rep. 2022; 4(10): 100557. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100557.
Feng J, Xu JM, Fu HY, Xie N, Bao WM, Tang YM. Prognostic scores in primary biliary cholangitis patients with advanced disease. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2023; 15(8): 1774-83. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i8.1774.