The preparation of Au decorated on ZnO nanorods by comparative DCMS/HIPIMS techniques for antibacterial activity
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: The mortality rate of antimicrobial-resistant infections has increased dramatically worldwide due to the increased use of antibiotics. The rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria has highlighted the need to develop novel materials with antimicrobial properties, and nanotechnology offers promising prospects for the development of new therapeutic approaches. Currently, hybrid nanomaterials are interesting alternatives that enhance the physical and antibacterial properties of nanomaterials with a large surface area, making them efficient and biocompatible.
Objectives: This study evaluated the antibacterial activity of Au nanoparticle-decorated ZnO Nanorods (NRs) with different characteristics of Au nanoparticles (Au NPs) on the ZnO surface.
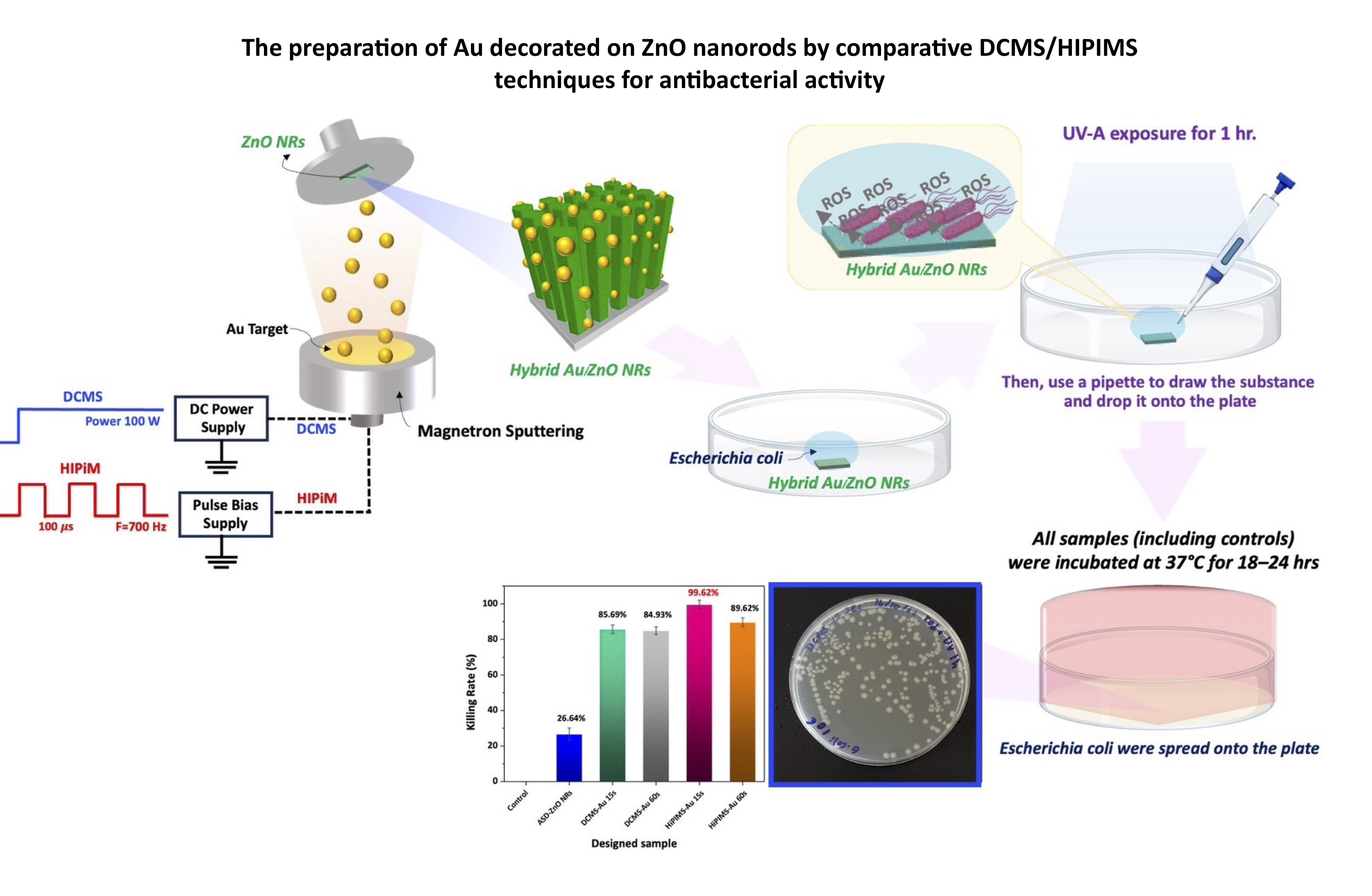
Materials and methods: ZnO NRs were grown on a silicon wafer using the hydrothermal method, and Au NPs were decorated on the ZnO NRs surface by DC magnetron sputtering and high-power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) techniques for comparison. The physical morphologies and crystallinity of the ZnO NRs and Au-nanoparticle-decorated ZnO NRs were investigated by field-emission electron microscopy (FE-SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD).
Results: FE-SEM results indicated changes in the physical morphologies of the Au NPs on the ZnO NRs. The antibacterial efficacy of the ZnO NRs and Au-decorated ZnO NRs against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus was evaluated under UV light irradiation with bacterial concentrations ranging from 100 to 108 CFU/mL to assess their inhibitory effects using the plate count technique.
Conclusion: The results demonstrated that the proposed Au-ZnO NRs exhibited a significant inhibitory effect on the growth of Escherichia coli indicating the potential of Au NPs decorated ZnO NRs as a novel antimicrobial material. Importantly, the results highlight the influence of bacterial concentration on the effectiveness of Au-ZnO NRs, offering insights for future applications in combating antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Personal views expressed by the contributors in their articles are not necessarily those of the Journal of Associated Medical Sciences, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University.
References
O’Neill J. Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: final report and recommendations. London: Wellcome Trust; 2016.
Naghavi M, Vollset SE, Ikuta KS, Swetschinski LR, Gray AP, Wool EE, et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990-2021: a systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. The Lancet. 2024; 404(10459): 1199-226. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)01867-1.
Xie J, Li H, Zhang T, Song B, Wang X, Gu Z. Recent advances in ZnO nanomaterial-mediated biological applications and action mechanisms. Nanomaterials. 2023;13(9):1500. doi: 10.3390/nano13091500.
Kalasung S, Aiempanakit K, Chatnuntawech I, Limsuwan N, Lertborworn K, Patthanasettakul V, et al. Trace-level detection and classifications of pentaerythritol tetranitrate via geometrically optimized film-based Au/ZnO SERS sensors. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2022; 366: 131986. doi: 10.1016/j. snb.2022.131986.
Khan SS, Ullah I, Ullah S, An R, Xu H, Nie K, et al. Recent advances in the surface functionalization of nanomaterials for antimicrobial applications. Materials. 2021;14(22): 6932. doi: 10.3390/ma14226932.
Nuchuay P, Laongwan C, Promcham W, Somboonsaksri P, Kalasung S, Chananonnawathorn C, et al. A study of the electrical and optical properties of AZO thin film by controlling pulse frequency of HiPIMS. J.Met.Mater.Miner.2023; 33(2): 103-7. doi: 10.55713/jmmm.v33i2.1696.
Sornsanit K, Horprathum M, Eiamchai P, Chananon-nawathorn C, Kalasung S, Kaewkhao J. Enhanced antibacterial activity by Au nanoparticle decorated ZnO nanorods. Key Eng Mater. 2016;113–6.
Dediu V, Busila M, Tucureanu V, Bucur FI, Iliescu FS, Brincoveanu O, et al. Synthesis of ZnO/Au Nanocomposite for Antibacterial Applications. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(21): 3832 doi: 10.3390/nano12213832.
Fageria P, Gangopadhyay S, Pande S. Synthesis of ZnO/Au and ZnO/Ag nanoparticles and their photocatalytic application using UV and visible light. RSC Adv. 2014; 4(48): 24962-72. doi: 10.1039/C4RA03158J.
Kalasung S, Kopwitthaya A, Horprathum M, Kaewkhao J, Tuscharoen S, Eiamchai P, et al. Functionalization of Au nanoparticles on ZnO nanorods through low-temperature synthesis. Key Eng Mater. 2016; 675-6: 45-8. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.675-676.45.
Kalasung S, Chatnuntawech I, Patthanasettakul V, Limwichean S, Lertborworn K, Horprathum M, et al. Au-decorated ZnO nanorod arrays for SERS-active substrates towards trace detection and classification of pentaerythritol tetranitrate. Mater Today Proc. 2022; 56: 2245–2251. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr. 2021.03.511
Busila M, Musat V, Alexandru P, Romanitan C, Brincoveanu O, Tucureanu V, et al. Antibacterial and Photocatalytic Activity of ZnO/Au and ZnO/Ag Nanocomposites. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(23): 16939 doi: 10.3390/ijms242316939
Abebe B, Zereffa EA, Tadesse A, Murthy HCA. A Review on Enhancing the Antibacterial Activity of ZnO: Mechanisms and Microscopic Investigation, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020; 15: 190 doi: 10.1186/s11671-020-03418-6.
Mlynarczyk-Bonikowska B, Kowalewski C, Krolak-Ulinska A, Marusza W. Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 22; 23(15): 8088. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158088.