The Effect of low voltage high frequency electric pulses on the extracellular conductivity, cell permeability and time-depended manner of MCF7 cell line
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Low voltage, high frequency electrochemotherapy (LVHF ECT) has recently been explored as a method to enhance the permeability of cell membranes to non-permanent chemotherapeutic agents.
Objective: Despite recent advances, it remains unclear whether classical ECT and LVHF ECT (using 50–150 V/cm at pulse frequencies of 4–6 kHz) affect the cell membrane through similar mechanisms.
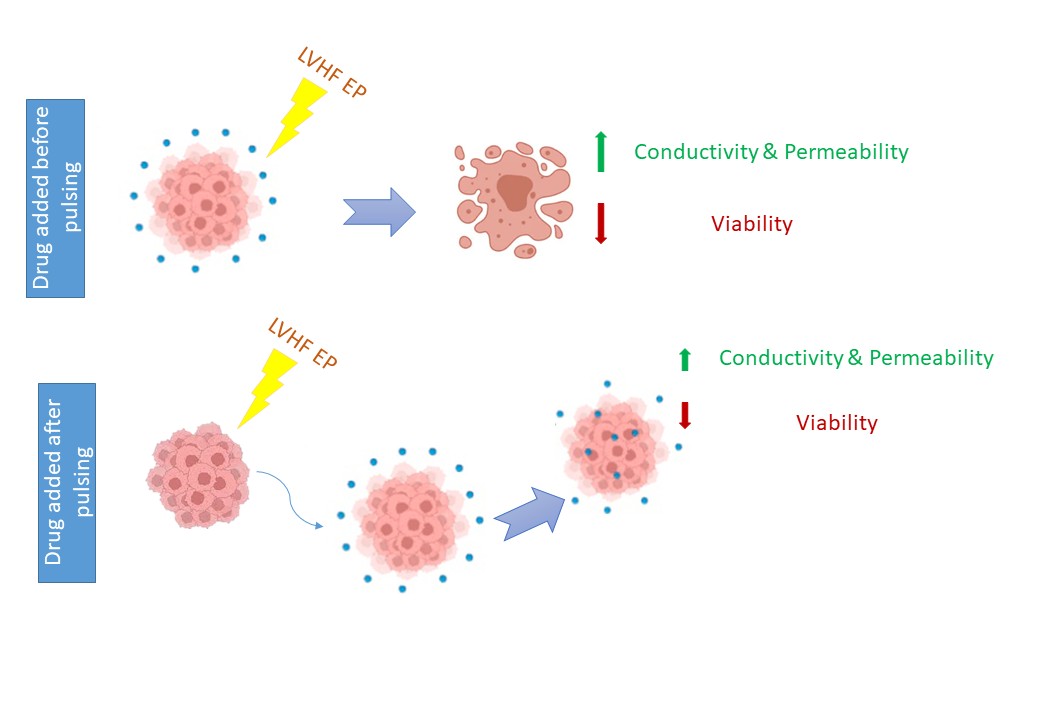
Materials and methods: We investigated the efficiency of reversible membrane permeabilization in the MCF7 cell line induced by LVHF electric pulses. Specifically, we examined changes in extracellular conductivity, the time-dependent nature of permeabilization, and the effects of this protocol on commonly used permeabilization markers
Results: LVHF ECT protocols significantly increased the conductivity of the extra-cellular medium, indicating enhanced membrane permeability in MCF7 cells. This increased permeability was closely associated with elevated membrane conductivity. Notably, most of the membrane permeabilization occurred during pulse application and subsided within one minute after the delivery of LVHF pulses. Experimental data indicate that these electric pulses induce the formation of short-lived pores in the membrane. Furthermore, LVHF pulses did not alter the cytotoxicity of bleomycin; however, this protocol resulted in the quenching of Lucifer yellow fluorescence, a classical marker for membrane permeabilization. These findings suggest that bleomycin is a reliable marker for cell electro permeabilization under LVHF ECT conditions.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that LVHF ECT induces transient, short-lived pores in the cell membrane and increases membrane permeability without affecting bleomycin cytotoxicity. Bleomycin appears to be a suitable marker for assessing electro-permeabilization in this context.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Personal views expressed by the contributors in their articles are not necessarily those of the Journal of Associated Medical Sciences, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University.
References
Blagus T, Markelc B, Cemazar M, Kosjek T, Preat V, Miklavcic D, et al. In vivo real-time monitoring system of electroporation mediated control of transdermal and topical drug delivery. J Control Rel. 2013; 172: 862-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.09.030.
Mir LM, Calvet CY, Andre FM, editors. Therapeutic effects of in vivo electroporation: Facilitating drug and gene delivery but not only…. General Assembly and Scientific Symposium (URSI GASS), 2014 XXXIth URSI; 2014 16-23 Aug. 2014.
Miklavcic D, Kotnik T, Electroporation for electro-chemotherapy and gene therapy. in: PJ. Rosch, MS Markov, Editors. Bioelectromagnetic Medicine, University of Ljubljana, Marcel Dekker, 2004, pp. 637-56.
Chen C, Smye SW, Robinson MP, Evans JA. Membrane electroporation theories: A review. Med Biol Engin Comput. 2006; 44: 5-14. doi: 10.1007/s11517-005-0020-2. Z. Shankayi et al. Journal of Associated Medical Sciences 2025; 58(3): 52-5958
Kotnik T, Kramar P, Pucihar G, Miklavcic D, Tarek M. Cell membrane electroporation- Part 1: The phenomenon. IEEE Electric Insulat Mag. 2012; 28: 14-23. doi: 10.1109/mei.2012.6268438.
Pavlin M, Kandušer M, Reberšek M, Pucihar G, Hart FX, Magjarevićcacute R, et al. Effect of cell electroporation on the conductivity of a cell suspension. Biophysic J. 2005; 88: 4378-90. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.048975.
Silve A, Leray I, Poignard C, Mir LM. Impact of external medium conductivity on cell membrane electropermeabilization by microsecond and nano-second electric pulses. Sci Report. 2016; 6: 19957. doi: 10.1038/srep19957.
Miklavčič D, Pucihar G, Pavlovec M, Ribarič S, Mali M, Maček-Lebar A, et al. The effect of high frequency electric pulses on muscle contractions and antitumor efficiency in vivo for a potential use in clinical electrochemotherapy. Bioelectrochem. 2005; 65: 121-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2004.07.004.
Županič A, Ribarič S, Miklavčič D. Increasing the repetition frequency of electric pulse delivery reducesunpleasant sensations that occur in electro-chemotherapy. Neoplasm 2007; 54: 246-50.
Sersa G, Kranjc S, Scancar J, Krzan M, Cemazar M. Electrochemotherapy of mouse sarcoma tumors using electric pulse trains with repetition frequencies of 1 Hz and 5 kHz. J Membrane. 2010; 236: 155-62. doi: 10.1007/s00232-010-9268-z.
Shankayi Z, Firoozabadi SM. Antitumor efficiency of electrochemotherapy by high and low frequencies and repetitive therapy in the treatment of invasive ductal carcinoma in Balb/c mice. Cell J. 2012; 14(2): 110-5. PMID: 23508227, PMCID: PMC3584427.
Shankayi Z, Firoozabadi SMP, Saraf Hassan Z. Comparison of low voltage amplitude electrochemotherapy with 1 Hz and 5 kHz frequency in volume reduction of mouse mammary tumor in Balb/c Mice. Koomesh. 2012; 13: 486-90.
Shankayi Z, Firoozabadi S, Hassan ZS. Optimization of electric pulse amplitude and frequency in vitro for low voltage and high frequency electrochemo- therapy. J Membrane Biol. 2014; 247: 147-54. doi: 10.1007/s00232-013-9617-9.
Shankayi Z, Firoozabadi SMP, Saraf HZ. The Endothelial Permeability Increased by Low Voltage and High Frequency Electroporation. J Biomed Physic Engineer. 2013; 3: 87.
Shankayi Z, Firoozabadi S. Tumor growth inhibited by low-voltage amplitude and 5-kHz frequency electro-chemotherapy. J Membrane Biol. 2011; 244: 121-8. doi: 10.1007/s00232-011-9405-3.
Tahereh Pourmirjafari Firoozabadi ZS, Azam Izadi, S. Mohammad P. Firoozabadi. Can lucifer yellow indicate correct permeability of biological cell membrane under an electric and magnetic field? Cell J. 2015; 16: 560-3. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2015.501.
Silve A, Leray I, Mir LM. Demonstration of cell membrane permeabilization to medium-sized molecules caused by a single 10ns electric pulse. Bioelectrochem. 2012; 87: 260-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2011.10.002.
Jaroszeski MJ, Gilbert R, Heller R. Electrochemother-apy: an emerging drug delivery method for the treatment of cancer. Advanc Drug Deliver Rev. 1997; 26: 185-97. doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(97)00034-3.
Chen J, Stubbe J. Bleomycins: towards better therapeutics. Natur Rev Cancer. 2005; 5: 102-12. doi: 10.1038/nrc1547.
Silve A, Mir LM. Cell electropermeabilization and cellular uptake of small molecules: the electrochemo therapy concept. Clin Aspect Electroporat: Springer; 2011, pp. 69-82.
Pucihar G, Kotnik T, Kandušer M, Miklavčič D. The influence of medium conductivity on elec-tropermeabilization and survival of cells in vitro. Bio-electrochem. 2001; 54: 107-15. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5394(01)00117-7.
Ivorra A, Villemejane J, Mir LM. Electrical modeling of the influence of medium conductivity on electroporation. Physic Chem Chem Physic. 2010; 12: 10055-64. doi: 10.1039/c004419a.
Pavlin M, Miklavčič D. Theoretical and experimental analysis of conductivity, ion diffusion and molecular transport during cell electroporation—relation between short-lived and long-lived pores. Bioelectro chem. 2008; 74: 38-46. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2008.04.016.
Shankayi Z, Firoozabadi S, Mansurian MG. The effect of pulsed magnetic field on the molecular uptake and medium conductivity of leukemia cell. Cell Biochem Biophysic. 2013; 65: 211-6. doi: 10.1007/s12013-012-9422-6.
Safyari M, Firoozabadi SM, Hassan ZS, Akbari H, Shankayi Z. Optimization of Low Voltage and High Frequency in vitro and in vivo for clinical application. Life Sci Student J. 2023; 1: 89-100.
Mofid B, Shankayi Z, Novin K, Dehghani S, Shankayi M, Haghighatkhah H, et al. Effective treatment of cervical lymph node metastasis of breast cancer by low voltage high-frequency electrochemotherapy. Act Medic Iran. 2017: 55(4):268-271. PMID: 28532140
Neu WK, Neu JC. Theory of Electroporation. In: Efimov IR, Kroll MW, Tchou PJ, (Eds). Cardiac Bioelectric Therapy: Mechanisms and Practical Implications. Boston, MA: Springer US; 2009. pp. 133-61.
Rems L, Miklavčič D. Tutorial: Electroporation of cells in complex materials and tissue. J Appli Physic. 2016; 119: 201101. doi.org/10.1063/1.4949264.
Suzuki DO, Ramos A, Ribeiro MC, Cazarolli LH, SilvaFR, Leite LD, et al. Theoretical and experimental analysis of electroporated membrane conductance in cell suspension. IEEE Transact Biomedic Engineer. 2011; 58: 3310-8. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2010.2103074.
Pavlin M, Leben V, Miklavčič D. Electroporation in dense cell suspension—Theoretical and experimental analysis of ion diffusion and cell permeabilization. Biochimic Biophysic Act. 2007; 1770: 12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2006.06.014. Z. Shankayi et al. Journal of Associated Medical Sciences 2025; 58(3): 52-5959
Gissel H, Lee RC, Gehl J. Electroporation and Cellular Physiology. In: Kee ST, Gehl J, Lee EW, Editors. Clin Aspect Electroporat. New York, NY: Springer New York; 2011, pp. 9-17.
Zaharoff DA, Henshaw JW, Mossop B, Yuan F. Mechanistic analysis of electroporation-induced cellular uptake of macromolecules. Experiment Biol Med. 2008; 233: 94-105. doi: 10.3181/0704-RM-113.
Prausnitz MR, Milano CD, Gimm JA, Langer R, Weaver JC. Quantitative study of molecular transport due to electroporation: uptake of bovine serum albumin by erythrocyte ghosts. Biophysic J. 1994; 66: 1522. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80943-9.
Ji Z, Kennedy SM, Booske JH, Hagness SC. Experimental studies of persistent poration dynamics of cell membranes induced by electric pulses. IEEE Transact Plasma Sci. 2006; 34: 1416-24. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2006.877250.
Bier M, Hammer SM, Canaday DJ, Lee RC. Kinetics of sealing for transient electropores in isolated mammalian skeletal muscle cells. Bioelectromagnet. 1999; 20: 194-201. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-186X(1999)20:3<194::AID-BEM6>3.0.CO;2-0.
Yadegari-Dehkordi S, Firoozabadi SM, Moghadam MF, Shankayi Z. Role of endocytosis pathways in electropermeablization of MCF7 cells using low voltage and high frequency electrochemotherapy. Cell J. 2021; 23: 445-50. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2021.7203
Pakhomov AG, Miklavcic D, Markov MS. Advanced electroporation techniques in biology and medicine: CRC Press; 2010.