Alternative X-ray attenuation material from iodide-starch-gel-based materials
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Iodine is often used as a contrast media because the k-shell binding energy (K-edge) is 33.2 keV, the average energy of a diagnostic X-ray. Thus, iodine can be utilized as a radiation attenuation material for X-rays.
Objective: This study aimed to produce low-energy X-ray attenuation materials used as X-ray shielding. A sodium iodide compound will be synthesized by polymerizing mung bean starch with sodium iodide.
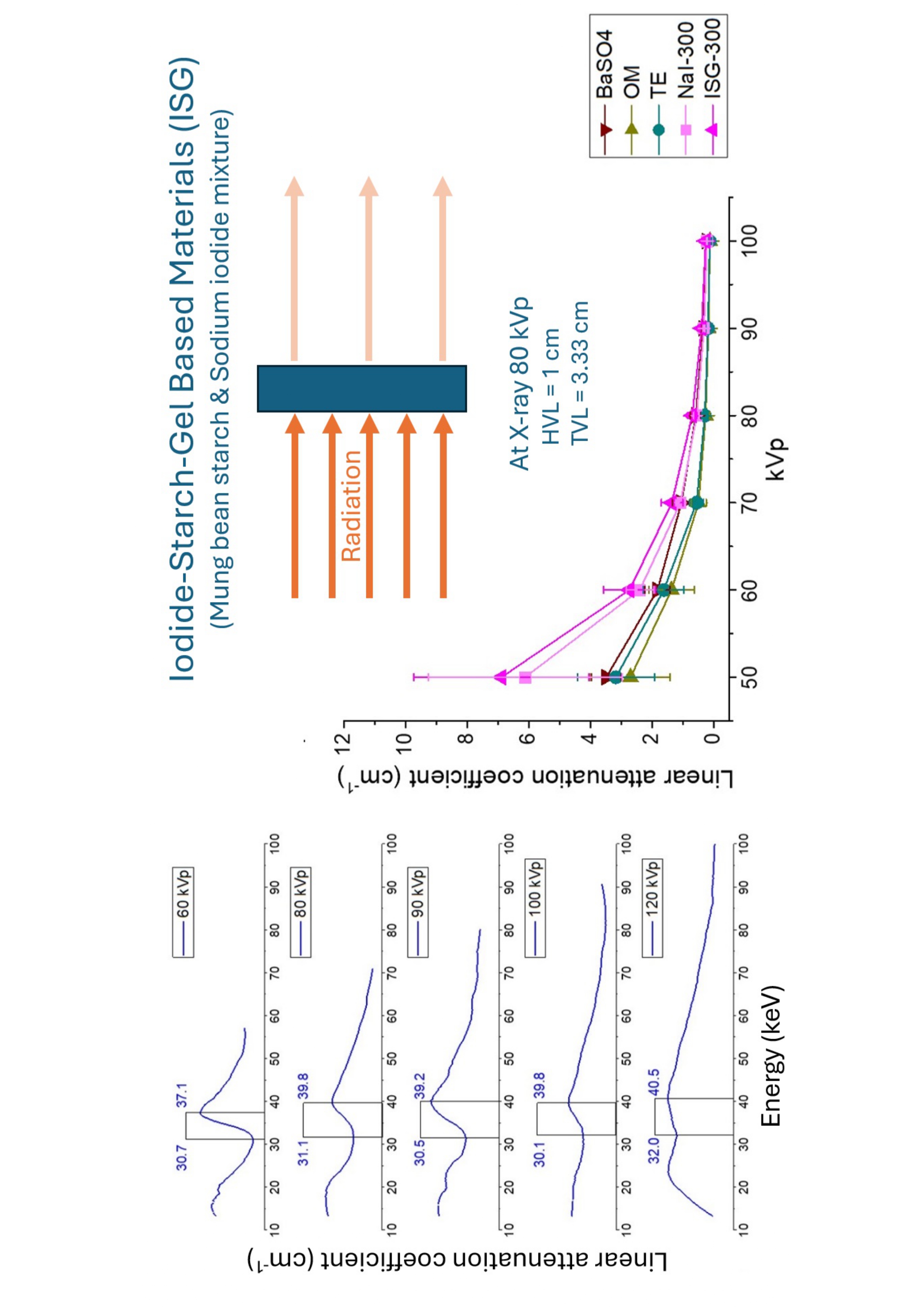
Materials and methods: The iodide-starch-gel-based material (ISG) was made by mixing a mung bean starch solution (10 %w/w) with a sodium iodide (NaI) solution (100, 200, 250, and 300 mg-Iodine/gm). The linear attenuation coefficient (µ) was determined using radiation dose acquired from the DR plate system and CdTe detector. The X-rays were done at 50 - 120 kVp to study the attenuation properties.
Results: The results showed that the linear attenuation coefficient of t ISG was slightly higher than that of sodium iodide solution at the same concentration. The spectrum still shows an X-ray absorption characteristic at about 30.1-40.5 keV K-edge range.
Conclusion: Iodide-starch-gel-based components can attenuate X-ray with a K-edge range from 30-40 kVp. The attenuation coefficient of X-ray radiation varies linearly with energy level. Moreover, the concentration of the NaI solution is directly proportional to the attenuation of X-ray radiation. Thus, based on these properties and the gel-like consistency of the substance, it can be developed into a surface coating material to reduce X-ray radiation exposure.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Personal views expressed by the contributors in their articles are not necessarily those of the Journal of Associated Medical Sciences, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University.
References
Aye KT, Wattanapongpitak S, Supawat B, Kothan S, Udomtanakunchai C, Tima S, et al. Effect of pre-lowdose irradiation on anticancer activities of gallic acid in leukemic K562 and K562/Dox cells: cell viability and cellular energetic state studies. Med Oncol. 2022; 39(12): 229. doi:10.1007/s12032-022-01835-4.
Supawat B, Homnuan P, Kanthawong N, Semrasa N, Tima S, Kothan S, et al. Different responses of normal cells (red blood cells) and cancer cells (K562 and K562/Dox cells) to low-dose (137)Cs gamma-rays. Mol Clin Oncol. 2021; 14(4): 74. doi:10.3892/mco. 2021.2236.
Pereira L, Ferreira MT, Lima AGF, Salata C, FerreiraMachado SC, Lima I, et al. Biological effects induced by doses of mammographic screening. Phys Med. 2021; 87: 90-8. doi:10.1016/j.ejmp.2021.06.002.
Smith T, Kearfott KJ. Practical Considerations for Gamma-Ray Spectroscopy with NaI(Tl): A Tutorial. Health Phys. 2018; 114(1): 94-106. doi:10.1097/HP. 0000000000000804.
Faucon AL, Bobrie G, Clement O. Nephrotoxicity of iodinated contrast media: From pathophysiology to prevention strategies. Eur J Radiol. 2019; 116: 231-41. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.03.008.
Wang L, Li Q, Wang XM, Hao GY, Jie B, Hu S, et al. Enhanced radiation damage caused by iodinated contrast agents during CT examination. Eur J Radiol. 2017;92:72-7. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.04.005.
Daowtak K, Pilapong C, Tochaikul G, Moonkum N. Effect of iodinated contrast media on peripheral blood mononuclear cells in terms of cell viability, cell cycle and oxidative stress in an in vitro system. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2023; 33(8): 667-74. doi.org/10.108 0/15376516.2023.2230486.
Wang Y, Ding P, Xu H, Li Q, Guo J, Liao X, et al. Advanced X-ray Shielding Materials Enabled by the Coordination of Well-Dispersed High Atomic Number Elements in Natural Leather. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2020; 12(17): 19916-26. doi:10.1021/ acsami.0c01663.
Moonkum N, Pilapong C, Daowtak K, Tochaikul G. Radiation Protection Device Composite of Epoxy Resin and Iodine Contrast Media for Low-Dose Radiation Protection in Diagnostic Radiology. Polymers (Basel). 2023; 15(2): 430. doi.org/10.3390/polym15020430.
Hayashi H, Okino H, Takegami K, Kimoto N, Maehata I, Kanazawa Y, et al. Experimental evaluation of response functions of a CdTe detector in the diagnostic region with the aim of carrying out a basic experiment concerning a next generation photon counting system. Poster presentation in ECR 2016. doi:10.1594/ecr 2016/C-0006.
Heyes GJ, Mill AJ, Charles MW. Enhanced biological effectiveness of low energy X-rays and implications for the UK breast screening programme. Br J Radiol. 2006; 79(939): 195-200. doi:10.1259/bjr/21958628.
Bulloch MN. Acute iodine toxicity from a suspected oral methamphetamine ingestion. Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2014; 7: 127-9. doi:10.4137/CCRep.S20086.
Mishkin MM. Contrast media safety; What do we know and how do we know it? Am J Cardiol. 1990; 66(14): F34-F6. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(90)90639-i.
Aral N, Nergis B, Candan C. An alternative X-ray shielding material based on coated textiles. Text Res J. 2015; 86(8): 803-11. doi:10.1177/00405175155 90409.